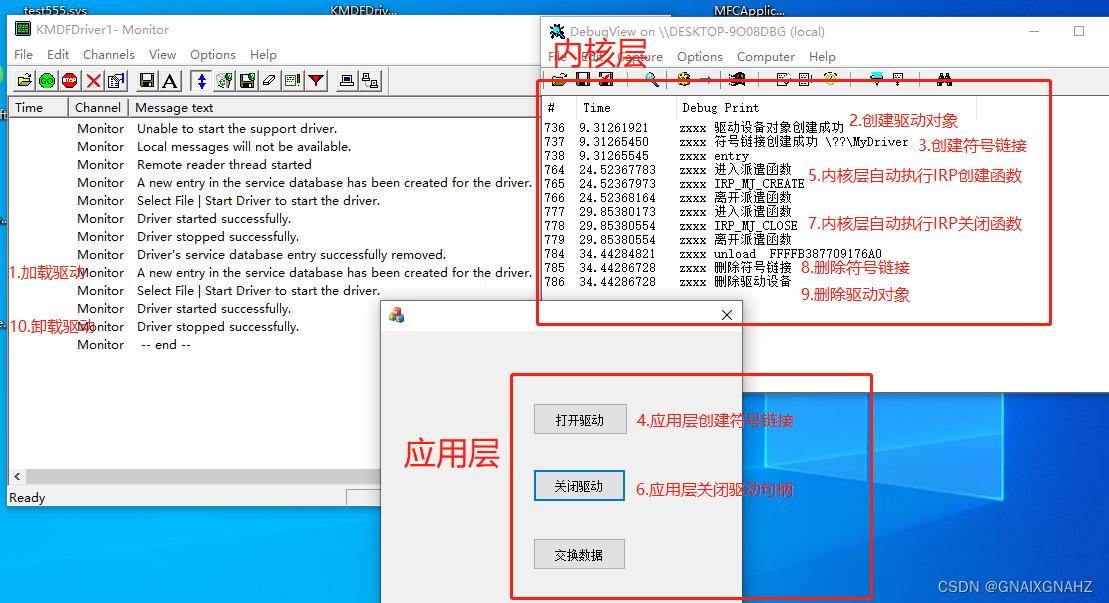
内存空间分为用户层和系统层,普通的应用程序只能运行在用户层,为了可以操作系统层的内存 所以引入了驱动程序,有了驱动就可以通过用户层来操作系统层的内存及函数,所以驱动就是应用层和系统层之间的一个桥梁
在应用层通过创建符号链接,自动产生驱动层的irp事件,即可执行系统层的irp函数,从而将应用层的数据传到系统层。
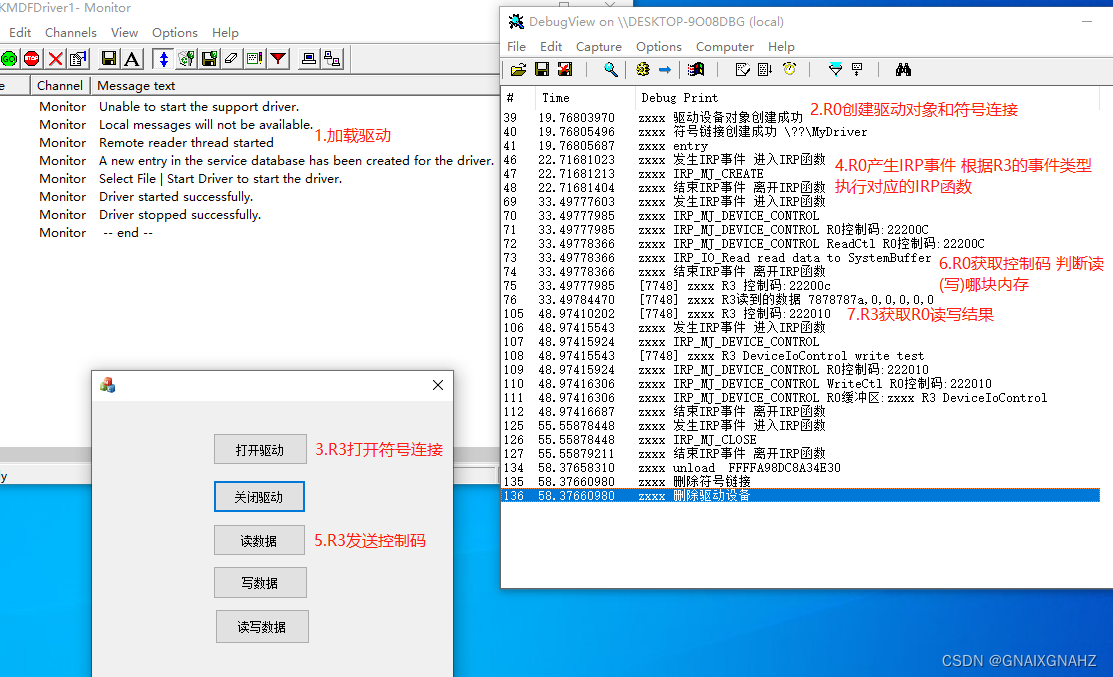
首先加载驱动使得系统层存在一个符号链接,然后应用层就可以创建跟系统层同名的符号链接
其实本质上是驱动加载完成时会产生一块共享内存用于r3和r0数据交换,控制码用于控制读写哪块内存
r0创建驱动对象->r0创建驱动设备->r0创建符号链接->r3打开符号链接->r3传入控制码(读、写)->r0执行irp函数 -> r0根据控制码判断读写哪块共享内存->r3收到r0的读写结果 ->r0删除符号链接 ->r0删除驱动设备
驱动层
#include<ntifs.h>
//控制码与用户层保持一致
#define readctl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x803,method_buffered,file_any_access) //读控制码
#define writectl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x804,method_buffered,file_any_access) //写控制码
#define rwctl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x805,method_buffered,file_any_access) //读写控制码
void irp_io_read(pirp pirp)
{
char* buff = (char*)pirp->associatedirp.systembuffer;
//获取r3传来的参数(控制码)
pio_stack_location irpstack = iogetcurrentirpstacklocation(pirp);
//将r0读取到的数据写入到向共享缓冲区
char r0returnbuf[] = "zxxx r0 read data \n";
ulong len = sizeof(r0returnbuf);
memcpy_s(buff, len, r0returnbuf, len);
kdprint(("zxxx irp_io_read read data to systembuffer \n"));
//每次irp执行完了 要执行下面三行 作为返回结果
pirp->iostatus.status = status_success;
pirp->iostatus.information = len; //共享缓冲区返回的长度
iocompleterequest(pirp, io_no_increment);
}
/*
void irp_io_write(pirp pirp)
{
}
void irp_io_readwrite(pirp pirp)
{
}
*/
//创建驱动对象->创建驱动设备->创建符号链接->使用符号链接 ->删除符号链接 ->删除驱动设备
//当用户层打开符号链接时 会产生irp事件执行irp函数 通过irp函数与内核通信
//创建驱动对象并绑定符号链接
ntstatus createdevice(pdriver_object driver)
{
ntstatus status;
unicode_string mydriver; //驱动名称
pdevice_object device; //驱动设备
rtlinitunicodestring(&mydriver,l"\\device\\mydriver");//初始化驱动名称
//在驱动对象上创建驱动设备
status = iocreatedevice(driver, sizeof(driver->driverextension),&mydriver,file_device_unknown,file_device_secure_open,false,&device);
if (status == status_success)
{
kdprint(("zxxx 驱动设备对象创建成功 \n"));
//创建符合链接
unicode_string uzsymbolname;
rtlinitunicodestring(&uzsymbolname,l"\\??\\mydriver"); //初始化符号链接 符号链接格式 l"\\??\\名字
//为驱动设备绑定符号链接 后续不会使用驱动对象与内核交换,而是使用符号链接与内核交换
status = iocreatesymboliclink(&uzsymbolname,&mydriver);
if (status == status_success)
{
kdprint(("zxxx 符号链接创建成功 %wz \n",&uzsymbolname));
}
else
{
kdprint(("zxxx 符号链接创建失败 %wz \n", &uzsymbolname));
}
}
else
{
kdprint(("zxxx 驱动设备对象创建失败 \n"));
iodeletedevice(device);
}
return status;
}
//传入驱动设备的irp事件
ntstatus irp_call(pdevice_object device,pirp pirp)
{
device;
kdprint(("zxxx 发生irp事件 进入irp函数 \n"));
pio_stack_location irpstackl;
irpstackl = iogetcurrentirpstacklocation(pirp);
switch (irpstackl->majorfunction)
{
case irp_mj_create:
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_create \n"));
break;
}
case irp_mj_close:
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_close \n"));
break;
}
case irp_mj_device_control:
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control \n"));
//取到的r3的控制码
uint32 ctlcode = irpstackl->parameters.deviceiocontrol.iocontrolcode;
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control r0控制码:%x \n", ctlcode));
if ( ctlcode == readctl )
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control readctl r0控制码:%x \n", ctlcode));
irp_io_read(pirp); //这里写入到共享缓冲剂即可,打印r3访问共享缓冲区打印
return status_success;
}
else if ( ctlcode == writectl )
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control writectl r0控制码:%x \n", ctlcode));
//取出r3缓冲区的数据
//根据控制代码来选择使用associatedirp.systembuffer的读缓冲区还是写缓冲区
char* r3buff = (char*)pirp->associatedirp.systembuffer;
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control r0缓冲区:%s \n", r3buff));
}
else if (ctlcode == rwctl )
{
kdprint(("zxxx irp_mj_device_control rwctl r0控制码:%x \n", ctlcode));
}
break;
}
}
//注意 只要pirp这个对象发生变化 就要跟着下面这三行
pirp->iostatus.status = status_success;
pirp->iostatus.information = 4;
iocompleterequest(pirp,io_no_increment);
kdprint(("zxxx 结束irp事件 离开irp函数 \n"));
return status_success;
}
//卸载驱动
void unload(pdriver_object pdriver)
{
kdprint(("zxxx unload %p \n", pdriver));
//先删除符号链接
//再删除驱动设备
if (pdriver->deviceobject)
{
unicode_string uzsymbolname;
rtlinitunicodestring(&uzsymbolname, l"\\??\\mydriver");
iodeletesymboliclink(&uzsymbolname);
iodeletedevice(pdriver->deviceobject);
kdprint(("zxxx 删除符号链接 \n"));
kdprint(("zxxx 删除驱动设备 \n"));
}
}
ntstatus
driverentry(
_in_ pdriver_object driverobject,
_in_ punicode_string registrypath
)
{
//初始化驱动对象
driverobject->driverunload = unload; //指定卸载驱动函数
driverobject->majorfunction[irp_mj_create] = irp_call; //指定irp事件函数
driverobject->majorfunction[irp_mj_close] = irp_call; //指定irp事件函数
driverobject->majorfunction[irp_mj_device_control] = irp_call; //指定irp事件函数
//创建驱动设备
createdevice(driverobject);
registrypath;
kdprint(("zxxx entry \n"));
return 0;
}
应用层(mfc)
//通过不同的控制码让驱动执行不同的函数
//控制码在用户层和驱动层都需要定义且保持一致
#include<winioctl.h>
#define readctl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x803,method_buffered,file_any_access) //读控制码
#define writectl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x804,method_buffered,file_any_access) //写控制码
#define rwctl ctl_code(file_device_unknown,0x805,method_buffered,file_any_access) //读写控制码
static handle devicehandle = null;
//打开驱动按钮
void cmfcapplication1dlg::onbnclickedbutton1()
{
// todo: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
//创建驱动
//执行 createfilew 会触发irp事件 执行irp函数 irp_mj_create被执行
devicehandle = createfilew(
l"\\??\\mydriver", //符号链接
generic_read | generic_write,
file_share_read | file_share_write,
null,
open_existing,
file_attribute_normal,
null
);
}
//关闭驱动按钮
void cmfcapplication1dlg::onbnclickedbutton2()
{
// todo: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
//执行 closehandle 会触发irp事件 执行irp函数 irp_mj_close被执行
closehandle(devicehandle);
}
//读数据按钮
void cmfcapplication1dlg::onbnclickedbutton3()
{
// todo: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
dword dwretsize = 0;
typedef struct tinput_buf
{
dword m_arg1;
dword m_arg2;
dword m_arg3;
dword m_arg4;
dword m_arg5;
dword m_arg6;
}tinput_buf;
//打印控制码 测试 验证r3与r0是否一致
char buftest[256];
sprintf_s(buftest, "zxxx r3 控制码:%x", readctl);
outputdebugstringa(buftest);
char writedata[100] = "zxxx r3 deviceiocontrol read test \n";
tinput_buf inbuf = { 0 }; //写数据 r3的数据写入到r0
char outbuf[512] = { 0 }; //输出缓冲区 //读数据 r0的数据读出到r3
//irp函数deviceiocontrol
//这里的控制码+缓冲区 指明了r3读(写)了哪块共享内存,后续驱动用控制码即可执行对应的读写操作
deviceiocontrol(
devicehandle, //createfile 打开驱动设备返回的句柄
readctl, //控制码 ctl_code 与irp事件对应
writedata, //输入缓冲区 &inbuf
sizeof(inbuf), //输入缓冲区大小
&outbuf, //输出缓冲区
512, //输出缓冲区大小
&dwretsize, //返回字节数
null
);
//打印返回参数
cstring csstr;
csstr.format(l"zxxx r3读到的数据 %x \n", outbuf[0]);
outputdebugstringa("zxxx r3读到的数据 \n");
strcat_s(outbuf," zxxx r3");
//r3读取到的结果
outputdebugstringa(outbuf);
}
//写数据按钮
void cmfcapplication1dlg::onbnclickedbutton4()
{
// todo: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
dword dwretsize = 0;
typedef struct tinput_buf
{
dword m_arg1;
dword m_arg2;
dword m_arg3;
dword m_arg4;
dword m_arg5;
dword m_arg6;
}tinput_buf;
//打印控制码 测试 验证r3与r0是否一致
char buftest[256];
sprintf_s(buftest,"zxxx r3 控制码:%x", writectl);
outputdebugstringa(buftest);
char writedata[100] = "zxxx r3 deviceiocontrol write test \n";
//打印缓冲区 测试 验证r3与r0是否一致
char buftest2[100];
memcpy(buftest2, writedata,100);
outputdebugstringa(buftest2);
tinput_buf inbuf = { 1,2,3,4,5,0x6abc666 }; //写数据 r3的数据写入到r0
dword outbuf[6] = { 0 }; //输出缓冲区 //读数据 r0的数据读出到r3
//irp函数deviceiocontrol
//这里的控制码+缓冲区 指明了r3读(写)了哪块共享内存,后续驱动使用控制码即可执行对应的读写操作
deviceiocontrol(
devicehandle, //createfile 打开驱动设备返回的句柄
writectl, //控制码 ctl_code 与irp事件对应
writedata, //输入缓冲区 &inbuf
sizeof(inbuf), //输入缓冲区大小
&outbuf, //输出缓冲区
sizeof(outbuf), //输出缓冲区大小
&dwretsize, //返回字节数
null
);
}mfc一些配置问题:
全部流程



发表评论