ctypes 是 python 的外部函数库。它提供了与 c 兼容的数据类型,并允许调用 dll 或共享库中的函数。可使用该模块以纯 python 形式对这些库进行封装。
基本数据类型对应关系
[ctypes] 定义了一些和c兼容的基本数据类型:
| ctypes 类型 | c 类型 | python 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| [c_bool] | _bool | bool (1) |
| [c_char] | char | 单字符字节串对象 |
| [c_wchar] | wchar_t | 单字符字符串 |
| [c_byte] | char | int |
| [c_ubyte] | unsigned char | int |
| [c_short] | short | int |
| [c_ushort] | unsigned short | int |
| [c_int] | int | int |
| [c_uint] | unsigned int | int |
| [c_long] | long | int |
| [c_ulong] | unsigned long | int |
| [c_longlong] | __int64 或 long long | int |
| [c_ulonglong] | unsigned __int64 或 unsigned long long | int |
| [c_size_t] | size_t | int |
| [c_ssize_t] | ssize_t 或 py_ssize_t | int |
| [c_float] | float | float |
| [c_double] | double | float |
| [c_longdouble] | long double | float |
| [c_char_p] | char * (nul terminated) | 字节串对象或 none |
| [c_wchar_p] | wchar_t * (nul terminated) | 字符串或 none |
| [c_void_p] | void * | int 或 none |
环境
开发工具:clion
c语言版本:c11
python版本:python3.8
创建项目
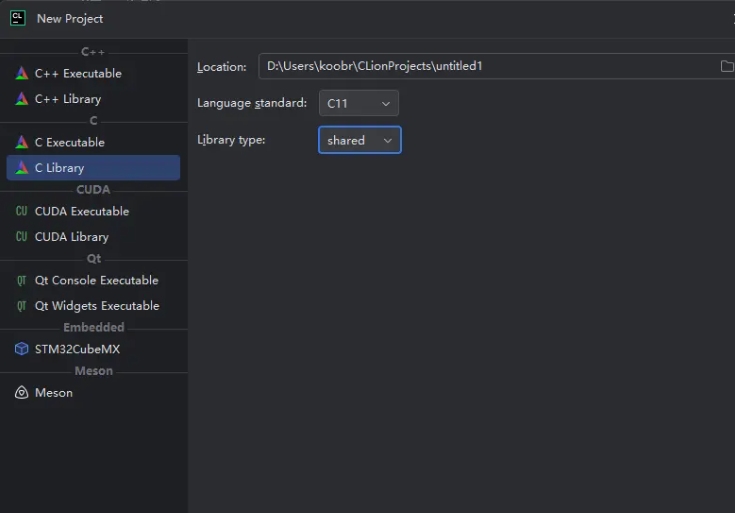
cmakelists.txt
# 指定 cmake 的最低版本要求 cmake_minimum_required(version 3.30) # 定义项目名称和支持的语言类型 project(clibshareddemo c) # 设置 c 标准版本为 c11 set(cmake_c_standard 11) # 添加共享库目标,将 library.c 编译为动态库 (windows 下为 .dll,linux 下为 .so,macos 下为 .dylib) add_library(clibshareddemo shared library.c)
library.h
#ifndef clibshareddemo_library_h
#define clibshareddemo_library_h
#include <wchar.h>
void plus(int a, int *result);
void *process_void_pointer(void *ptr);
_bool is_even(int num);
int add_int(int a, int b);
short add_short(short a, short b);
long add_long(long a, long b);
long long add_longlong(long long a, long long b);
unsigned int add_unsigned_int(unsigned int a, unsigned int b);
unsigned short add_unsigned_short(unsigned short a, unsigned short b);
unsigned long add_unsigned_long(unsigned long a, unsigned long b);
unsigned long long add_unsigned_longlong(unsigned long long a, unsigned long long b);
float add_float(float a, float b);
double add_double(double a, double b);
char to_upper(char c);
wchar_t to_upper_wchar(wchar_t wc);
char *copy_string(const char *src, char *dest);
wchar_t *copy_wstring(const wchar_t *src, wchar_t *dest);
size_t add_size_t(size_t a, size_t b);
ssize_t add_ssize_t(ssize_t a, ssize_t b);
void fill_array(int *arr, int size);
typedef struct {
char name[50];
int age;
} person;
person update_person_by_value(person p);
void update_person_by_pointer(person *p);
#endif //clibshareddemo_library_h
library.c
#include "library.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <wchar.h>
// void
void plus(const int a, int *result) {
*result = a + 1;
}
// void *
void *process_void_pointer(void *ptr) {
return ptr;
}
// _bool
_bool is_even(const int num) {
return num % 2 == 0;
}
// int
int add_int(const int a, const int b) {
return a + b;
}
// short
short add_short(const short a, const short b) {
return a + b;
}
// long
long add_long(const long a, const long b) {
return a + b;
}
// long long
long long add_longlong(const long long a, const long long b) {
return a + b;
}
// unsigned int
unsigned int add_unsigned_int(const unsigned int a, const unsigned int b) {
return a + b;
}
// unsigned short
unsigned short add_unsigned_short(const unsigned short a, const unsigned short b) {
return a + b;
}
// unsigned long
unsigned long add_unsigned_long(const unsigned long a, const unsigned long b) {
return a + b;
}
// unsigned long long
unsigned long long add_unsigned_longlong(const unsigned long long a, const unsigned long long b) {
return a + b;
}
// float
float add_float(const float a, const float b) {
return a + b;
}
// double
double add_double(const double a, const double b) {
return a + b;
}
// char
char to_upper(const char c) {
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {
return c - ('a' - 'a');
}
return c;
}
// wchar_t
wchar_t to_upper_wchar(const wchar_t wc) {
if (wc >= l'a' && wc <= l'z') {
return wc - (l'a' - l'a');
}
return wc;
}
// char *
char *copy_string(const char *src, char *dest) {
strcpy(dest, src);
return dest;
}
// wchar_t *
wchar_t *copy_wstring(const wchar_t *src, wchar_t *dest) {
wcscpy(dest, src);
return dest;
}
// size_t
size_t add_size_t(const size_t a, const size_t b) {
return a + b;
}
// ssize_t
ssize_t add_ssize_t(const ssize_t a, const ssize_t b) {
return a + b;
}
// arr
void fill_array(int *arr, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] * i;
}
}
// struct
person update_person_by_value(person p) {
p.age += 1; // 修改 age
return p;
}
void update_person_by_pointer(person *p) {
if (p != null) {
p->age += 1; // 修改 age
}
}
编译
选择菜单【build】 - 【build project】,编译生成动态库在 cmake-build-debug 目录下。
使用
# main.py
import ctypes
import platform
"""
官方参考文档:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.8/library/ctypes.html
"""
# 获取当前操作系统的名称
current_platform = platform.system()
# 根据操作系统设置库的路径
if current_platform == "windows":
lib = ctypes.cdll("./cmake-build-debug/libclibshareddemo.dll") # windows
elif current_platform == "linux":
lib = ctypes.cdll("./cmake-build-debug/libclibshareddemo.so") # linux
elif current_platform == "darwin": # macos的名称是 darwin
lib = ctypes.cdll("./cmake-build-debug/libclibshareddemo.dylib") # macos
else:
raise oserror("unsupported platform")
""" 空值 """
# void
lib.plus.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int, ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int))
lib.plus.restype = none
result = ctypes.c_int() # 创建一个 ctypes 整型变量作为结果
lib.plus(5, ctypes.byref(result)) # 使用 ctypes.byref 传递指针
print("void:", result.value) # 输出: result: 6
# void *
lib.process_void_pointer.argtypes = (ctypes.c_void_p,)
lib.process_void_pointer.restype = ctypes.c_void_p
ptr = ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int(42))
print("void *: ", lib.process_void_pointer(ptr)) # 输出: 2320620323976
""" 布尔 """
# _bool -> c_bool
lib.is_even.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int,)
lib.is_even.restype = ctypes.c_bool
print("_bool:", lib.is_even(4)) # 输出: true
""" 整数/浮点数 """
# int -> c_int
lib.add_int.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int, ctypes.c_int)
lib.add_int.restype = ctypes.c_int
print("int:", lib.add_int(10, 20)) # 输出: 30
# short -> c_short
lib.add_short.argtypes = (ctypes.c_short, ctypes.c_short)
lib.add_short.restype = ctypes.c_short
print("short:", lib.add_short(3200, 10)) # 输出: 3210
# long -> c_long
lib.add_long.argtypes = (ctypes.c_long, ctypes.c_long)
lib.add_long.restype = ctypes.c_long
print("long:", lib.add_long(10000, 2000)) # 输出: 12000
# long long -> c_longlong
lib.add_longlong.argtypes = (ctypes.c_longlong, ctypes.c_longlong)
lib.add_longlong.restype = ctypes.c_longlong
print("long long:", lib.add_longlong(100000000000, 200000000000)) # 输出: 300000000000
# unsigned int -> c_uint
lib.add_unsigned_int.argtypes = (ctypes.c_uint, ctypes.c_uint)
lib.add_unsigned_int.restype = ctypes.c_uint
print("unsigned int:", lib.add_unsigned_int(10, 20)) # 输出: 30
# unsigned short -> c_ushort
lib.add_unsigned_short.argtypes = (ctypes.c_ushort, ctypes.c_ushort)
lib.add_unsigned_short.restype = ctypes.c_ushort
print("unsigned short:", lib.add_unsigned_short(3200, 10)) # 输出: 3210
# unsigned long -> c_ulong
lib.add_unsigned_long.argtypes = (ctypes.c_ulong, ctypes.c_ulong)
lib.add_unsigned_long.restype = ctypes.c_ulong
print("unsigned long:", lib.add_unsigned_long(10000, 2000)) # 输出: 12000
# unsigned long long -> c_ulonglong
lib.add_unsigned_longlong.argtypes = (ctypes.c_ulonglong, ctypes.c_ulonglong)
lib.add_unsigned_longlong.restype = ctypes.c_ulonglong
print("unsigned long long:", lib.add_unsigned_longlong(100000000000, 200000000000)) # 输出: 300000000000
# float -> c_float
lib.add_float.argtypes = (ctypes.c_float, ctypes.c_float)
lib.add_float.restype = ctypes.c_float
print("float:", lib.add_float(3.5, 2.0)) # 输出: 5.5
# double -> c_double
lib.add_double.argtypes = (ctypes.c_double, ctypes.c_double)
lib.add_double.restype = ctypes.c_double
print("double:", lib.add_double(1.5, 2.5)) # 输出: 4.0
""" 字符/字符串 """
# char -> c_char
lib.to_upper.argtypes = (ctypes.c_char,)
lib.to_upper.restype = ctypes.c_char
print("char:", lib.to_upper("a".encode()).decode()) # 输出: 'a'
# wchar_t -> c_wchar
lib.to_upper_wchar.argtypes = (ctypes.c_wchar,)
lib.to_upper_wchar.restype = ctypes.c_wchar
print("wchar_t:", lib.to_upper_wchar("a")) # 输出: 'a'
# char * -> c_char_p
lib.copy_string.argtypes = (ctypes.c_char_p, ctypes.c_char_p)
lib.copy_string.restype = ctypes.c_char_p
src_str = "hello"
dest_str = ctypes.create_string_buffer(100) # 预留 100 字节缓冲区
result = lib.copy_string(src_str.encode(), dest_str)
print("char *:", result.decode()) # 输出: 'hello'
# wchar_t * -> c_wchar_p
lib.copy_wstring.argtypes = (ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_wchar_p)
lib.copy_wstring.restype = ctypes.c_wchar_p
src_wstr = "hello wide"
dest_wstr = ctypes.create_unicode_buffer(100) # 预留 100 个宽字符缓冲区
result = lib.copy_wstring(src_wstr, dest_wstr)
print("wchar_t *:", result) # 输出: 'hello wide'
""" 指针 """
# int * -> ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int)
lib.plus.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int, ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int))
lib.plus.restype = none
result = ctypes.c_int()
lib.plus(5, ctypes.byref(result)) # ctypes.byref 直接传递原有变量的地址
print("int *:", result.value) # 输出: result: 6
result = ctypes.c_int()
lib.plus(5, ctypes.pointer(result)) # ctypes.pointer 显式地创建一个指针对象
print("int *:", result.value) # 输出: result: 6
""" 内存大小 """
# size_t -> c_size_t
lib.add_size_t.argtypes = (ctypes.c_size_t, ctypes.c_size_t)
lib.add_size_t.restype = ctypes.c_size_t
print("size_t:", lib.add_size_t(10, 20)) # 输出: 30
# ssize_t -> c_ssize_t
lib.add_ssize_t.argtypes = (ctypes.c_ssize_t, ctypes.c_ssize_t)
lib.add_ssize_t.restype = ctypes.c_ssize_t
print("ssize_t:", lib.add_ssize_t(10, 20)) # 输出: 30
""" 数组 """
lib.fill_array.argtypes = (ctypes.pointer(ctypes.c_int), ctypes.c_int)
lib.fill_array.restype = none
ls = [1, 3, 5]
arr = (ctypes.c_int * len(ls))(*ls)
lib.fill_array(arr, len(arr))
print("array:", list(arr)) # array: [0, 3, 10]
""" 结构体 """
class person(ctypes.structure):
_fields_ = [("name", ctypes.c_char * 50), ("age", ctypes.c_int)]
# 情况 1:入参和返回值都是结构体
lib.update_person_by_value.argtypes = (person,)
lib.update_person_by_value.restype = person
person1 = person(name="alice".encode(), age=25)
print(f"before (value): name={person1.name.decode()}, age={person1.age}")
updated_person = lib.update_person_by_value(person1)
print(f"after (value): name={updated_person.name.decode()}, age={updated_person.age}")
# 情况 2:入参为结构体指针
lib.update_person_by_pointer.argtypes = (ctypes.pointer(person),)
lib.update_person_by_pointer.restype = none
person2 = person(name="bob".encode(), age=30)
print(f"before (pointer): name={person2.name.decode()}, age={person2.age}")
lib.update_person_by_pointer(ctypes.byref(person2))
print(f"after (pointer): name={person2.name.decode()}, age={person2.age}")
到此这篇关于python调用c语言动态库的方法小结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python调用c语言动态库内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论