一.workqueues模型
workqueues(任务模式):让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。
架构:
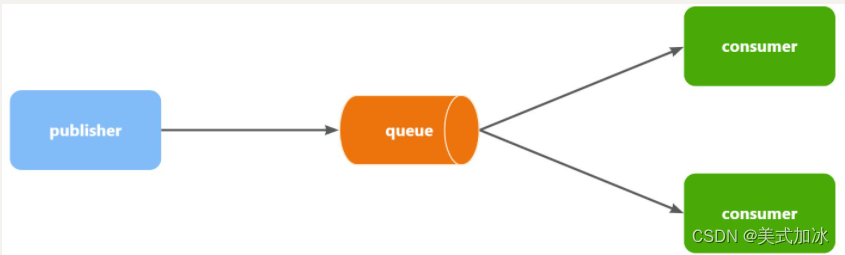
所需场景:
当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。 此时就可以使用work 模型,多个消费者共同处理消息处理,消息处理的速度就能大大提高了。
1.新建队work.queue
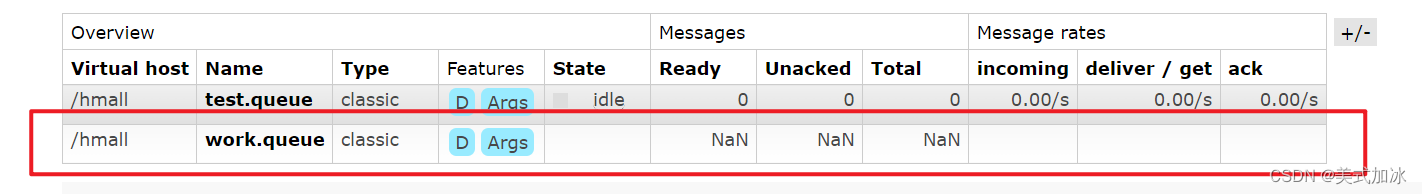
2.生产者模块循环发送消息
@test
void testworkqueue() throws interruptedexception {
string queuename = "work.queue";
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
string msg = "hello, worker, message_" + i;
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(queuename, msg);
thread.sleep(20);
}
}3.消费者模块模拟多个消费者绑定该队列
@rabbitlistener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenworkqueuemsg1(string msg) throws interruptedexception {
system.out.println("消费者一接收到work.queue的信息" + msg+ localdatetime.now());
thread.sleep(20);
}
@rabbitlistener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenworkqueuemsg2(string msg) throws interruptedexception {
system.out.println("消费者2接收到work.queue的信息" + msg+localdatetime.now());
thread.sleep(200);
}消费者1 sleep了20毫秒,相当于每秒钟处理50个消息
消费者1 sleep了20毫秒,相当于每秒钟处理50个消息
4.测试
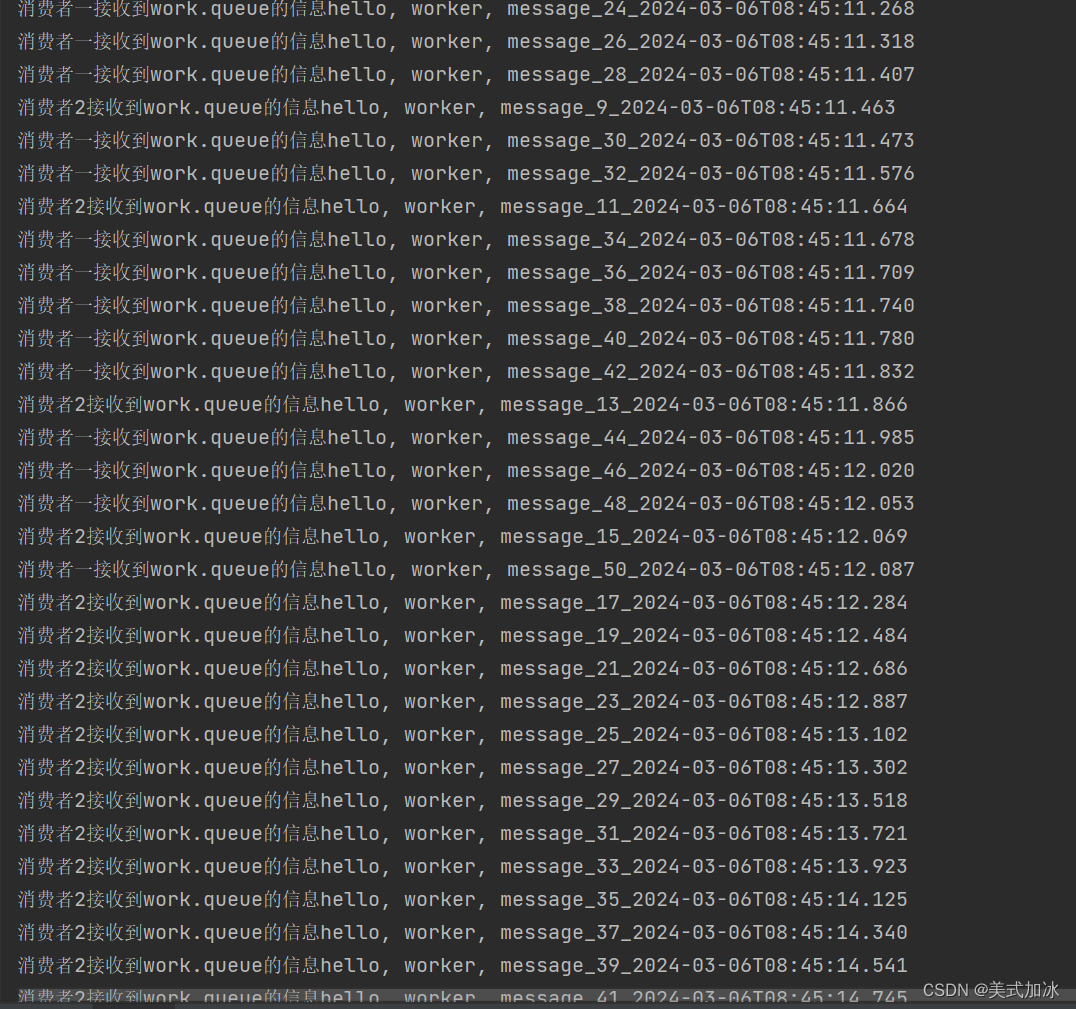


测试结果中:尽管给消费者二设置了比消费者一十倍长的休眠时间。但是两个消费者的处理信息个数是相同的。且消费者一很快就处理完消息,而剩下的消息只有消费者二去消费。并没有充分利用每一个消费者的能力。
可以通过配置消费者模块的yml文件解决该问题
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息5.二次测试
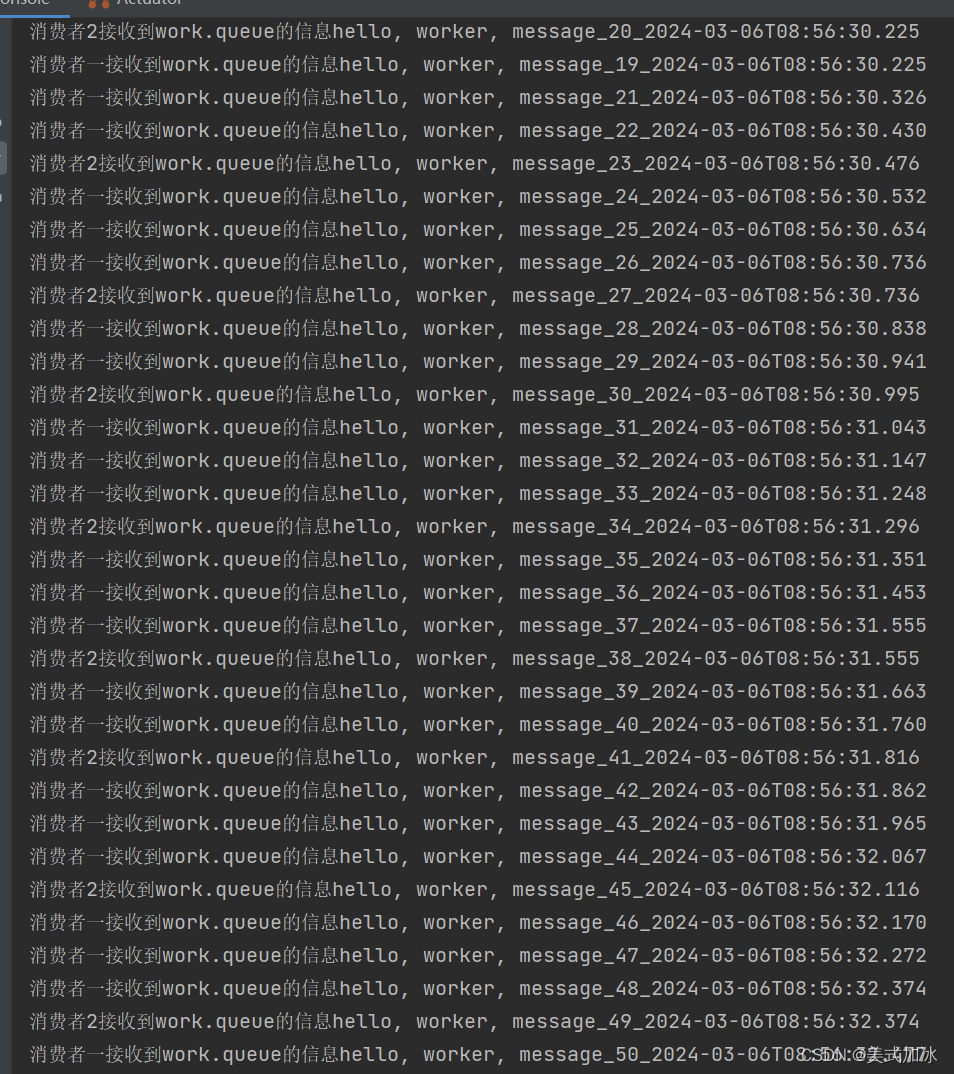


6.总结:
work模型的使用:
-
多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
-
通过设置prefetch来控制消费者预取的消息数量
二.exchange(交换机)
exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失。
交换机的类型有四种:
-
fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列。我们最早在控制台使用的正是fanout交换机
-
direct:订阅,基于routingkey(路由key)发送给订阅了消息的队列
-
topic:通配符订阅,与direct类似,只不过routingkey可以使用通配符
-
headers:头匹配,基于mq的消息头匹配,用的较少。
三.fanout交换机(广播)
架构:
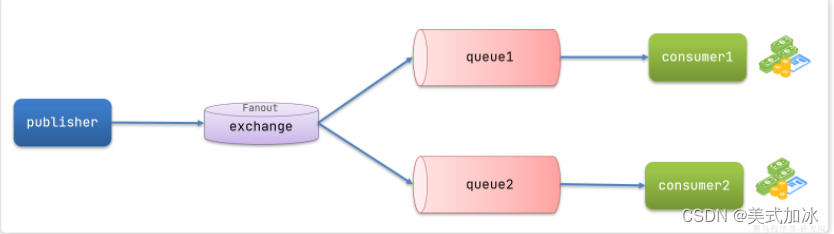
广播模式发送流程:
-
1) 可以有多个队列
-
2) 每个队列都要绑定到exchange(交换机)
-
3) 生产者发送的消息,只能发送到交换机
-
4) 交换机把消息发送给绑定过的所有队列
-
5) 订阅队列的消费者都能拿到消息
一.创建两个队列:fanout.queue1,fanout.queue2

二.创建一个交互机:fanout
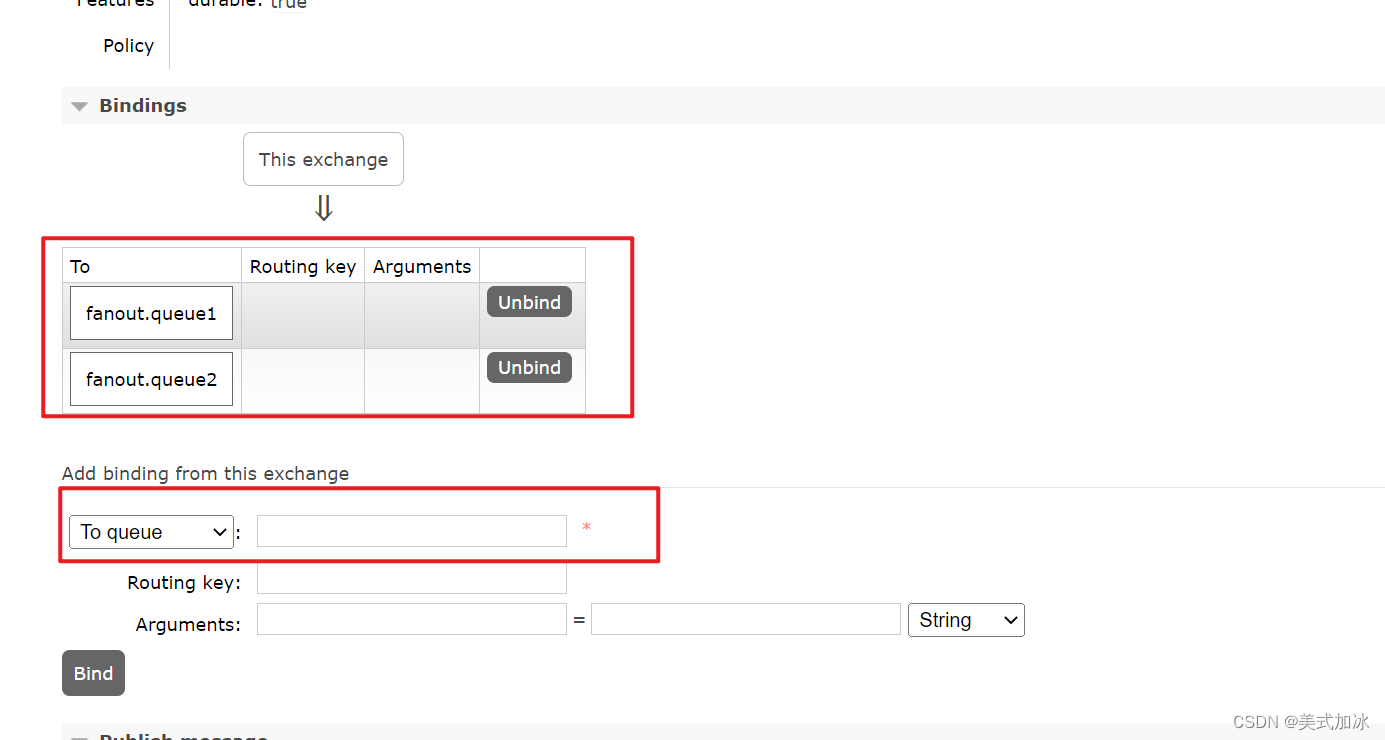
三.将队列绑定至交互机
四.编写测试代码
生产者端:
@test
void testsendfanout() {
string exchangename = "hmall.fanout";//交换机
string msg = "hello, everyone!";
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename, null, msg);
}消费端:
@rabbitlistener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenfanoutqueue1(string msg) throws interruptedexception {
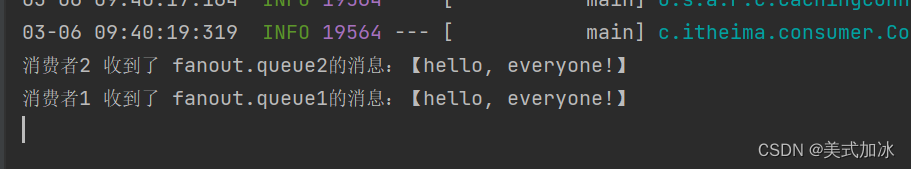
system.out.println("消费者1 收到了 fanout.queue1的消息:【" + msg +"】");
}
@rabbitlistener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenfanoutqueue2(string msg) throws interruptedexception {
system.out.println("消费者2 收到了 fanout.queue2的消息:【" + msg +"】");
}测试结果:
五.总结
交换机的作用
-
接收publisher发送的消息
-
将消息按照规则路由到与之绑定的队列
-
不能缓存消息,路由失败,消息丢失
-
fanoutexchange的会将消息路由到每个绑定的队列
四.direct交换机(订阅)
在fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有订阅的队列都消费。但是,在某些场景下,我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费。这时就要用到direct类型的exchange。
结构:
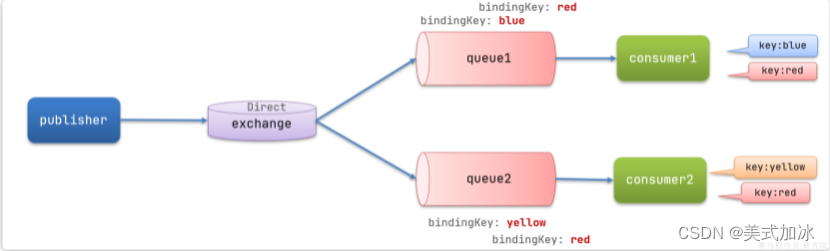
在direct模型下
-
队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个
routingkey(路由key) -
消息的发送方在 向 exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的
routingkey。 -
exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的
routing key进行判断,只有队列的routingkey与消息的routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
一.测试逻辑:
-
声明一个名为
hmall.direct的交换机 -
声明队列
direct.queue1,绑定hmall.direct,bindingkey为blud和red -
声明队列
direct.queue2,绑定hmall.direct,bindingkey为yellow和red -
在
consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听direct.queue1和direct.queue2 -
在publisher中编写测试方法,向
hmall.direct发送消息
二.创建两个队列direct.queue1和direct.queue2

三.创建一个direct类型交换机 hmall.direct并绑定队列
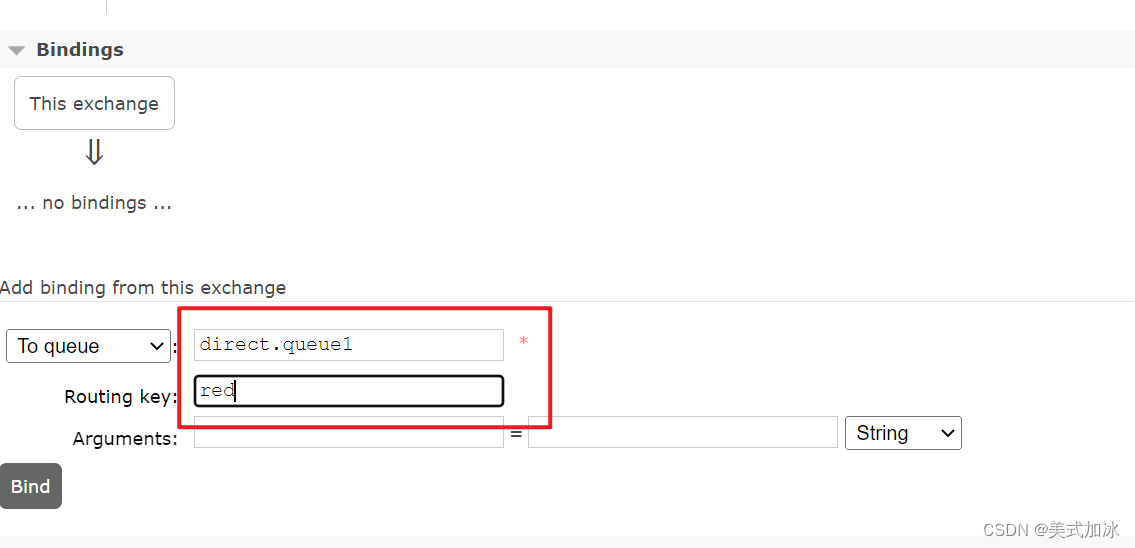
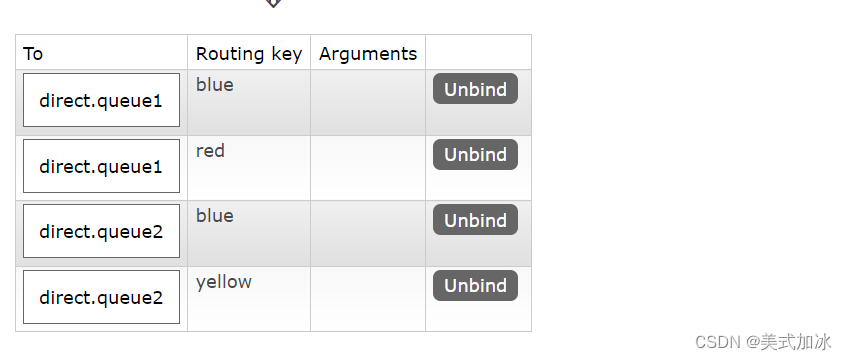
四.编写测试类
消费模块:
@rabbitlistener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void listendirectqueue1(string msg){
system.out.println("消费者1 收到了 direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg +"】");
}
@rabbitlistener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void listendirectqueue2(string msg){
system.out.println("消费者2 收到了 direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg +"】");
}生产模块:
@test
void testsenddirect() {
string exchangename = "hmall.direct";
string msg = "蓝色通知,警报解除,哥斯拉是放的气球";
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename, "blue", msg);
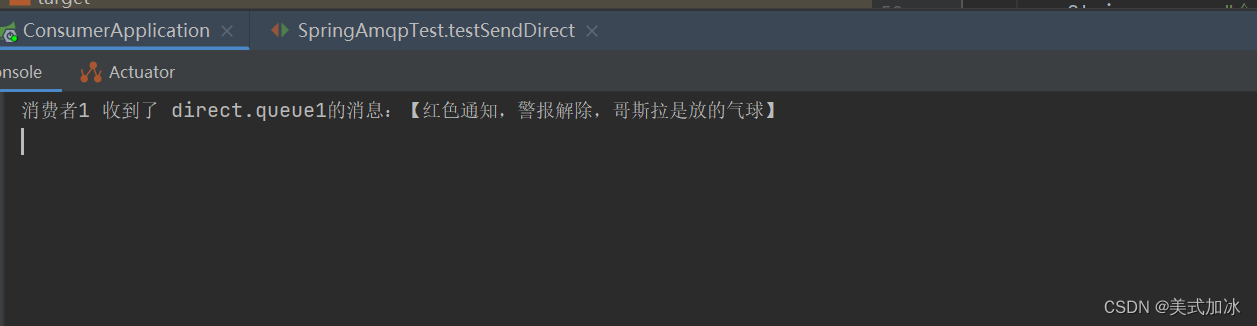
}测试结果:
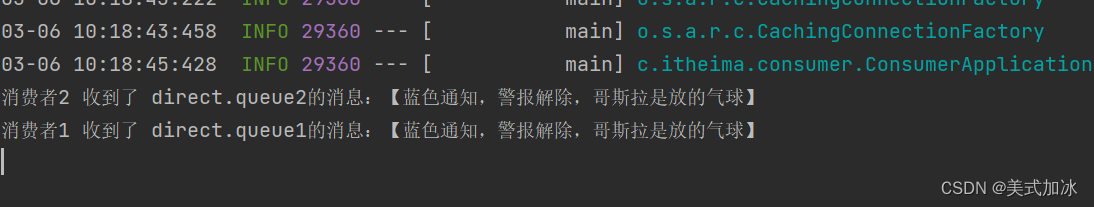
将rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename, "blue", msg)改为rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename, "red", msg)
测试结果:
五.总结:
direct交换机与fanout交换机的差异
-
fanout交换机将消息路由给每一个与之绑定的队列
-
direct交换机根据routingkey判断路由给哪个队列
-
如果多个队列具有相同的routingkey,则与fanout功能类似
五.topic交换机
架构:
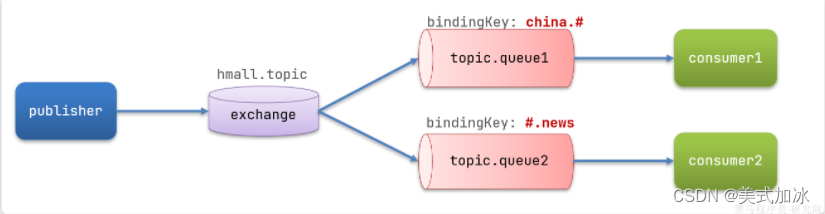
topic类型的exchange与direct相比,都是可以根据routingkey把消息路由到不同的队列。 只不过topic类型exchange可以让队列在绑定bindingkey 的时候使用通配符!
bindingkey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以.分割,例如: item.insert
通配符规则:
-
#:匹配一个或多个词 -
*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
举例:
-
item.#:能够匹配item.spu.insert或者item.spu -
item.*:只能匹配item.spu
一.测试逻辑
假如此时生产者发送的消息使用的routingkey共有四种:
-
china.news代表有中国的新闻消息; -
china.weather代表中国的天气消息; -
usa.news则代表美国新闻 -
usa.weather代表美国的天气消息;
解释:
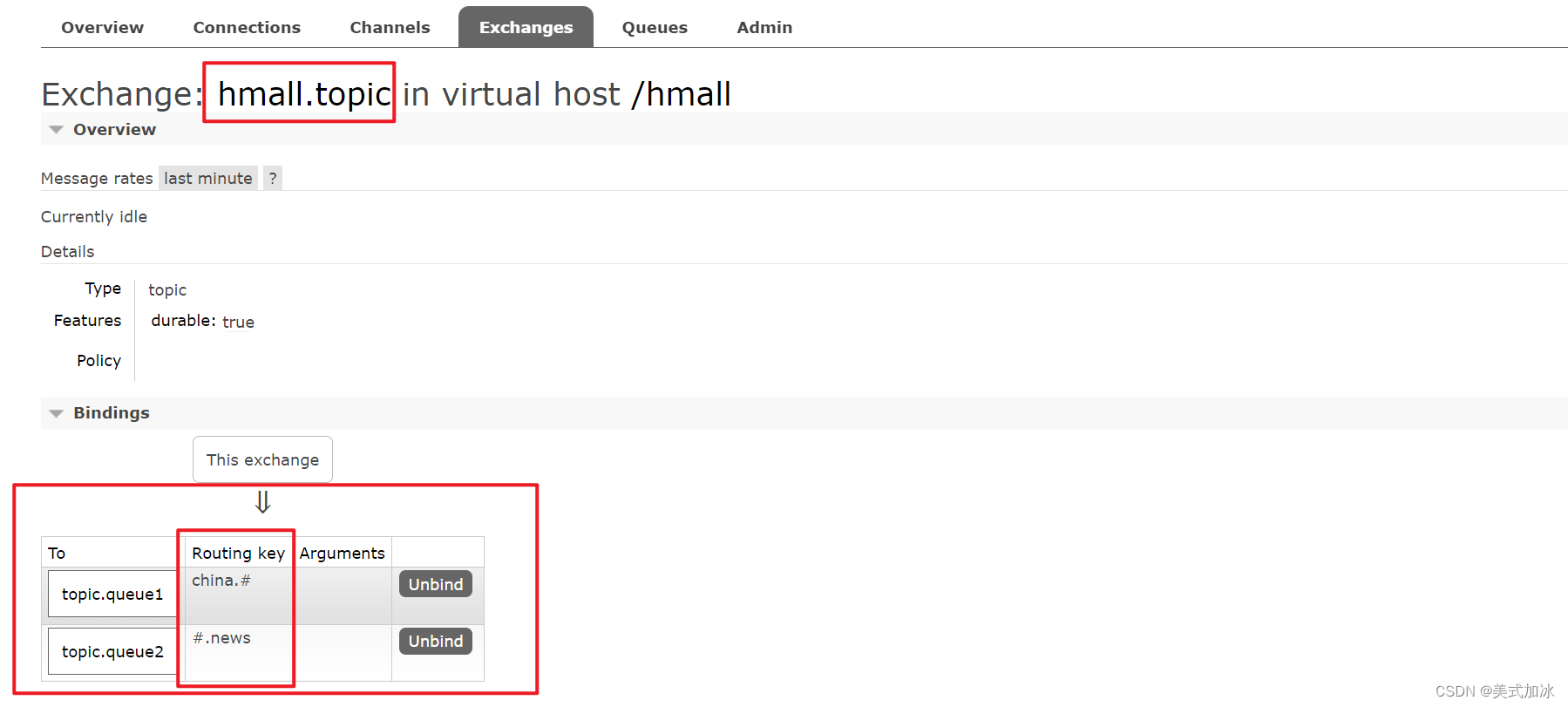
-
topic.queue1:绑定的是china.#,凡是以china.开头的routing key都会被匹配到,包括:-
china.news -
china.weather
-
-
topic.queue2:绑定的是#.news,凡是以.news结尾的routing key都会被匹配。包括:-
china.news -
usa.news
-
二.绑定交互机与队列
三.编写测试代码
消费者:
@rabbitlistener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void listentopicqueue1(string msg){
system.out.println("消费者1接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@rabbitlistener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void listentopicqueue2(string msg){
system.out.println("消费者2接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}生产者:
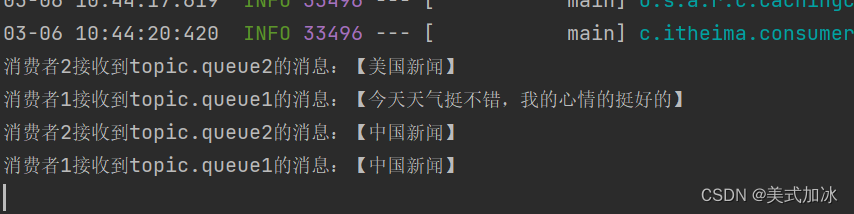
@test
void testsendtopic() {
string exchangename = "hmall.topic";
string msg = "今天天气挺不错,我的心情的挺好的";
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename, "china.weather", msg);
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename,"usa.news","美国新闻");
rabbittemplate.convertandsend(exchangename,"china.news","中国新闻");
}测试结果
四.总结
direct交换机与topic交换机的差异
-
topic交换机接收的消息routingkey必须是多个单词,以
**.**分割 -
topic交换机与队列绑定时的bindingkey可以指定通配符
-
#:代表0个或多个词 -
*:代表1个词


发表评论