predict模式用于在新图像或视频上使用经过训练的yolov8模型进行预测,在此模式下,模型从checkpoint 文件加载,用户可以提供图像或视频来执行推理。模型预测输入图像或视频中对象的类别和位置。
from ultralytics import yolo
from pil import image
import cv2
model = yolo("model.pt")
# 接受所有格式-image/dir/path/url/video/pil/ndarray。0用于网络摄像头
results = model.predict(source="0")
results = model.predict(source="folder", show=true) # 展示预测结果
# from pil
im1 = image.open("bus.jpg")
results = model.predict(source=im1, save=true) # 保存绘制的图像
# from ndarray
im2 = cv2.imread("bus.jpg")
results = model.predict(source=im2, save=true, save_txt=true) # 将预测保存为标签
# from list of pil/ndarray
results = model.predict(source=[im1, im2])
yolov8预测模式可以为各种任务生成预测,在使用流模式时返回结果对象列表或结果对象的内存高效生成器。通过在预测器的调用方法中传递stream=true来启用流模式。stream=true的流媒体模式应用于长视频或大型预测源,否则结果将在内存中累积并最终导致内存不足错误。
inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
results = model(inputs, stream=true) # generator of results objects
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # masks object for segmentation masks outputs
probs = result.probs # class probabilities for classification outputs
相关参数如下:
| key | value | description |
|---|---|---|
source | 'ultralytics/assets' | source directory for images or videos |
conf | 0.25 | object confidence threshold for detection |
iou | 0.7 | intersection over union (iou) threshold for nms |
half | false | use half precision (fp16) |
device | none | device to run on, i.e. cuda device=0/1/2/3 or device=cpu |
show | false | show results if possible |
save | false | save images with results |
save_txt | false | save results as .txt file |
save_conf | false | save results with confidence scores |
save_crop | false | save cropped images with results |
hide_labels | false | hide labels |
hide_conf | false | hide confidence scores |
max_det | 300 | maximum number of detections per image |
vid_stride | false | video frame-rate stride |
line_thickness | 3 | bounding box thickness (pixels) |
visualize | false | visualize model features |
augment | false | apply image augmentation to prediction sources |
agnostic_nms | false | class-agnostic nms |
retina_masks | false | use high-resolution segmentation masks |
classes | none | filter results by class, i.e. class=0, or class=[0,2,3] |
boxes | true | show boxes in segmentation predictions |
yolov8可以接受各种输入源,如下表所示。这包括图像、url、pil图像、opencv、numpy数组、torch张量、csv文件、视频、目录、全局、youtube视频和流。该表指示每个源是否可以在流模式下使用stream=true✅以及每个源的示例参数。
| source | model(arg) | type | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| image | 'im.jpg' | str, path | |
| url | 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' | str | |
| screenshot | 'screen' | str | |
| pil | image.open('im.jpg') | pil.image | hwc, rgb |
| opencv | cv2.imread('im.jpg')[:,:,::-1] | np.ndarray | hwc, bgr to rgb |
| numpy | np.zeros((640,1280,3)) | np.ndarray | hwc |
| torch | torch.zeros(16,3,320,640) | torch.tensor | bchw, rgb |
| csv | 'sources.csv' | str, path | rtsp, rtmp, http |
| video ✅ | 'vid.mp4' | str, path | |
| directory ✅ | 'path/' | str, path | |
| glob ✅ | 'path/*.jpg' | str | use * operator |
| youtube ✅ | 'https://youtu.be/zgi9g1ksqhc' | str | |
| stream ✅ | 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' | str | rtsp, rtmp, http |
图像类型
| image suffixes | example predict command | reference |
|---|---|---|
| .bmp | yolo predict source=image.bmp | microsoft bmp file format |
| .dng | yolo predict source=image.dng | adobe dng |
| .jpeg | yolo predict source=image.jpeg | jpeg |
| .jpg | yolo predict source=image.jpg | jpeg |
| .mpo | yolo predict source=image.mpo | multi picture object |
| .png | yolo predict source=image.png | portable network graphics |
| .tif | yolo predict source=image.tif | tag image file format |
| .tiff | yolo predict source=image.tiff | tag image file format |
| .webp | yolo predict source=image.webp | webp |
| .pfm | yolo predict source=image.pfm | portable floatmap |
视频类型
| video suffixes | example predict command | reference |
|---|---|---|
| .asf | yolo predict source=video.asf | advanced systems format |
| .avi | yolo predict source=video.avi | audio video interleave |
| .gif | yolo predict source=video.gif | graphics interchange format |
| .m4v | yolo predict source=video.m4v | mpeg-4 part 14 |
| .mkv | yolo predict source=video.mkv | matroska |
| .mov | yolo predict source=video.mov | quicktime file format |
| .mp4 | yolo predict source=video.mp4 | mpeg-4 part 14 - wikipedia |
| .mpeg | yolo predict source=video.mpeg | mpeg-1 part 2 |
| .mpg | yolo predict source=video.mpg | mpeg-1 part 2 |
| .ts | yolo predict source=video.ts | mpeg transport stream |
| .wmv | yolo predict source=video.wmv | windows media video |
| .webm | yolo predict source=video.webm | webm project |
预测结果对象包含以下组件:
results.boxes: — 具有用于操作边界框的属性和方法的boxes
results.masks: — 用于索引掩码或获取段坐标的掩码对象
results.probs: — 包含类概率或logits
results.orig_img: — 载入内存的原始图像
results.path: — 包含输入图像路径的路径
默认情况下,每个结果都由一个torch. tensor组成,它允许轻松操作:
results = results.cuda()
results = results.cpu()
results = results.to('cpu')
results = results.numpy()
from ultralytics import yolo
import cv2
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.benchmarks import benchmark
model = yolo("yolov8-seg.yaml").load('yolov8n-seg.pt')
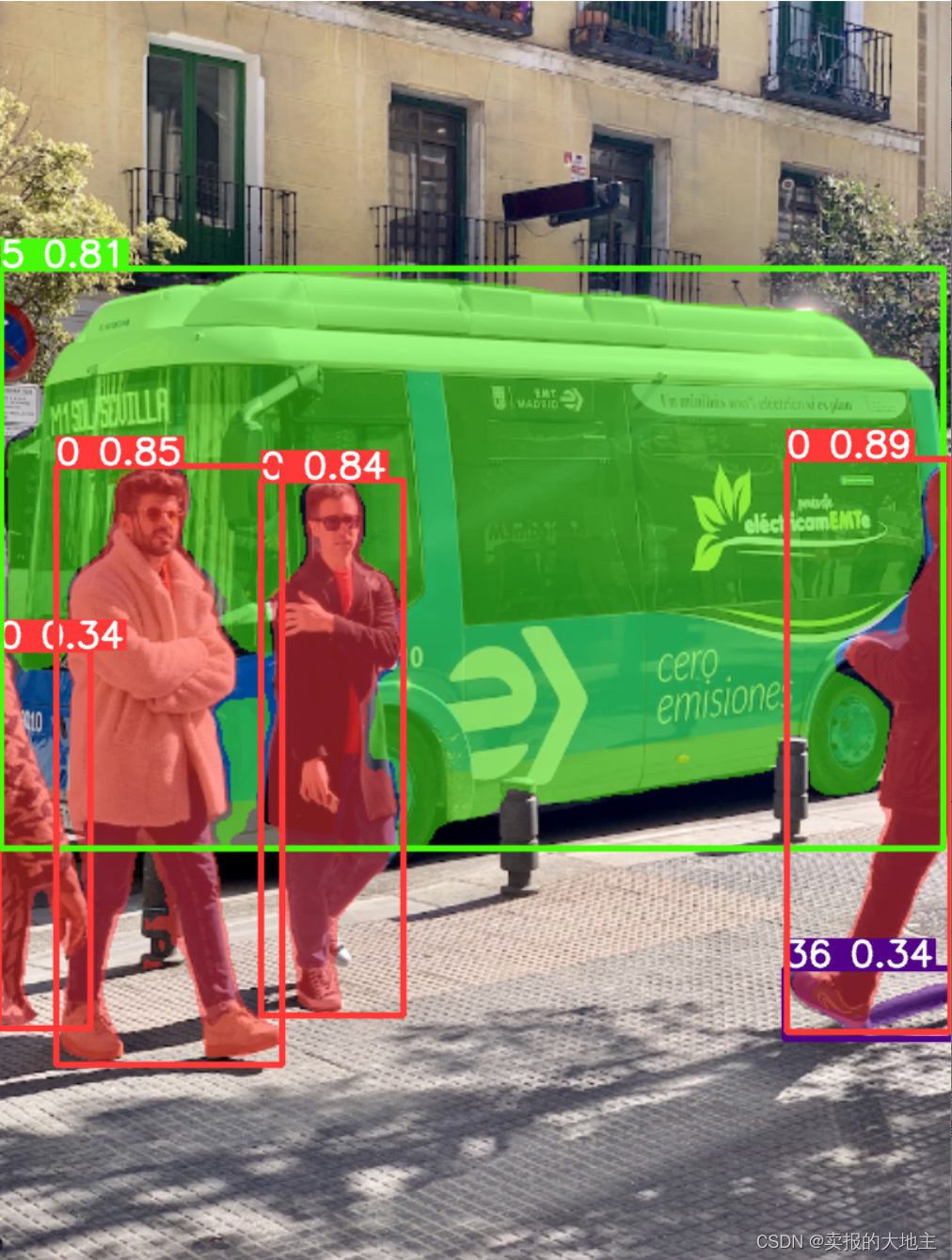
results = model.predict(r'e:\cs\dl\yolo\yolov8study\bus.jpg')
boxes = results[0].boxes
masks = results[0].masks
probs = results[0].probs
print(f"boxes:{boxes[0]}")
print(f"masks:{masks.xy }")
print(f"probs:{probs}")
output:
image 1/1 e:\cs\dl\yolo\yolov8study\bus.jpg: 640x480 4 0s, 1 5, 1 36, 25.9ms
speed: 4.0ms preprocess, 25.9ms inference, 10.0ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 640, 640)
warning 'boxes.boxes' is deprecated. use 'boxes.data' instead.
boxes:ultralytics.yolo.engine.results.boxes object with attributes:
boxes: tensor([[670.1221, 389.6674, 809.4929, 876.5032, 0.8875, 0.0000]], device='cuda:0')
cls: tensor([0.], device='cuda:0')
conf: tensor([0.8875], device='cuda:0')
data: tensor([[670.1221, 389.6674, 809.4929, 876.5032, 0.8875, 0.0000]], device='cuda:0')
id: none
is_track: false
orig_shape: tensor([1080, 810], device='cuda:0')
shape: torch.size([1, 6])
xywh: tensor([[739.8075, 633.0853, 139.3708, 486.8358]], device='cuda:0')
xywhn: tensor([[0.9133, 0.5862, 0.1721, 0.4508]], device='cuda:0')
xyxy: tensor([[670.1221, 389.6674, 809.4929, 876.5032]], device='cuda:0')
xyxyn: tensor([[0.8273, 0.3608, 0.9994, 0.8116]], device='cuda:0')
masks:[array([[ 804.94, 391.5],
[ 794.81, 401.62],
[ 794.81, 403.31],
[ 791.44, 406.69],
......
probs:none
我们可以使用result对象的plot()函数在图像对象中绘制结果。它绘制在结果对象中找到的所有组件(框、掩码、分类日志等)
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# display the annotated frame
cv2.imshow("yolov8 inference", annotated_frame)
cv2.waitkey()
cv2.destroyallwindows()
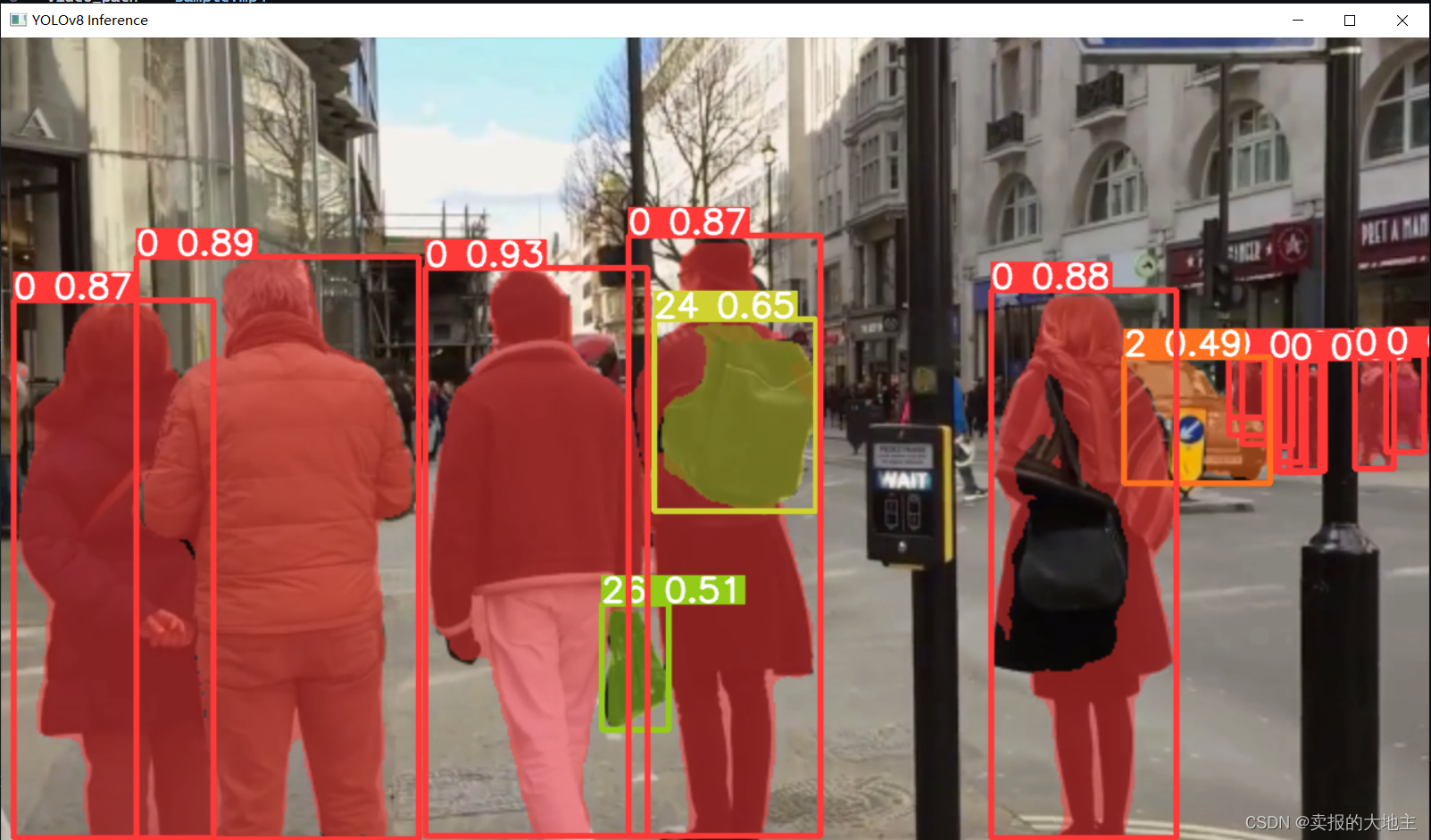
使用opencv(cv2)和yolov8对视频帧运行推理的python脚本。
import cv2
from ultralytics import yolo
# load the yolov8 model
model = model = yolo("yolov8-seg.yaml").load('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# open the video file
video_path = "sample.mp4"
cap = cv2.videocapture(video_path)
# loop through the video frames
while cap.isopened():
# read a frame from the video
success, frame = cap.read()
if success:
# run yolov8 inference on the frame
results = model(frame)
# visualize the results on the frame
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# display the annotated frame
cv2.imshow("yolov8 inference", annotated_frame)
# break the loop if 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitkey(1) & 0xff == ord("q"):
break
else:
# break the loop if the end of the video is reached
break
# release the video capture object and close the display window
cap.release()
cv2.destroyallwindows()



发表评论