i2c总线二级外设驱动开发是一个涉及多个步骤和函数调用的过程,主要目的是使得挂接在i2c总线上的外设能够正常工作。
一、i2c总线二级外设驱动开发概述
i2c总线是一种广泛使用的串行通信总线,用于连接微控制器及其外围设备。在linux内核中,i2c总线驱动开发包括i2c总线控制器驱动(也称为适配器驱动)和挂接在i2c总线上的二级外设驱动(也称为客户驱动或设备驱动)。
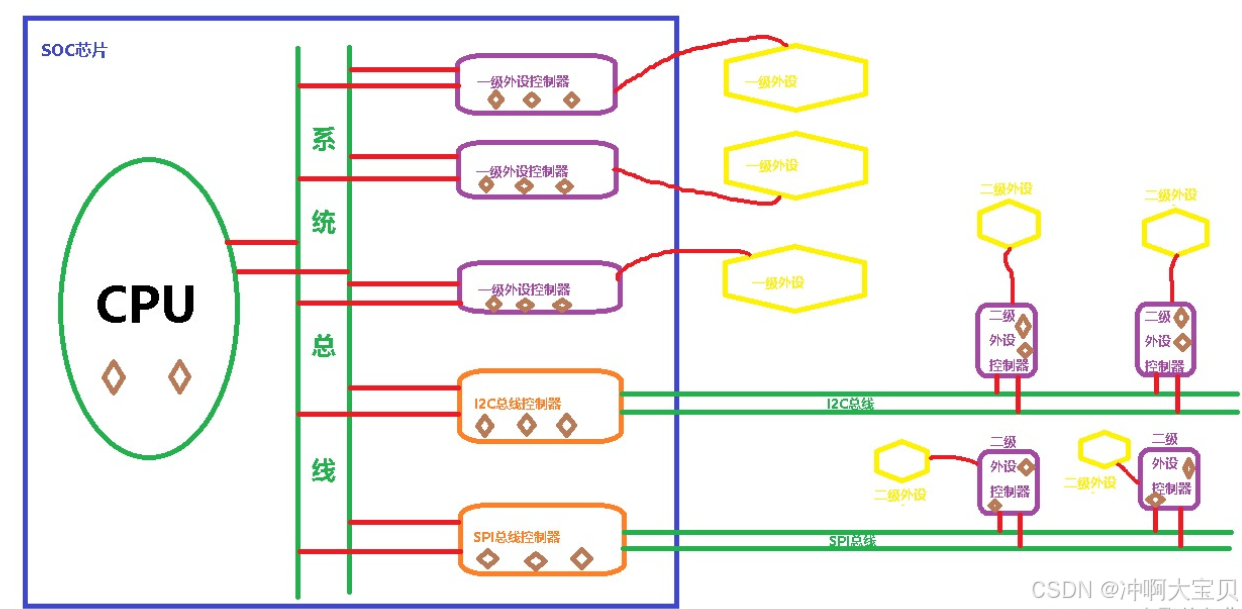
疑惑1:二级外设驱动编写好,那总线上的那个iic驱动不需要编写吗
当你为挂接在i2c总线上的二级外设编写驱动程序(也称为客户驱动或设备驱动)时,你通常不需要从头开始编写整个i2c总线(也称为i2c适配器)的驱动程序,除非该i2c总线控制器是全新的、且linux内核中尚不支持的。
linux内核对i2c总线的支持
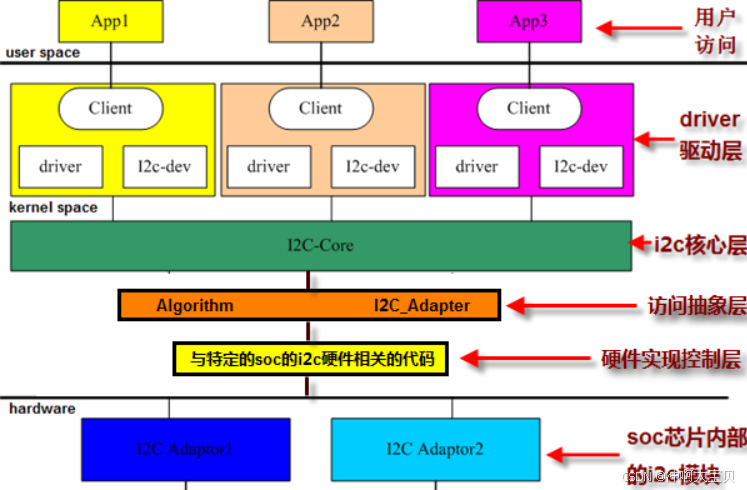
本次实验仅是对driver驱动层进行开发,在iic核心层以下则是开发商已经帮我们做好的第一次移植,我们进行第二次移植即可(用mpu6050作为示例,芯片为fs4412)。
i2c设备驱动(driver驱动层)我们需要设计的地方
即挂接在i2c总线上的二级外设的驱动,也称客户(client)驱动,实现对二级外设的各种操作,二级外设的几乎所有操作全部依赖于对其自身内部寄存器的读写,对这些二级外设寄存器的读写又依赖于i2c总线的发送和接收
i2c总线驱动(访问抽象层、硬件实现控制层)内核已经做好初始化,了解如何使用api即可
即对i2c总线自身控制器的驱动,一般soc芯片都会提供多个i2c总线控制器,每个i2c总线控制器提供一组i2c总线(sda一根+scl一根),每一组被称为一个i2c通道,linux内核里将i2c总线控制器叫做适配器(adapter),适配器驱动主要工作就是提供通过本组i2c总线与二级外设进行数据传输的接口,每个二级外设驱动里必须能够获得其对应的adapter对象才能实现数据传输
i2c核心 内核已经做好初始化
承上启下,为i2c设备驱动和i2c总线驱动开发提供接口,为i2c设备驱动层提供管理多个i2c_driver、i2c_client对象的数据结构,为i2c总线驱动层提供多个i2c_algorithm、i2c_adapter对象的数据结构
四大核心对象之间的关系图
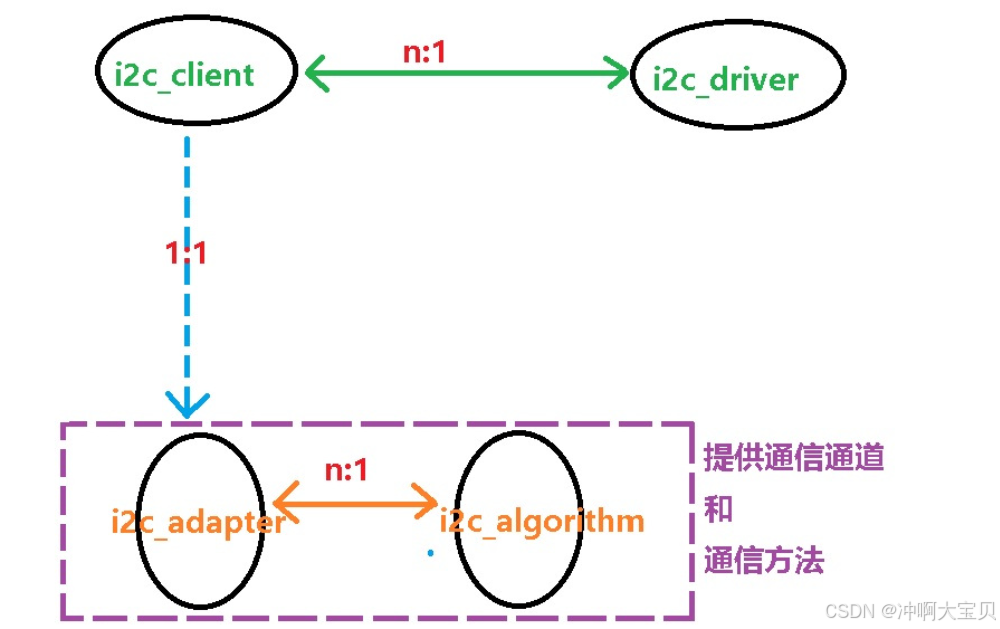
结合第一张图可知:(重点)
- 一个i2c总线控制器(也叫i2c适配器)的算法(i2c_algorithm) 可以被n个i2c总线控制器使用。
- 一个二级外设设备驱动程序(
i2c_driver)可以被n个外设(i2c_client)使用。每个外设(通过其i2c_client表示)在系统中都是唯一的,并且通常只与一个i2c_driver相关联。 - 每个外设(
i2c_client)都要与一个i2c总线控制器i2c_adapter(通过其总线编号和i2c地址)和一个i2c_driver(通过其id表或其他匹配机制)相关联。
二、开发步骤详解
1. 查阅fs4412开发板以及mpu6050原理图
目的:了解二级外设挂在哪条i2c总线上,以及外设的身份标识(如设备地址)。
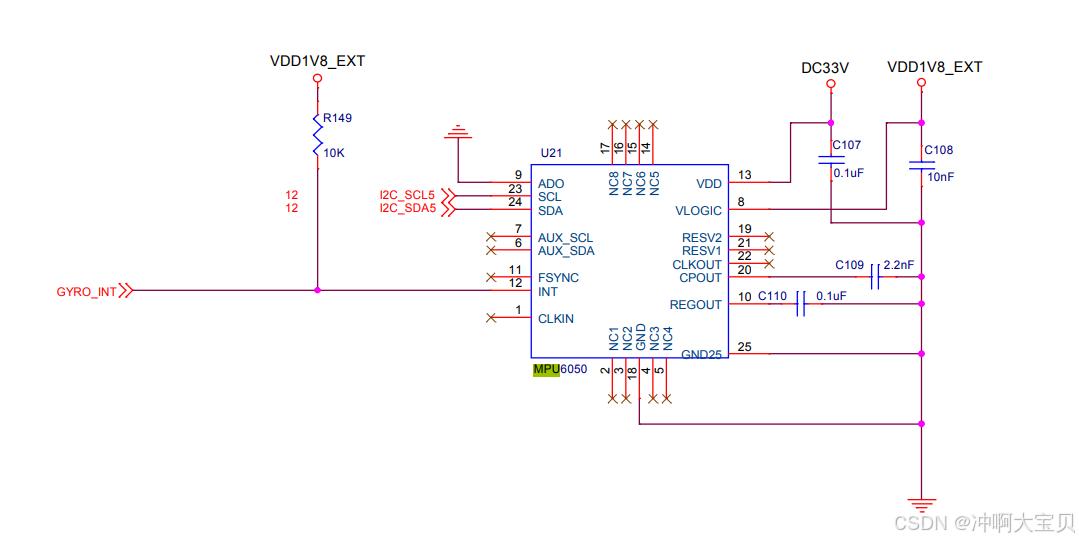
再去mpu-6050原理图可得:
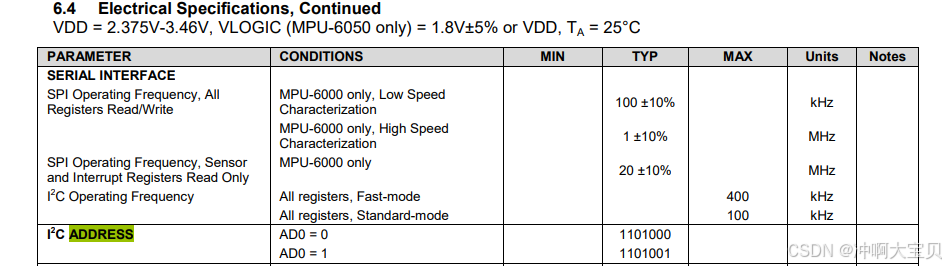
上图可知:ado接地为0,scl与sda复用引脚gpb2,3查询可得使用i2c5号总线。
以及一些必要的宏设置:
#define smplrt_div 0x19 //陀螺仪采样率,典型值:0x07(125hz)
#define config 0x1a //低通滤波频率,典型值:0x06(5hz)
#define gyro_config 0x1b //陀螺仪自检及测量范围,典型值:0xf8(不自检,+/-2000deg/s)
#define accel_config 0x1c //加速计自检、测量范围,典型值:0x19(不自检,+/-g)
#define accel_xout_h 0x3b
#define accel_xout_l 0x3c
#define accel_yout_h 0x3d
#define accel_yout_l 0x3e
#define accel_zout_h 0x3f
#define accel_zout_l 0x40
#define temp_out_h 0x41
#define temp_out_l 0x42
#define gyro_xout_h 0x43
#define gyro_xout_l 0x44
#define gyro_yout_h 0x45
#define gyro_yout_l 0x46
#define gyro_zout_h 0x47
#define gyro_zout_l 0x48
#define pwr_mgmt_1 0x6b //电源管理,典型值:0x00(正常启用)
2. 搭建驱动框架
目的:参照platform样式或其他标准驱动框架,为二级外设驱动搭建驱动框架。
//其它struct file_operations函数实现原理同硬编驱动
static int mpu6050_probe(struct i2c_client *pclt,const struct i2c_device_id *pid)
{
//做硬编驱动模块入口函数的活
}
static int mpu6050_remove(struct i2c_client *pclt)
{
//做硬编驱动模块出口函数的活
}
/*名称匹配时定义struct i2c_device_id数组*/
static struct i2c_device_id mpu6050_ids =
{
{"mpu6050",0},
//.....
{}
};
/*设备树匹配时定义struct of_device_id数组*/
static struct of_device_id mpu6050_dts =
{
{.compatible = "invensense,mpu6050"},
//....
{}
};
/*通过定义struct i2c_driver类型的全局变量来创建i2c_driver对象,同时对其主要成员进行初始化
1.向linux内核的i2c子系统注册一个能够管理和控制这些设备的驱动程序。
2.i2c_driver结构包含了驱动程序与i2c子系统交互所需的所有关键信息,
包括如何识别设备、如何与设备通信、如何初始化设备以及如何处理设备的特定操作等。
*/
struct i2c_driver mpu6050_driver =
{
.driver = {
.name = "mpu6050",
.owner = this_module,
.of_match_table = mpu6050_dts,
},
.probe = mpu6050_probe,
.remove = mpu6050_remove,
.id_table = mpu6050_ids,
};
/*以下其实是个宏,展开后相当于实现了模块入口函数和模块出口函数*/
module_i2c_driver(mpu6050_driver);
/*
实则为:
int __init mpu6050_driver_init(void)
{
i2c_add_driver(&mpu6050_driver);//功能:向内核注册一个i2c_driver对象
}
void __exit mpu6050_driver_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&mpu6050_driver);//从内核注销一个i2c_driver对象
}
module_init(mpu6050_driver_init);
module_exit(mpu6050_driver_exit);
*/
module_license("gpl");
上述代码框架解释:
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
/* 标准驱动模型接口 */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* 与枚举无关的驱动模型接口 */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
/* 类似ioctl的命令,可用于执行特定功能 */
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* 用于自动设备创建的设备检测回调 */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
/* 重要成员:
probe:在i2c_client与i2c_driver匹配后执行该函数
remove:在取消i2c_client与i2c_driver匹配绑定后执行该函数
driver:这个成员类型在平台设备驱动层中也有,而且使用其中的name成员来实现平台设备匹配,但是i2c子系统中不使用其中的name进行匹配,这也是i2c设备驱动模型和平台设备模型匹配方法的一点区别
id_table:用来实现i2c_client与i2c_driver匹配绑定,当i2c_client中的name成员和i2c_driver中id_table中name成员相同的时候,就匹配上了。
补充:i2c_client与i2c_driver匹配问题
- i2c_client中的name成员和i2c_driver中id_table中name成员相同的时候
- i2c_client指定的信息在物理上真实存放对应的硬件,并且工作是正常的才会绑定上,并执行其中的probe接口函数这第二点要求和平台模型匹配有区别,平台模型不要求设备层指定信息在物理上真实存在就能匹配
*/
/* 功能:向内核注册一个i2c_driver对象
返回值:0成功,负数 失败*/
#define i2c_add_driver(driver) i2c_register_driver(this_module, driver)
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver);
/* 功能:从内核注销一个i2c_driver对象
返回值:无 */
void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver);
然后需要:
- 定义i2c_client结构体:每个二级外设都需要一个对应的i2c_client结构体来表示。这个结构体包含了外设的地址、名称、适配器(adapter)等信息。
- 实现probe和remove函数:probe函数是驱动加载时调用的函数,用于初始化外设;remove函数是驱动卸载时调用的函数,用于清理资源。
- 定义i2c_driver结构体:这个结构体包含了驱动的名称、probe和remove函数指针等,用于向i2c核心注册驱动。
i2c_client结构体注释:
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr;
char name[i2c_name_size];
struct i2c_adapter *adapter;
struct i2c_driver *driver;
struct device dev;
int irq;
struct list_head detected;
};
/*重要成员:
flags:地址长度,如是10位还是7位地址,默认是7位地址。如果是10位地址器件,则设置为i2c_client_ten
addr:具体i2c器件如(at24c02),设备地址,低7位
name:设备名,用于和i2c_driver层匹配使用的,可以和平台模型中的平台设备层platform_driver中的name作用是一样的。
adapter:本设备所绑定的适配器结构(cpu有很多i2c适配器,类似单片机有串口1、串口2等等,在linux中每个适配器都用一个结构描述)
driver:指向匹配的i2c_driver结构,不需要自己填充,匹配上后内核会完成这个赋值操作
dev:内嵌的设备模型,可以使用其中的platform_data成员传递给任何数据给i2c_driver使用。
irq:设备需要使用到中断时,把中断编号传递给i2c_driver进行注册中断,如果没有就不需要填充。(有的i2c器件有中断引脚编号,与cpu相连)
*/
struct i2c_adapter *i2c_get_adapter(int nr);
/* 获得/释放 i2c_adapter 路径:i2c-core.c linux-3.5\drivers\i2c */
/*功能:通过i2c总线编号获得内核中的i2c_adapter结构地址,然后用户可以使用这个结构地址就可以给i2c_client结构使用,从而实现i2c_client进行总线绑定,从而增加适配器引用计数。
返回值:
null:没有找到指定总线编号适配器结构
非null:指定nr的适配器结构内存地址*/
void i2c_put_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap);
/*减少引用计数:当使用·i2c_get_adapter·后,需要使用该函数减少引用计数。(如果你的适配器驱动不需要卸载,可以不使用)*/
具体实现代码(部分):
struct mpu6050_dev
{
struct cdev mydev;//说明是一个字符设备
struct i2c_client *pclt;
/*存储了mpu6050设备在i2c总线上的相关信息,如设备的i2c地址、适配器(即i2c主设备)、传输速率等。
通过pclt指针,驱动程序可以访问mpu6050设备在i2c总线上的配置信息,并执行数据的读写操作。*/
};
struct mpu6050_dev *pgmydev = null;
static int mpu6050_probe(struct i2c_client *pclt,const struct i2c_device_id *pid)
{
int ret = 0;
dev_t devno = mkdev(major, minor);
/* 手动申请设备号 */
ret = register_chrdev_region(devno, char_num, "mpu6050");
if (ret) {
/* 动态申请设备号 */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, minor, char_num, "mpu6050");
if(ret){
printk("get devno failed\n");
return -1;
}
/*申请成功 更新设备号*/
major = major(devno);
}
pgmydev = (struct mpu6050_dev *)kmalloc(sizeof(struct mpu6050_dev), gfp_kernel);
if(null == pgmydev)
{
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, char_num);
printk("kmalloc for 'struct mpu6050_dev' failed\n");
return -1;
}
memset(pgmydev, 0, sizeof(struct mpu6050_dev));
/* 给struct cdev对象指定操作函数集 */
cdev_init(&pgmydev->mydev, &myops);
/* 将struct cdev对象添加到内核对应的数据结构中 */
pgmydev->mydev.owner = this_module;
cdev_add(&pgmydev->mydev, devno, char_num);
return 0;
}
static int mpu6050_remove(struct i2c_client *pclt)
{
dev_t devno = mkdev(major, minor);
/* 从内核中移除一个字符设备 */
cdev_del(&pgmydev->mydev);
/* 回收设备号 */
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, char_num);
/* 释放内存 */
kfree(pgmydev);
pgmydev = null;
return 0;
}
/*名称匹配时定义struct i2c_device_id数组*/
struct i2c_device_id mpu6050_ids[] =
{
{"mpu6050",0},
{}
};
struct i2c_driver mpu6050_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "mpu6050",
.owner = this_module,
},
.probe = mpu6050_probe,
.remove = mpu6050_remove,
.id_table = mpu6050_ids,
};3.注册和匹配以及初始化mpu6050
- 名称匹配:通过定义i2c_device_id结构体数组,并在i2c_driver结构体中指定id_table成员,实现名称匹配。这种方法需要事先知道外设的名称。(本文使用的方法)
- 设备树匹配:在设备树(device tree)中定义外设的信息,如compatible属性,然后在i2c_driver结构体中指定of_match_table成员,实现设备树匹配。这种方法更加灵活,适用于大多数现代linux系统。(本文使用的方法)
- 初始化mpu6050.
void init_mpu6050(struct i2c_client *pclt)
{
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,pwr_mgmt_1,0x00);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,smplrt_div,0x07);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,config,0x06);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,gyro_config,0xf8);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,accel_config,0x19);
}4.数据传输
- 使用i2c_transfer函数:通过这个函数可以发送和接收数据(mpu6050_write_byte,mpu6050_read_byte)。它允许你指定传输的方向(读或写)、传输的数据长度以及数据缓冲区。
- 处理中断和错误:根据需要处理外设产生的中断,并处理可能的错误情况,如传输失败、设备无响应等。
i2c_transfer函数注释:
/*i2c收发一体化函数,收还是发由参数msgs的成员flags决定*/
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
/*
功能:根据msgs进行手法控制
参数:
adap:使用哪一个适配器发送信息,一般是取i2c_client结构中的adapter指针作为参数
msgs:具体发送消息指针,一般情况下是一个数组
num:表示前一个参数msgs数组有多少个消息要发送的
返回值:
负数:失败
> 0 表示成功发送i2c_msg数量
*/
struct i2c_adapter
/*i2c_adapter 结构体封装了与特定 i2c 总线相关的所有必要信息,包括硬件细节、当前状态、传输函数等,使得内核能够管理和控制该总线上的设备。*/
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address */
__u16 flags;
#define i2c_m_ten 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define i2c_m_rd 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
__u16 len; /* msg length */
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};
/* 重要成员:
addr:要读写的二级外设地址
flags:表示地址的长度,读写功能。如果是10位地址必须设置i2c_m_ten,如果是读操作必须设置有i2c_m_rd······,可以使用或运算合成。
buf:要读写的数据指针。写操作:数据源 读操作:指定存放数据的缓存区
len:读写数据的数据长度
*/
发送和接收数据函数详解:
int mpu6050_read_byte(struct i2c_client *pclt,unsigned char reg)
{
int ret = 0;
char txbuf[1] = {reg};
char rxbuf[1] = {0};
struct i2c_msg msg[2] =
{
{pclt->addr,0,1,txbuf},
{pclt->addr,i2c_m_rd,1,rxbuf}
};
//利用i2c_transfer将msg里面两个数组发送给mpu6050,其中第一个数组是告诉mpu6050要读取哪个寄存器,然后mpu6050将该寄存器地址里面的数据通过msg[1]的rxbuf返回
ret = i2c_transfer(pclt->adapter,msg,array_size(msg));
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("ret = %d,in mpu6050_read_byte\n",ret);
return ret;
}
return rxbuf[0];
}
int mpu6050_write_byte(struct i2c_client *pclt,unsigned char reg,unsigned char val)
{
int ret = 0;
char txbuf[2] = {reg,val};
struct i2c_msg msg[1] =
{
{pclt->addr,0,2,txbuf},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(pclt->adapter,msg,array_size(msg));
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("ret = %d,in mpu6050_write_byte\n",ret);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}5.i2c总线二级外设驱动开发之名称匹配
这种匹配方式需要自己创建i2c_client对象
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[i2c_name_size];
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr;
void *platform_data;
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
struct device_node *of_node;
int irq;
};
/*用来协助创建i2c_client对象
重要成员
type:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的name成员
flags:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的flags成员
addr:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的addr成员
platform_data:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的.dev.platform_data成员
archdata:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的.dev.archdata成员
irq:用来初始化i2c_client结构中的irq成员
关键就是记住该结构和i2c_client结构成员的对应关系。在i2c子系统不直接创建i2c_client结构,只是提供struct i2c_board_info结构信息,让子系统动态创建,并且注册。
*/
介绍两种方法:
1.i2c_new_device:明确二级外设地址的情况下可用
mpu6050_client.c:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
//用来协助创建i2c_client对象
static struct i2c_board_info mpu6050_info =
{
i2c_board_info("mpu6050",0x68)
//一个在 linux 内核 i2c 子系统中使用的宏,用于定义一个 i2c 设备的信息
};
/*用于存储通过i2c总线找到的mpu6050设备的i2c_client结构体指针。*/
static struct i2c_client *gpmpu6050_client = null;
static int __init mpu6050_client_init(void)
{
struct i2c_adapter *padp = null;
/*通过i2c适配器编号(这里是5)获取i2c适配器的指针*/
padp = i2c_get_adapter(5);
/*使用之前获取的i2c适配器和设备信息,创建一个新的i2c设备。
如果成功,它会返回一个指向新创建的i2c_client结构体的指针,并将其存储在gpmpu6050_client中。*/
gpmpu6050_client = i2c_new_device(padp,&mpu6050_info);
/*释放之前获取的i2c适配器指针。*/
i2c_put_adapter(padp);
return 0;
}
static void mpu6050_client_exit(void)
{
/*注销之前注册的mpu6050 i2c设备*/
i2c_unregister_device(gpmpu6050_client);
}
module_init(mpu6050_client_init);
module_exit(mpu6050_client_exit);
module_license("gpl");
完整代码展示:
mpu6050.h:
#ifndef mpu_6050_h
#define mpu_6050_h
//加速度
struct accel_data
{
unsigned short x;
unsigned short y;
unsigned short z;
};
//角速度
struct gyro_data
{
unsigned short x;
unsigned short y;
unsigned short z;
};
//联合体
union mpu6050_data
{
struct accel_data accel;
struct gyro_data gyro;
unsigned short temp;//温度
};
#define mpu6050_magic 'k'
#define get_accel _ior(mpu6050_magic,0,union mpu6050_data)//读操作
#define get_gyro _ior(mpu6050_magic,1,union mpu6050_data)
#define get_temp _ior(mpu6050_magic,2,union mpu6050_data)
#endif
mpu6050_drv.c:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/ioctl.h>
#include "mpu6050.h"
/****************mpu6050内部寄存器地址****************/
#define smplrt_div 0x19 //陀螺仪采样率,典型值:0x07(125hz)
#define config 0x1a //低通滤波频率,典型值:0x06(5hz)
#define gyro_config 0x1b //陀螺仪自检及测量范围,典型值:0x18(不自检,2000deg/s)
#define accel_config 0x1c //加速计自检、测量范围及高通滤波频率,典型值:0x18(不自检,2g,5hz)
#define accel_xout_h 0x3b
#define accel_xout_l 0x3c
#define accel_yout_h 0x3d
#define accel_yout_l 0x3e
#define accel_zout_h 0x3f
#define accel_zout_l 0x40
#define temp_out_h 0x41
#define temp_out_l 0x42
#define gyro_xout_h 0x43
#define gyro_xout_l 0x44
#define gyro_yout_h 0x45
#define gyro_yout_l 0x46
#define gyro_zout_h 0x47
#define gyro_zout_l 0x48
#define pwr_mgmt_1 0x6b //电源管理,典型值:0x00(正常启用)
#define who_am_i 0x75 //iic地址寄存器(默认数值0x68,只读)
#define slaveaddress 0x68 //mpu6050-i2c地址
int major = 11; //主设备号
int minor = 0; //次设备号
int char_num = 1; //设备号数量
struct mpu6050_dev
{
struct cdev mydev;//说明是一个字符设备
struct i2c_client *pclt;
/*存储了mpu6050设备在i2c总线上的相关信息,如设备的i2c地址、适配器(即i2c主设备)、传输速率等。
通过pclt指针,驱动程序可以访问mpu6050设备在i2c总线上的配置信息,并执行数据的读写操作。*/
};
struct mpu6050_dev *pgmydev = null;
int mpu6050_read_byte(struct i2c_client *pclt,unsigned char reg)
{
int ret = 0;
char txbuf[1] = {reg};
char rxbuf[1] = {0};
struct i2c_msg msg[2] =
{
{pclt->addr,0,1,txbuf},
{pclt->addr,i2c_m_rd,1,rxbuf}
};
//利用i2c_transfer将msg里面两个数组发送给mpu6050,其中第一个数组是告诉mpu6050要读取哪个寄存器吗?然后mpu6050将该寄存器地址里面的数据通过msg[1]的rxbuf返回
ret = i2c_transfer(pclt->adapter,msg,array_size(msg));
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("ret = %d,in mpu6050_read_byte\n",ret);
return ret;
}
return rxbuf[0];
}
int mpu6050_write_byte(struct i2c_client *pclt,unsigned char reg,unsigned char val)
{
int ret = 0;
char txbuf[2] = {reg,val};
struct i2c_msg msg[1] =
{
{pclt->addr,0,2,txbuf},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(pclt->adapter,msg,array_size(msg));
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("ret = %d,in mpu6050_write_byte\n",ret);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
int mpu6050_open (struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)//打开设备
{
pfile->private_data = (void *) (container_of(pnode->i_cdev, struct mpu6050_dev,mydev));
return 0;
}
int mpu6050_close(struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)//关闭设备
{
return 0;
}
long mpu6050_ioctl(struct file *pfile, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct mpu6050_dev *pmydev = (struct mpu6050_dev *)pfile->private_data;
union mpu6050_data data;
switch(cmd)
{
case get_accel:
data.accel.x = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_xout_l);
data.accel.x = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_xout_h) << 8;
data.accel.y = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_yout_l);
data.accel.y = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_yout_h) << 8;
data.accel.z = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_zout_l);
data.accel.z = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,accel_zout_h) << 8;
break;
case get_gyro:
data.gyro.x = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_xout_l);
data.gyro.x = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_xout_h) << 8;
data.gyro.y = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_yout_l);
data.gyro.y = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_yout_h) << 8;
data.gyro.z = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_zout_l);
data.gyro.z = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,gyro_zout_h) << 8;
break;
case get_temp:
data.temp = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,temp_out_l);
data.temp = mpu6050_read_byte(pmydev->pclt,temp_out_h) << 8;
break;
default:
return -einval;
}
if(copy_to_user((void *)arg,&data,sizeof(data)))//用于将数据从内核空间安全地复制到用户空间
{
return -efault;
}
return sizeof(data);
}
void init_mpu6050(struct i2c_client *pclt)
{
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,pwr_mgmt_1,0x00);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,smplrt_div,0x07);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,config,0x06);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,gyro_config,0xf8);
mpu6050_write_byte(pclt,accel_config,0x19);
}
struct file_operations myops = {
.owner = this_module,
.open = mpu6050_open,
.release = mpu6050_close,
.unlocked_ioctl = mpu6050_ioctl,
};
static int mpu6050_probe(struct i2c_client *pclt,const struct i2c_device_id *pid)
{
int ret = 0;
dev_t devno = mkdev(major, minor);
/* 手动申请设备号 */
ret = register_chrdev_region(devno, char_num, "mpu6050");
if (ret) {
/* 动态申请设备号 */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, minor, char_num, "mpu6050");
if(ret){
printk("get devno failed\n");
return -1;
}
/*申请成功 更新设备号*/
major = major(devno);
}
pgmydev = (struct mpu6050_dev *)kmalloc(sizeof(struct mpu6050_dev), gfp_kernel);
if(null == pgmydev)
{
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, char_num);
printk("kmalloc for 'struct mpu6050_dev' failed\n");
return -1;
}
memset(pgmydev, 0, sizeof(struct mpu6050_dev));
pgmydev->pclt = pclt;
/* 给struct cdev对象指定操作函数集 */
cdev_init(&pgmydev->mydev, &myops);
/* 将struct cdev对象添加到内核对应的数据结构中 */
pgmydev->mydev.owner = this_module;
cdev_add(&pgmydev->mydev, devno, char_num);
init_mpu6050(pgmydev->pclt);
return 0;
}
static int mpu6050_remove(struct i2c_client *pclt)
{
dev_t devno = mkdev(major, minor);
/* 从内核中移除一个字符设备 */
cdev_del(&pgmydev->mydev);
/* 回收设备号 */
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, char_num);
/* 释放内存 */
kfree(pgmydev);
pgmydev = null;
return 0;
}
/*名称匹配时定义struct i2c_device_id数组*/
struct i2c_device_id mpu6050_ids[] =
{
{"mpu6050",0},
{}
};
struct i2c_driver mpu6050_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "mpu6050",
.owner = this_module,
},
.probe = mpu6050_probe,
.remove = mpu6050_remove,
.id_table = mpu6050_ids,
};
#if 0
int __init mpu6050_driver_init(void)
{
i2c_add_driver(&mpu6050_driver);
}
void __exit mpu6050_driver_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&mpu6050_driver);
}
module_init(mpu6050_driver_init);
module_exit(mpu6050_driver_exit);
#else
module_i2c_driver(mpu6050_driver);
#endif
module_license("gpl");
testapp.c:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mpu6050.h"
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int fd = -1;
union mpu6050_data data;
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("the argument is too few\n");
return 1;
}
fd = open(argv[1],o_rdonly);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s failed \n",argv[1]);
return 2;
}
while(1)
{
sleep(2);
ioctl(fd,get_accel,&data);
printf("accel-x=0x%x\n",data.accel.x);
printf("accel-y=0x%x\n",data.accel.y);
printf("accel-z=0x%x\n",data.accel.z);
ioctl(fd,get_gyro,&data);
printf("gyro-x=0x%x\n",data.gyro.x);
printf("gyro-y=0x%x\n",data.gyro.y);
printf("gyro-z=0x%x\n",data.gyro.z);
ioctl(fd,get_temp,&data);
printf("temp=0x%x\n",data.temp);
printf("\n");
}
close(fd);
fd = -1;
return 0;
}
实验结果:
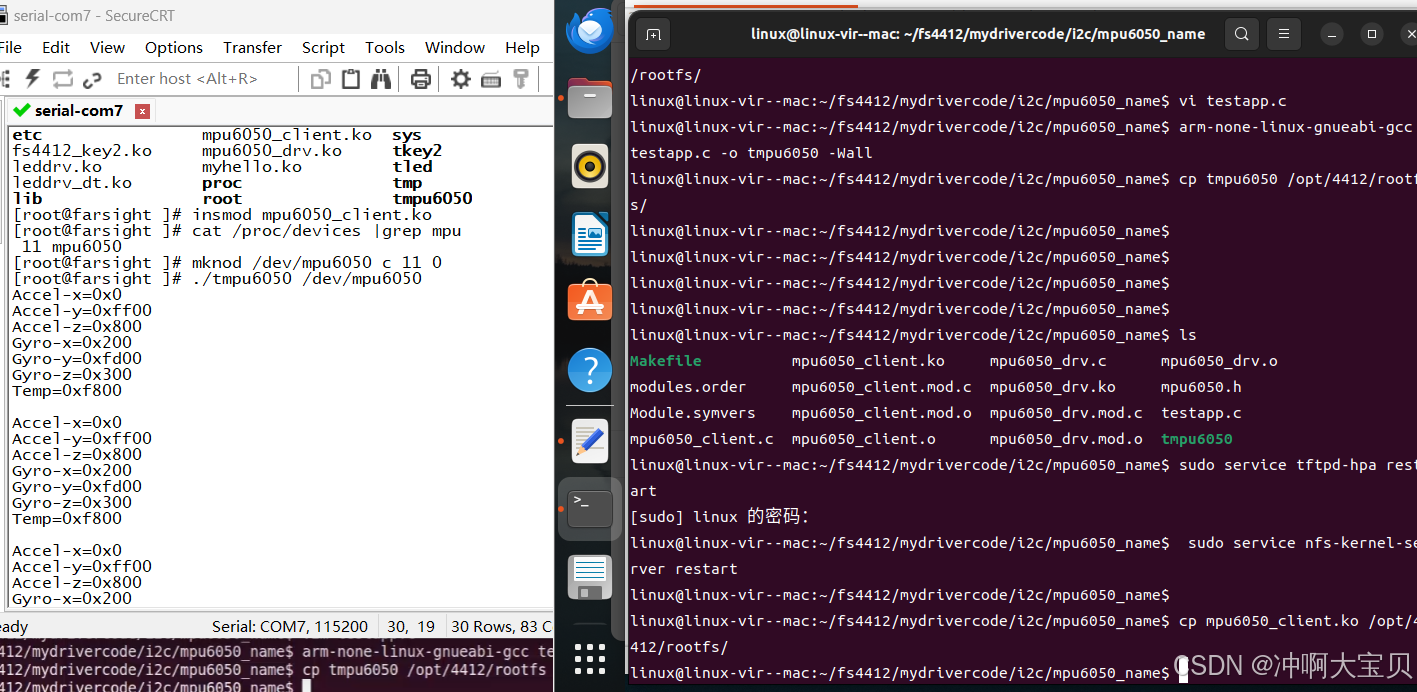
2. i2c_new_probed_device:不明确二级外设地址
i2c二级外设client框架:不明确二级外设地址,但是知道是可能几个值之一的情况下可用
将外设程序改为如下程序:(其他代码不变即可)
mpu6050_client_probed.c:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
//数组列出了mpu6050可能的i2c地址(0x68和0x69),并以i2c_client_end作为结束标记。
static unsigned short mpu6050_addr_list[] =
{
0x68,
0x69,
i2c_client_end
};
//用于存储找到的mpu6050设备的i2c客户端信息
static struct i2c_client *gpmpu6050_client = null;
static int __init mpu6050_client_init(void)
{
struct i2c_adapter *padp = null;
struct i2c_board_info mpu6050_info = {""};
strcpy(mpu6050_info.type,"mpu6050");
padp = i2c_get_adapter(5);
//尝试在指定的i2c总线上找到与mpu6050_info和mpu6050_addr_list匹配的设备。
gpmpu6050_client = i2c_new_probed_device(padp,&mpu6050_info,mpu6050_addr_list,null);
i2c_put_adapter(padp);
if(gpmpu6050_client != null)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return -enodev;
}
}
static void mpu6050_client_exit(void)
{
i2c_unregister_device(gpmpu6050_client);
}
module_init(mpu6050_client_init);
module_exit(mpu6050_client_exit);
module_license("gpl");
6.i2c总线二级外设驱动开发之设备树匹配
将驱动程序改为:
//设备树
struct of_device_id mpu6050_dt[] =
{
{.compatible = "invensense,mpu6050"},
{}
};
struct i2c_device_id mpu6050_ids[] =
{
{"mpu6050",0},
{}
};
struct i2c_driver mpu6050_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "mpu6050",
.owner = this_module,
.of_match_table = mpu6050_dt,
},
.probe = mpu6050_probe,
.remove = mpu6050_remove,
.id_table = mpu6050_ids,
};实验结果:
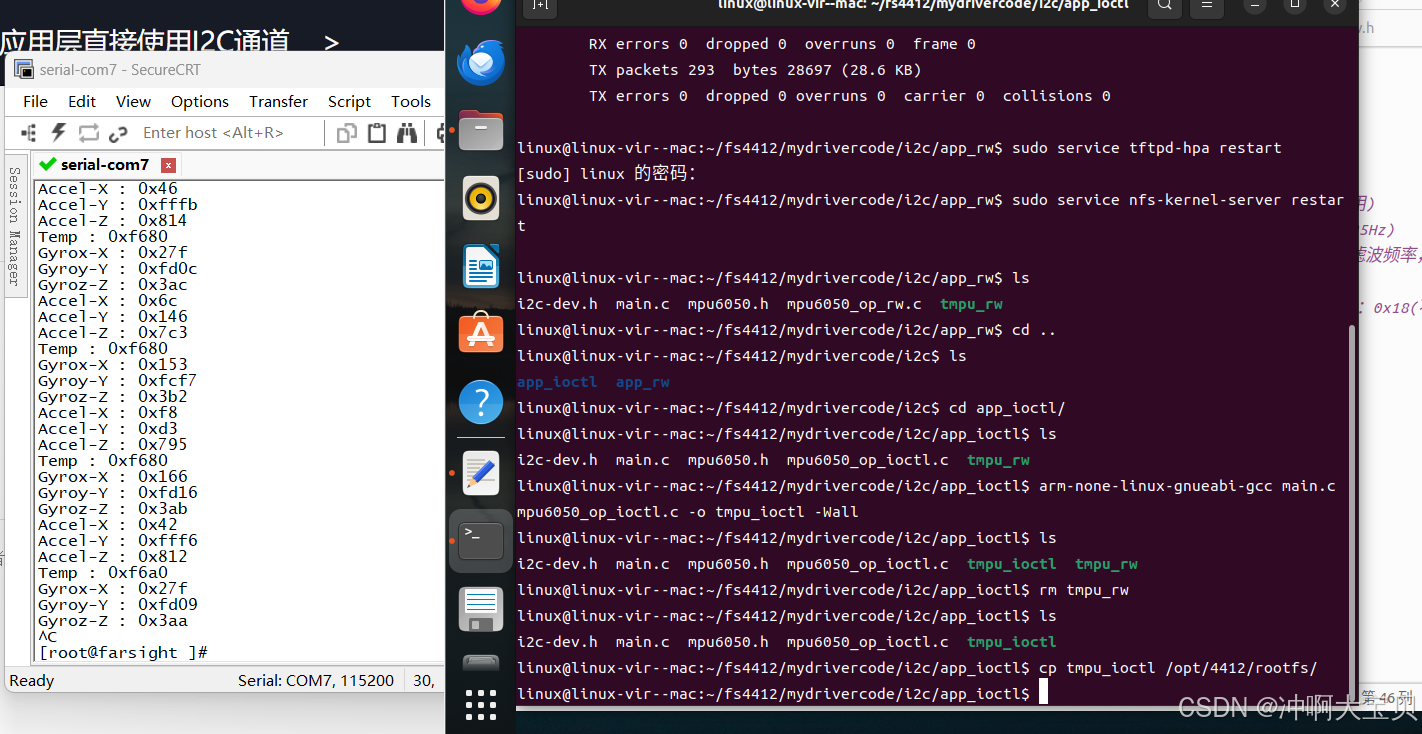




发表评论