一、项目背景
搜索引擎是现代设备中被广泛利用的一种系统软件,诸如百度、谷歌、搜索、bing等,或者抖音、快手、b站、小红书,甚至软件应用市场,windows(操作系统)中的各类提供搜索功能的背后都有搜索引擎的影子。
二、使用技术
spring + springmvc + mybatis
spring 负责提供:ioc、aop
springmvc 负责提供:web 业务处理
mybatis 负责提供:方便 sql 处理
三、项目功能
根据用户检索的内容,把检索到的相关信息展现给用户。
四、整体逻辑图

五、具体实现
1.基本流程(用户角度):
用户输入搜索词(一个词或者多个词),在已有文档中,找到文档包含这些词的所有文档信息,再给出搜索后的列表。
2.设计
(1)初步想法(不可行)
首先,我们可以分析到,这实际上就是需要一个文档表,里面记录他的 id、标题、内容。然后在数据库中查找:select * from 文档表 where 标题 like '%搜索词%' or 内容 like '%搜索词%'
但我们不使用这种方式(sql),因为上述 sql 的查找性能非常差。
文档个数记为 m,文档的平均长度(标题 + 内容)记为 n。o(m*n)。
现实中,m 非常大(几百亿篇文档),所以从性能上这个方案不可行。
(2)可实行的方法
使用倒排索引(inverted index)
倒排索引的大概结构:key-value 形式。key:词,value:词出现在哪些文档中。
①提前构造好倒排索引,倒排索引中有 id、单词、这个单词对应的文章编号、这个单词的权重。
②当我们比如说去搜索 “list” 这个单词的时候,根据倒排索引,我们可以找到这个单词出现在哪些文档中,根据文档的编号,取出对应的文档内容。
③我们再维护一个正排索引,这里面有 docid(文章的编号)、文章标题、文章的 url、文章的内容
④当我们根据倒排索引搜索到单词对应的文章id时,比如只取前 20 篇文章,那我们就只需要进行 20 次正排索引查找即可。
补充:文档是什么文档不重要,可以是 html、pdf、图片、视频等等。
我们经常用到的搜索引擎(百度、搜狗),他背后的数据获取一般使用爬虫自动在互联网上搜集信息,将所有内容爬成文档下来,然后进行检索和排序等操作。
我们这个项目只针对 jdk api 文档库中的 html 做搜索
(3)构建两大模块
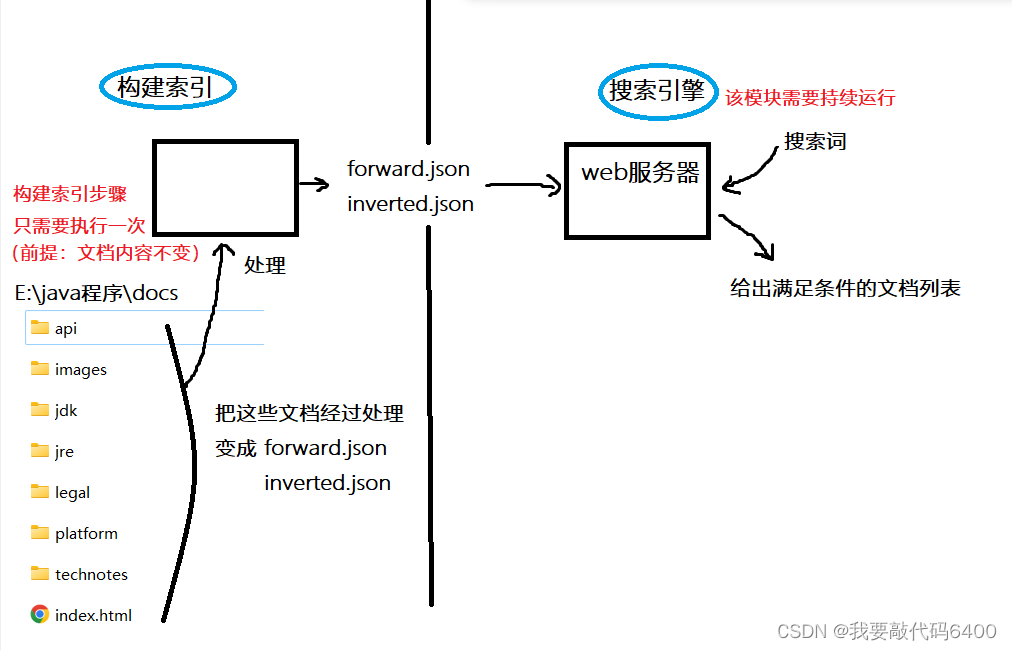
3.构建索引模块
不需要使用 web 功能,只需要执行一次
我们写一个 indexer 类(indexer/command/indexer),这是:构建索引的模块,是整个程序的逻辑入口。@slf4j ——添加 spring 日志的使用 @component —— 注册成 spring 的 bean

我们让这个类实现 commandlinerunner 接口。
@component
public class indexer implements commandlinerunner {
@override
public void run(string... args) throws exception {
log.info("这里的整个程序的逻辑入口");
}
}
构造索引的大概步骤:
1.扫描文档目录下的所有文档:目录遍历的过程 filescanner
// 1. 扫描出来所有的 html 文件
log.debug("开始扫描目录,找出所有的 html 文件。{}", properties.getdocrootpath());
list<file> htmlfilelist = filescanner.scanfile(properties.getdocrootpath(), file -> {
return file.isfile() && file.getname().endswith(".html");
});
log.debug("扫描目录结束,一共得到 {} 个文件。", htmlfilelist.size());我们把这个类注册成 spring bean —— @service
具体在 indexer.util.filescanner 中完成。
- 以 rootpath 作为根目录,开始进行文件的扫描,把所有符合条件的 file 对象,作为结果,以 list 形式返回(把这个过程想象成一棵树)
- 针对目录树进行遍历,深度优先 or 广度优先即可,确保每个文件都没遍历到即可,我们这里采用深度优先遍历,使用递归完成
1. 先通过目录,得到该目录下的孩子文件有哪些
file[] files = directoryfile.listfiles();2. 遍历每个文件,检查是否符合条件
for (file file : files) {
// 通过 filter.accept(file) 的返回值,判断是否符合条件
if (filter.accept(file)) {
// 说明符合条件,需要把该文件加入到结果 list 中
resultlist.add(file);
}
}3. 遍历每个文件,针对是目录的情况,继续深度优先遍历(递归)
for (file file : files) {
if (file.isdirectory()) {
traversal(file, filter, resultlist);
}
}
2.针对每一篇文档进行分析、处理
得到文档的 标题(这里就把他的文件名作为标题)、最终访问的 url(实际上是一个相对路径)、文档下的内容(io 读操作)
标题:
url: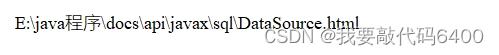

进行分词后才能得到倒排索引中保存的key,也就是你想要搜索的词。
这个分词引入第三方库来做nlp
// 2. 针对每个 html 文件,得到其 标题、url、正文信息,把这些信息封装成一个对象(文档 document)
file rootfile = new file(properties.getdocrootpath());
list<document> documentlist = htmlfilelist.stream()
.parallel() // 【注意】由于我们使用了 stream 用法,所以,可以通过添加 .parallel(),使得整个操作变成并行,利用多核增加运行速度
.map(file -> new document(file, properties.geturlprefix(), rootfile))
.collect(collectors.tolist());
log.debug("构建文档完毕,一共 {} 篇文档", documentlist.size());具体在 indexer.model.document 中完成
- 扫描出来所有的 html 文件(需要依赖filescanner 对象,构造方法注入的方式,让 spring 容器,注入 filescanner 对象进来)
这里最好,把要扫描的文件路径放在配置文件(src/main/resources/application.yml)中,这样有利于以后修改会更方便
list<file> htmlfilelist = filescanner.scanfile(properties.getdocrootpath(), file -> {
return file.isfile() && file.getname().endswith(".html");
});searcher:
indexer:
doc-root-path: e:\java程序\docs\api
url-prefix: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/之后用 properties 的方式来读取
package com.lingqi.searcher.indexer.properties;
import lombok.*;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
@component // 是注册到 spring 的一个 bean
@configurationproperties("searcher.indexer")
@data // = @getter + @setter + @tostring + @equalsandhashcode
public class indexerproperties {
// 对应 application.yml 配置下的 searcher.indexer.doc-root-path
private string docrootpath;
}
- 针对每个 html 文件,得到其 标题、url、正文信息,把这些信息封装成一个对象(文档 document——model/document)
标题:从文件名中,将 .html 后缀去掉,剩余的看作标题
private string parsetitle(file file) {
// 从文件名中,将 .html 后缀去掉,剩余的看作标题
string name = file.getname();
string suffix = ".html";
return name.substring(0, name.length() - suffix.length());
}url:需要得到一个相对路径,file 相对于 rootfile 的相对路径 。
把所有反斜杠(\) 变成正斜杠(/)
最终得到 java/sql/datasource.html
正文信息:
随便打开一篇文档:
因此使用正则表达式完成上述工作
先把文章一行一行全部读取到 stringbuilder 中,再把 stringbuilder 中不需要的那些内容进行删除或者替换
return contentbuilder.tostring()
// 首先去掉 <script ...>...</script>
.replaceall("<script.*?>.*?</script>", " ")
// 去掉标签
.replaceall("<.*?>", " ")
// 把最后多出来的空格删除掉
.replaceall("\\s+", " ")
.trim();
3.进行正排索引的保存
拿到分词后,我们就知道每一篇文档的 标题、url、内容、标题和内容的每个词
利用上述信息就可以构建索引了。正排索引、倒排索引
正排索引有1w条数据,倒排索引有600w条。如果一条一条插入,需要循环600w次才可以插入完成。但我们可以设置成一次插入1000条数据,这样只需要循环6000次就可以了。
因此我们只需要两张表存在数据库中:
正排索引表(docid-pk、title、url、content)整体数量级不大,只有1w条,但是每一条比较大(content大)——批量插入的时候,每次记录不用太多(每次插入 10 条)
倒排索引(id-pk、word、docid、weight)整体数量级较大,有600w条,每一条的记录比较小——批量插入的时候,每次记录多插入一些(每次插入 1w条)
我们docid的生成方式利用 mysql 的表中的自增机制作为docid
写sql的:
@repository // 注册 spring bean
@mapper // 是一个 mybatis 管理的 mapper
public interface indexdatabasemapper {
// 正排
void batchinsertforwardindexes(@param("list") list<document> documentlist);
//倒排
void batchinsertinvertedindexes(@param("list") list<invertedrecord> recordlist);
}准备一个xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!doctype mapper
public "-//mybatis.org//dtd mapper 3.0//en"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lingqi.searcher.indexer.mapper.indexdatabasemapper">
在配置文件中也加入。在 spring 的配置文件中,指定 mybatis 查找 mapper xml 文件的路径
classpath:代表从 src/main/resources 下进行查找(这实际上是错误的理解,暂且可以这么简单理解关系不大)
index-mapper.xml文件中设置的
<mapper namespace="com.lingqi.searcher.indexer.mapper.indexdatabasemapper">
实际上对应的就是 我们用于写sql 的类 indexdatabasemapper。
因为我们这里实际上就是一个插入,所以是 insert 语句,因此我们在index-mapper.xml中写入insert语句
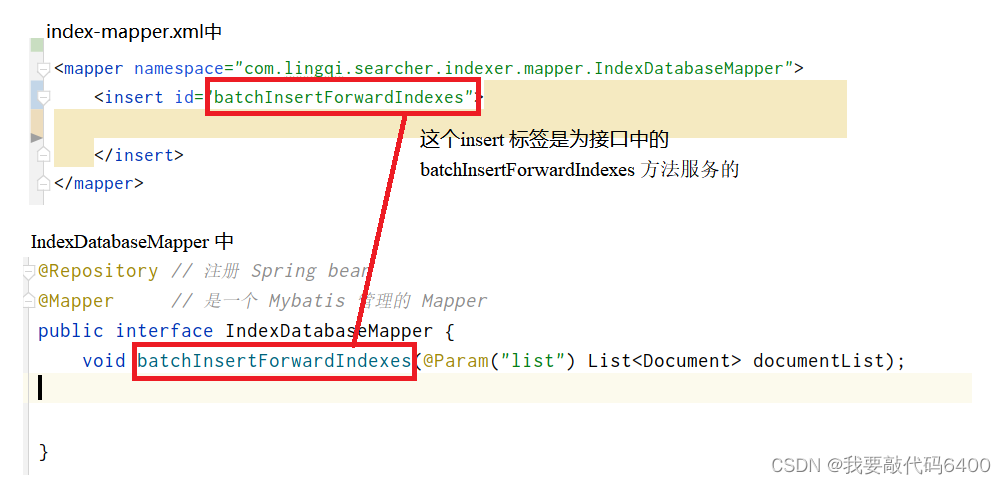
sql语句(写在index-mapper.xml中):

最终的到的 sql 就是拼接好的sql。
<insert id="batchinsertforwardindexes" usegeneratedkeys="true" keyproperty="docid" keycolumn="docid">
insert into forward_indexes (title, url, content) values
<!-- 一共有多少条记录,得根据用户传入的参数来决定,所以这里采用动态 sql 特性 -->
<foreach collection="list" item="doc" separator=", ">
(#{doc.title}, #{doc.url}, #{doc.content})
</foreach>
</insert>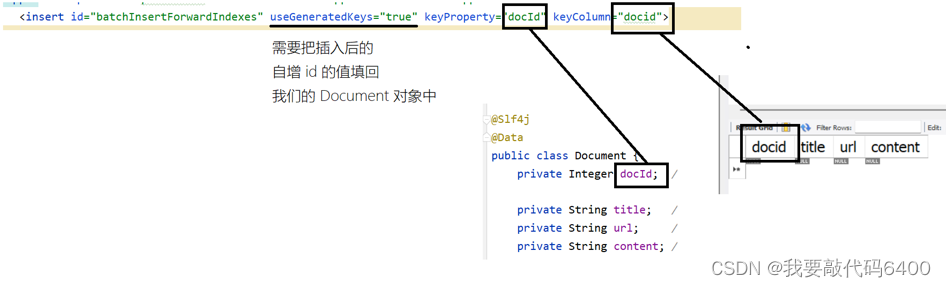
我们在 indexer/core/indexmanager 中完成插入
- 批量生成、保存正排索引
indexmanager.saveforwardindexesconcurrent(documentlist);单线程版本:
1. 批量插入时,每次插入多少条记录(由于每条记录比较大,所以这里使用 10 条就够了)
int batchsize = 10;2. 一共需要执行多少次 sql? 向上取整(documentlist.size() / batchsize)
int listsize = documentlist.size();
int times = (int) math.ceil(1.0 * listsize / batchsize); // ceil(天花板): 向上取整3. 开始分批次插入
for (int i = 0; i < listsize; i += batchsize) {
// 从 documentlist 中截取这批要插入的 文档列表(使用 list.sublist(int from, int to)
int from = i;
int to = integer.min(from + batchsize, listsize);
list<document> sublist = documentlist.sublist(from, to);
// 针对这个 sublist 做批量插入
mapper.batchinsertforwardindexes(sublist);
}多线程版本:
前面两步和单线程版本相同,在第三步循环插入中,把他们放到任务中去执行
我们需要一个线程池,定义在 indexer/config/appconfig 中:
@configuration
public class appconfig {
@bean
public executorservice executorservice() {
threadpoolexecutor executor = new threadpoolexecutor(
8, 20, 30, timeunit.seconds,
new arrayblockingqueue<>(5000),
(runnable task) -> {
thread thread = new thread(task);
thread.setname("批量插入线程");
return thread;
},
new threadpoolexecutor.abortpolicy()
);
return executor;
}
}@timing("构建 + 保存正排索引 —— 多线程版本")
@sneakythrows
public void saveforwardindexesconcurrent(list<document> documentlist) {
// 1. 批量插入时,每次插入多少条记录(由于每条记录比较大,所以这里使用 10 条就够了)
int batchsize = 10;
// 2. 一共需要执行多少次 sql? 向上取整(documentlist.size() / batchsize)
int listsize = documentlist.size();
int times = (int) math.ceil(1.0 * listsize / batchsize); // ceil(天花板): 向上取整
log.debug("一共需要 {} 批任务。", times);
countdownlatch latch = new countdownlatch(times); // 统计每个线程的完全情况,初始值是 times(一共多少批)
// 3. 开始分批次插入
for (int i = 0; i < listsize; i += batchsize) {
// 从 documentlist 中截取这批要插入的 文档列表(使用 list.sublist(int from, int to)
int from = i;
int to = integer.min(from + batchsize, listsize);
runnable task = () -> { // 内部类 / lambda 表达式里如果用到了外部变量,外部变量必须的 final(或者隐式 final 的变量)
list<document> sublist = documentlist.sublist(from, to);
// 针对这个 sublist 做批量插入
mapper.batchinsertforwardindexes(sublist);
latch.countdown(); // 每次任务完成之后,countdown(),让 latch 的个数减一
};
executorservice.submit(task); // 主线程只负责把一批批的任务提交到线程池,具体的插入工作,由线程池中的线程完成
}
// 4. 循环结束,只意味着主线程把任务提交完成了,但任务有没有做完是不知道的
// 主线程等在 latch 上,只到 latch 的个数变成 0,也就是所有任务都已经执行完了
latch.await();
}
4.倒排索引的生成和保存
针对文档进行分词,并且分别计算每个词的权重
在倒排索引中,我们需要进行分词、处理词的权重问题,这里我们统一放到 document 类中处理
对于每个 document 进行分词处理,需要第三方库的支持
在pom.xml 中添加依赖,它支持中文和英文分词
<dependency>
<groupid>org.ansj</groupid>
<artifactid>ansj_seg</artifactid>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>用法示例:
public void ansj() {
result result = toanalysis.parse("我爱北京天安门,天安门上太阳升。");
list<term> termlist = result.getterms();
for (term term : termlist) {
system.out.print(term.getname() + ", ");
system.out.print(term.getnaturestr() + ", ");
system.out.println(term.getrealname());
}
}
权重的设计
比如说用户要查找 “list” 这个单词,找到了好几篇文档都含有 “list” ,那么哪篇文章显示在前,哪篇在后?
所以,我们针对每个单词 ---> 每篇文档,都伴随一个 weight(权重),根据这个权重去排序(d倒序)
权重的计算:10 * 单词出现在标题的次数 + 1 * 单词出现在正文中的次数。
这里我们使用map 来维护,key就是某个词,value就是该词对应的权重
- 标题 | 分词
list<string> wordintitle = toanalysis.parse(title) //对title进行分词
.getterms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(term::getname)
.filter(s -> !ignoredwordset.contains(s))
.collect(collectors.tolist());- 标题 | 出现次数
map<string, integer> titlewordcount = new hashmap<>();
for (string word : wordintitle) {
int count = titlewordcount.getordefault(word, 0);
titlewordcount.put(word, count + 1);
}- 正文 | 分词
list<string> wordincontent = toanalysis.parse(content)
.getterms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(term::getname)
.collect(collectors.tolist());- 正文 | 出现次数
map<string, integer> contentwordcount = new hashmap<>();
for (string word : wordincontent) {
int count = contentwordcount.getordefault(word, 0);
contentwordcount.put(word, count + 1);
}- 计算权重值
用map,某个词对应的权重是多少
map<string, integer> wordtoweight = new hashmap<>();1. 先计算出有哪些词,不重复
就是使用set ,把所有的标题中的词初始化就都放入,然后再把所有正文的词也放入,set 中的元素是不能重复的。
2.遍历set中的元素,看这个词在标题中出现多少次,在正文中出现多少次,最后计算权重:
10 * 单词出现在标题的次数 + 1 * 单词出现在正文中的次数。
3.最后把该词和他的权重放到map中,最后返回这个map即可。
上述准备工作处理完成之后,我们开始进行倒排索引的生成和保护(在indexmanager类中)
1.定义一个类 ,里面的对象用来映射 inverted_indexes 表中的一条记录
// 这个对象映射 inverted_indexes 表中的一条记录(我们不关心表中的 id,就不写 id 了)
@data
public class invertedrecord {
private string word;
private int docid;
private int weight;
public invertedrecord(string word, int docid, int weight) {
this.word = word;
this.docid = docid;
this.weight = weight;
}
}2.执行 sql 在index-mapper.xml 中
<!-- 不关心自增 id -->
<insert id="batchinsertinvertedindexes">
insert into inverted_indexes (word, docid, weight) values
<foreach collection="list" item="record" separator=", ">
(#{record.word}, #{record.docid}, #{record.weight})
</foreach>
</insert>单线程版本:
3.设置 批量插入时,最多 10000 条
int batchsize = 10000;4.准备一个list (recordlist),里面是 invertedrecord 类型的,然后根据分词不断向里面放入,放够10000条了就插入一次。(也就是本批次要插入的数据)
5.遍历document 文件,调用 document.segwordandcalcweight() 方法,拿到分词结果。
6.遍历每个单词,得到单词和权重,再得到他的docid。构建出这三个后把他们放入recordlist中。
7.如果 recordlist.size() == batchsize,说明够一次插入了,够10000条了,就进行插入,插入完成之后清空 recordlist。然后就会重新循环再走。
8. recordlist 还剩一些,之前放进来,但还不够 batchsize 个的,所以最后再批量插入一次。执行完成之后就可以认为是所有插入都完成了。
多线程版本:
一次插入10000条,一次处理50篇文档
int batchsize = 10000; // 批量插入时,最多 10000 条
int groupsize = 50;提前把线程一批一批分好,分好之后交给线程去提交。
static class invertedinserttask implements runnable {
private final countdownlatch latch;
private final int batchsize;
private final list<document> documentlist;
private final indexdatabasemapper mapper;
invertedinserttask(countdownlatch latch, int batchsize, list<document> documentlist, indexdatabasemapper mapper) {
this.latch = latch;
this.batchsize = batchsize;
this.documentlist = documentlist;
this.mapper = mapper;
}
@override
public void run() {
list<invertedrecord> recordlist = new arraylist<>(); // 放这批要插入的数据
for (document document : documentlist) {
map<string, integer> wordtoweight = document.segwordandcalcweight();
for (map.entry<string, integer> entry : wordtoweight.entryset()) {
string word = entry.getkey();
int docid = document.getdocid();
int weight = entry.getvalue();
invertedrecord record = new invertedrecord(word, docid, weight);
recordlist.add(record);
// 如果 recordlist.size() == batchsize,说明够一次插入了
if (recordlist.size() == batchsize) {
mapper.batchinsertinvertedindexes(recordlist); // 批量插入
recordlist.clear(); // 清空 list,视为让 list.size() = 0
}
}
}
// recordlist 还剩一些,之前放进来,但还不够 batchsize 个的,所以最后再批量插入一次
mapper.batchinsertinvertedindexes(recordlist); // 批量插入
recordlist.clear();
latch.countdown();
}
}
@timing("构建 + 保存倒排索引 —— 多线程版本")
@sneakythrows
public void saveinvertedindexesconcurrent(list<document> documentlist) {
int batchsize = 10000; // 批量插入时,最多 10000 条
int groupsize = 50;
int listsize = documentlist.size();
int times = (int) math.ceil(listsize * 1.0 / groupsize);
countdownlatch latch = new countdownlatch(times);
for (int i = 0; i < listsize; i += groupsize) {
int from = i;
int to = integer.min(from + groupsize, listsize);
list<document> sublist = documentlist.sublist(from, to);
runnable task = new invertedinserttask(latch, batchsize, sublist, mapper);
executorservice.submit(task);
}
latch.await();
}
4.搜索模块
依赖索引构建完成之后才能进行,需要 web 功能
使用springmvc 实现了web服务
只针对一个词进行搜索
前端传过来这个词,根据词 去 倒排索引 + 正排索引中搜索,得到文档列表(可以做分页)
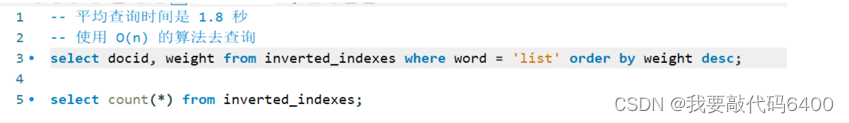
查询很慢,只是一个词就需要1.8秒,如果搜索的多了,时间更久,没有人愿意等待这么久
这里我们使用向表中新建索引来解决这个问题(针对 word 列去建索引)
建索引的过程,就是把 word 列作为 key,docid 作为 value,新建一棵搜索树(b+树)
从 key 查找 value,则时间复杂度变成o(log(n)) 21次 远远小于o(n) 200w 次
建索引的速度很慢,而且会导致数据插入很慢,所以,在表中的数据已经插入完成的情况下,再添加索引
给 word 和 weight 都添加索引,先用word 查,查完之后利用 weight 我们可以利用索引直接进行排序。
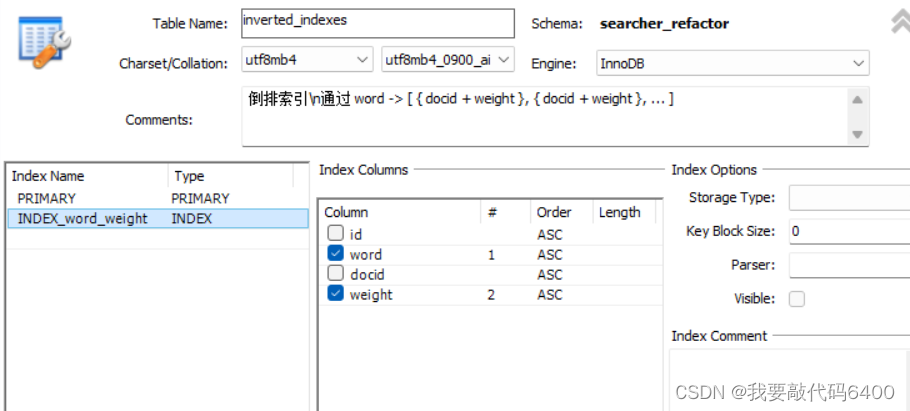
建立索引之后,查询只需要0.2秒

搜索树的 key:索引中的字段 word + weight(复合索引)
左边是word,右边weight
左边可以比较大小:索引的命中规则遵守靠左原则,select ... from 表 where word = ' ... ' 可以用上索引
随后按weight 进行排序,因为 key 里就有 weight ,所以 key 本身就是按照 weight 排序好的(搜索树的有序原则)
1.动态资源 /web, qurty=... 必须填的 page=...选填,但必须是数字
写一个controller ,叫做 searchcontroller ,通过 @controller 注解修饰,代表这是一个控制器。实现 @getmapping("/web"),查询的url 是 /web。里面 return "search";最后会渲染 search.html 这个模板
2.之后就需要进行查询,定义一个 document 类 模板,其中需要 title、url、content。
3.这些东西需要根据数据库去查,因此我们需要一个接口——searchmapper,用@repository @mapper 这两个注解来修饰。里面返回的是一组 document 类型的 list
@repository
@mapper
public interface searchmapper {
list<document> query(
@param("word") string word,
@param("limit") int limit,
@param("offset") int offset);
list<documentwightweight> querywithweight(
@param("word") string word,
@param("limit") int limit,
@param("offset") int offset
);
}配置文件:
spring:
main:
log-startup-info: false
banner-mode: off
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/searcher_refactor?characterencoding=utf8&usessl=false&servertimezone=asia/shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/search-mapper.xml
logging:
level:
com.lingqi.searcher.web: debug具体的查询语句,这里使用 mybatis ,在 search-mapper.xml 语句中写具体的查询语句
<!-- #{...} 会添加引号上去; ${...} 不会添加引号 -->
<select id="query" resultmap="documentresultmap">
select ii.docid, title, url, content
from inverted_indexes ii
join forward_indexes fi
on ii.docid = fi.docid
where word = #{word}
order by weight desc
limit ${limit}
offset ${offset}
</select>4. 在 searchcontroller 中写具体步骤
- 得到查询的词是哪个词(query)参数的合法性检查 + 处理
if (query == null) {
log.debug("query 为 null,重定向到首页");
return "redirect:/";
}
query = query.trim().tolowercase();
if (query.isempty()) {
log.debug("query 为空字符串,重定向到首页");
return "redirect:/";
}- 分词
list<string> querylist = toanalysis.parse(query)
.getterms()
.stream()
.map(term::getname)
.collect(collectors.tolist());
- 如果分词后,querylist 为空,也就是分词后一个词都没有,那么证明没有找到这个词,让他重定向到首页
- 处理分页的问题 (得到page,计算出limit + offset)
int limit = 20;
int offset = 0;
int page = 1;
if (pagestring != null) {
pagestring = pagestring.trim();
try {
page = integer.parseint(pagestring);
if (page <= 0) {
page = 1;
}
limit = page * 20;
} catch (numberformatexception ignored) {}
}- 执行sql进行查询
- 将数据添加到 model 中,是为了在 渲染模板的时候用到(这里使用了springmvc的模板渲染技术(viewresover),这里具体使用的是 thymeleaf)
- model 添加渲染需要的数据:query、doclist、page
model.addattribute("query", query);
model.addattribute("doclist", documentlist);
model.addattribute("page", page);- 指定使用哪个模板来进行渲染 return "search" 对应 resources/templates/search.html
5.搜索出来之后,展示基本内容部分
首先我们可以拿到这个文本的内容,我们可以前面截取120 个字,后面截取120 个字。
public document build(list<string> querylist, document doc) {
// 找到 content 中包含关键字的位置
// query = "list"
// content = "..... hello list go come do ...."
// desc = "hello <i>list</i> go com..."
string content = doc.getcontent().tolowercase();
string word = "";
int i = -1;
for (string query : querylist) {
i = content.indexof(query);
if (i != -1) {
word = query;
break;
}
}
if (i == -1) {
// 这里中情况如果出现了,说明咱的倒排索引建立的有问题
log.error("docid = {} 中不包含 {}", doc.getdocid(), querylist);
throw new runtimeexception();
}
// 前面截 120 个字,后边截 120 个字
int from = i - 120;
if (from < 0) {
// 说明前面不够 120 个字了
from = 0;
}
int to = i + 120;
if (to > content.length()) {
// 说明后面不够 120 个字了
to = content.length();
}
string desc = content.substring(from, to);
// 这里添加i标签,可以使这个单词高亮显示
desc = desc.replace(word, "<i>" + word + "</i>");
doc.setdesc(desc);
return doc;
}针对多个词进行搜索
和单词搜索的区别就是 权重值需要重新计算

多次中,就需要有一个权重值聚合的问题
docid 相同的,weight=sum(w1,w2,w3)
docid=1 weight = 13 + 7 + 1
docid=2 weight = 22
把实际业务抽象成如下的简单题:给定3个有序数组(按照权重从大到排序),最终结果的权重(sum=w1+w2+w3|docid相同),给出第 x 到第 y 个元素
如果数据量太大,这种找法是不可能的,内存空间可能不足,时间效率也很低
因此实际中我们会舍弃他的准确性,比如说某次考试,前1000名学生,各自的排名多少是非常重要的,不能出错。后1000名同学,排名略有错误,其实也不重要。实际上上就是牺牲正确性来换取性能。
结果必须重新计算,所以没办法使用mysql帮我们排序了
- 首先我们先对所有的词进行查找,查找出来先放到 totallist 中
list<documentwightweight> totallist = new arraylist<>();
for (string s : querylist) {
list<documentwightweight> documentlist = mapper.querywithweight(s, limit, offset);
totallist.addall(documentlist);
}- 针对所有文档列表,做权重聚合工作
维护:docid -> document 的 map
1.我们遍历 totallist 针对每一个docid 我们往里面放。遇到重复的,不断累加。

2.此时我们就有了每个单词对应的权重了,这放在 documentmap 中,我们需要对这个权重进行一个排序,首要要拿到这些权重,放在 collection 中
3.但 collection 没有排序这个概念(只有线性结构才有排序的概念),所以我们需要一个 list
4. 按照 weight 的从大到小排序
collections.sort(list, (item1, item2) -> {
return item2.weight - item1.weight;
});5. 从 list 中把分页区间取出来
int from = (page - 1) * 20;
int to = from + 20;
list<documentwightweight> sublist = list.sublist(from, to);
list<document> documentlist = sublist.stream()
.map(documentwightweight::todocument)
.collect(collectors.tolist());具体的查询语句,这里使用 mybatis ,在 search-mapper.xml 语句中写具体的查询语句:
<select id="querywithweight" resultmap="documentwithweightresultmap">
select ii.docid, title, url, content, weight
from inverted_indexes ii
join forward_indexes fi
on ii.docid = fi.docid
where word = #{word}
order by weight desc
limit ${limit}
offset ${offset}
</select>完整代码:


发表评论