概述
set 是一种常用的数据结构,它表示一组唯一元素的集合。在不同的编程语言和库中,set 可能有不同的实现方式和特性。
set 集合数据结构具有以下特性:
- 唯一性:set 中的元素是唯一的,不允许重复。这意味着在 set 中添加重复的元素不会产生任何变化。
- 无序性:set 中的元素没有顺序。不能通过索引访问 set 中的元素,也不能对 set 中的元素进行排序。
- 可变性:set 通常是可变的,这意味着你可以添加或删除元素。
- 集合运算:set 支持多种集合运算,如并集、交集和差集。
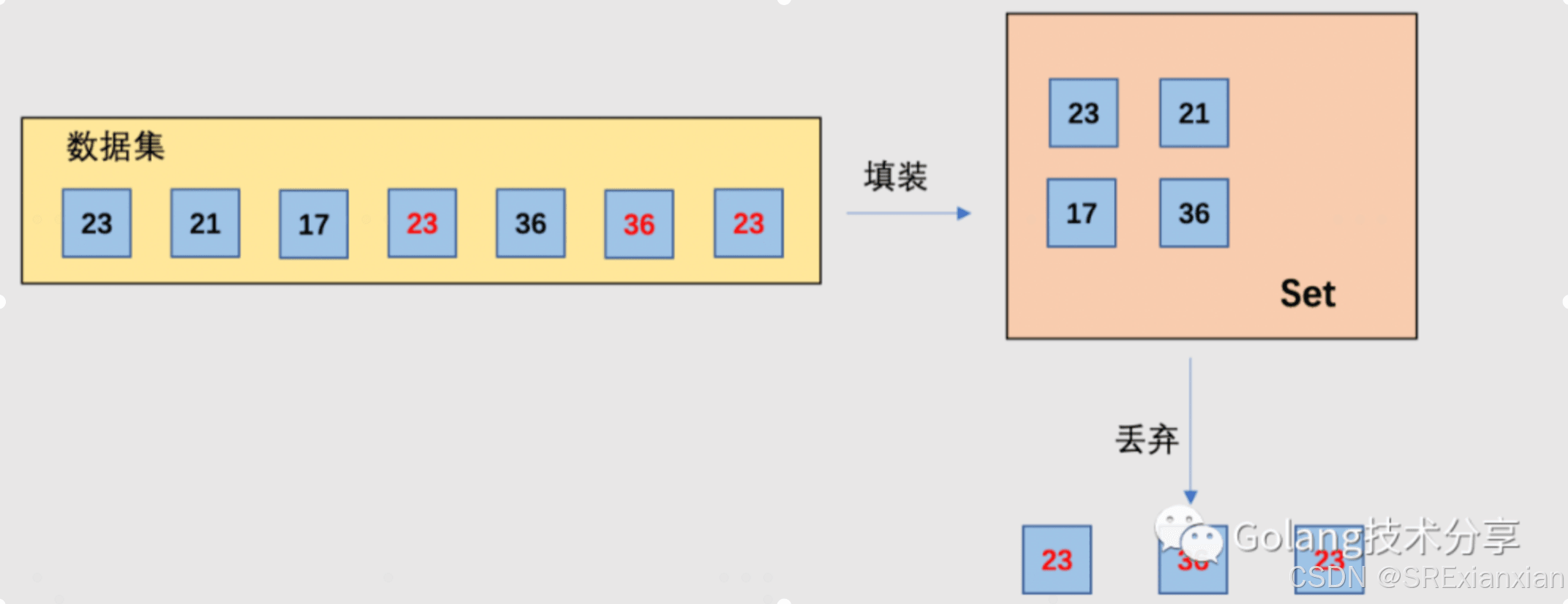
go语言中最常用的两种数据结构分别是 slice 和 map。 除了 go 内置的数据结构,还有一些数据结构是由 go 的官方 container 包提供,如 heap 堆、list 双向链表和ring 回环链表。但go语言中并没有内置set这种数据结构。本文聊聊go语言中set的实现方式。
我们知道 map 的键是具有唯一性,所以可以用 map 来实现数据结构 set。
set的实现
使用map使用一个set集合,意味着我们只关心 key 的存在,其 value 值并不重要,直接将vlaue设置为空接口。
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"sync"
)
/*
用map实现一个线程安全的set
*/
type void struct{}
var member void
type idata interface{}
type set struct {
mapset map[idata]struct{}
mutex sync.mutex
}
func newset() *set {
return &set{
mapset: make(map[idata]struct{}),
mutex: sync.mutex{},
}
}
func (s *set) add(data idata) bool {
s.mutex.lock()
defer s.mutex.unlock()
s.mapset[data] = member
return true
}
func (s *set) remove(data idata) error {
s.mutex.lock()
defer s.mutex.unlock()
for k, _ := range s.mapset {
if k == data {
delete(s.mapset, k)
return nil
}
}
return errors.new("not found")
}
func (s *set) pop() idata {
s.mutex.lock()
defer s.mutex.unlock()
if len(s.mapset) <= 0 {
return nil
}
for k, _ := range s.mapset {
return s.mapset[k]
}
return nil
}
func (s *set) size() int {
s.mutex.lock()
defer s.mutex.unlock()
return len(s.mapset)
}
func (s *set) all() []idata {
s.mutex.lock()
defer s.mutex.unlock()
datas := make([]idata, 0)
for k, _ := range s.mapset {
datas = append(datas, k)
}
return datas
}
func main() {
// test
myset := newset()
myset.add(1)
myset.add(2)
myset.add(1)
fmt.println(myset.all()) // [1 2]
myset.add(3)
fmt.println(myset.size()) //3
fmt.println(myset.all()) // [1 2 3]
myset.remove(2)
fmt.println(myset.all()) // [1 2 3]
}
set的三方库
在kubernetes中也实现了stirng,int32,int43,byte等几种基本类型为值的set集合。接下来我们分析下源码实现。找到源码为位置k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/sets
// sets.string is a set of strings, implemented via map[string]struct{} for minimal memory consumption.
// string类型定义,使用map来实现set集合,集合的元素是string
type string map[string]empty
// newstring creates a string from a list of values.
// 构造一个set,set集合存放的值是string类型
func newstring(items ...string) string {
ss := string{}
ss.insert(items...)
return ss
}
// insert adds items to the set.
// 插入元素到集合
func (s string) insert(items ...string) string {
for _, item := range items {
s[item] = empty{}
}
return s
}
// delete removes all items from the set.
// 从set中删除指定string
func (s string) delete(items ...string) string {
for _, item := range items {
delete(s, item)
}
return s
}
// has returns true if and only if item is contained in the set.
// 判断set是否包含指定的string
func (s string) has(item string) bool {
_, contained := s[item]
return contained
}
// hasall returns true if and only if all items are contained in the set.
// 判断set是否包括一组所有的字符串
func (s string) hasall(items ...string) bool {
for _, item := range items {
if !s.has(item) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// hasany returns true if any items are contained in the set.
// 判断一组字符串是否有包括在set中
func (s string) hasany(items ...string) bool {
for _, item := range items {
if s.has(item) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
总结
本文介绍了set的特点,并介绍go语言中如何用map实现一个set,最后我们分析了kubernete源码中的set库的源码。由于源码比较简单,就没有展开分析。
到此这篇关于go语言中数据接口set集合的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关go语言 set集合内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论