目录
4、channeloption.so_sndbuf和channeloption.so_rcvbuf
一、基于netty创建udp服务端以及对应通道设置关键
@configuration
@refreshscope
public class nettyudpserver {
@value("${netty.server.udpport}")
private int port;
private eventloopgroup bossgroup;//主线程
private channel channel;//通道
private channelfuture future; //回调
@autowired
private datacollector datacollector;;
public channel start() throws interruptedexception {
//判断是否支持epoll模式,从而创建不同的线程组
bossgroup = epoll.isavailable()? new epolleventloopgroup() : new nioeventloopgroup();
try {
bootstrap b = new bootstrap();
//linux平台下增加so_reuseport特性提高性能,支持多个进程或者线程绑定到同一个端口,提高服务器程序的吞吐性能
if(epoll.isavailable()) {
//设置反应器线程组
b.group(bossgroup)
.handler(new epolludpserverinitializer(datacollector))
//设置nio类型的通道
.channel(epolldatagramchannel.class)
.option(channeloption.so_broadcast, true)
.option(channeloption.so_reuseaddr, true)
.option(channeloption.so_rcvbuf, 1024 * 1024)
.option(epollchanneloption.so_reuseport, true);
}else{
//设置反应器线程组
b.group(bossgroup)
.handler(new udpserverinitializer(datacollector))
//设置nio类型的通道
.channel(niodatagramchannel.class)
//设置通道的参数
.option(channeloption.so_broadcast, true)
.option(channeloption.so_reuseaddr, true);
}
//channel channel = server.bind(port).sync().channel();
//开始绑定服务器,通过调用sync()同步方法阻塞直到绑定成功
//channelfuture channelfuture = b.bind(port).sync();
//等待通道关闭的异步任务结束
//channelfuture closefuture = channelfuture.channel().closefuture();
//closefuture.sync();
channelfuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
channel = f.channel();
if(f.issuccess()){
//masterselector registry = new masterselector("","netty-services", port);
system.out.println("udp服务器启动,监听在端口:" + port);
}else {
channel.closefuture().sync();
}
} finally {
//bossgroup.shutdowngracefully().sync();
}
system.out.println("udp服务器启动,监听在端口:"+port);
return channel;
}
}以上代码中epoll.isavailable()用户判断是window还是linux环境,linux环境默认采用epoll相关通道,所以显式设置epolldatagramchannel通道。在处理(handler)的设置中要根据不同的通道设置初始化的通道类型:
linux环境下epolldatagramchannel通道设置 .handler(new epolludpserverinitializer(datacollector))具体代码
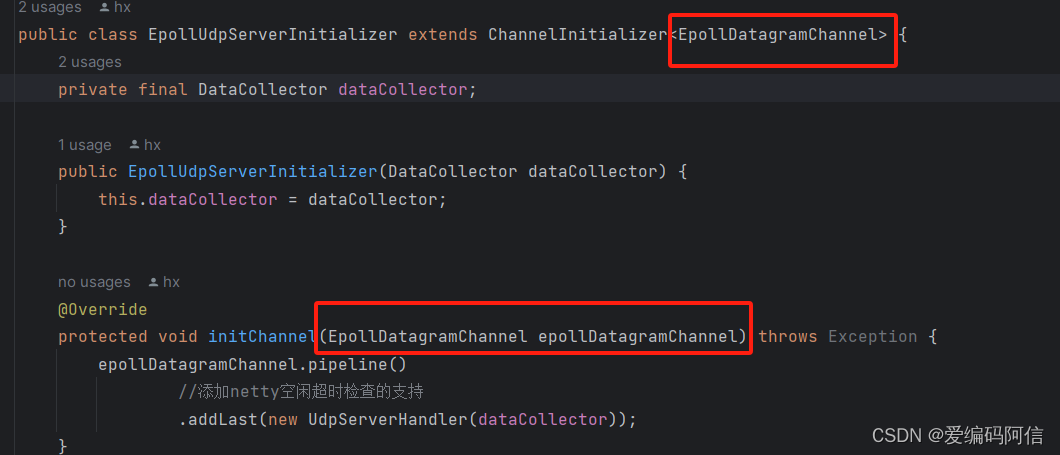
public class epolludpserverinitializer extends channelinitializer<epolldatagramchannel> {
private final datacollector datacollector;
public epolludpserverinitializer(datacollector datacollector) {
this.datacollector = datacollector;
}
@override
protected void initchannel(epolldatagramchannel epolldatagramchannel) throws exception {
epolldatagramchannel.pipeline()
//添加netty空闲超时检查的支持
.addlast(new udpserverhandler(datacollector));
}要使 通过服务器端通过epolldatagramchannel通道发送数据,客户端能够正常接收到数据,下图中标红的泛型通道类要与服务器端设置的通道类一致
同意要支持nio类型通道为niodatagramchannel.class时,通道初始化为:
public class udpserverinitializer extends channelinitializer<niodatagramchannel> {
private final datacollector datacollector;
public udpserverinitializer(datacollector datacollector) {
this.datacollector = datacollector;
}
@override
protected void initchannel(niodatagramchannel niodatagramchannel) throws exception {
niodatagramchannel.pipeline()
//添加netty空闲超时检查的支持
.addlast(new udpserverhandler(datacollector));
}
} 要使 通过服务器端通过niodatagramchannel通道发送数据,客户端能够正常接收到数据,下图中标红的泛型通道类要与服务器端设置的通道类一致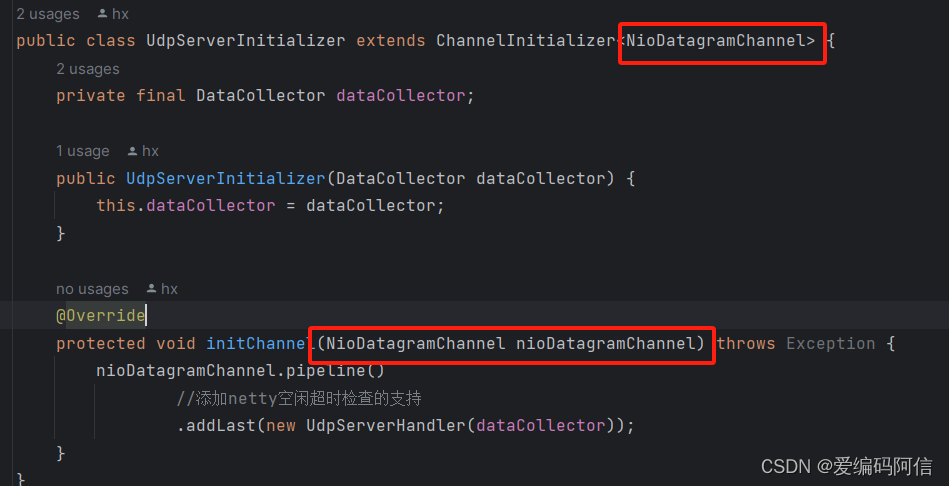
二、发送数据
关键代码,采用writeandflush发送数据,注意:要发送udp数据报,
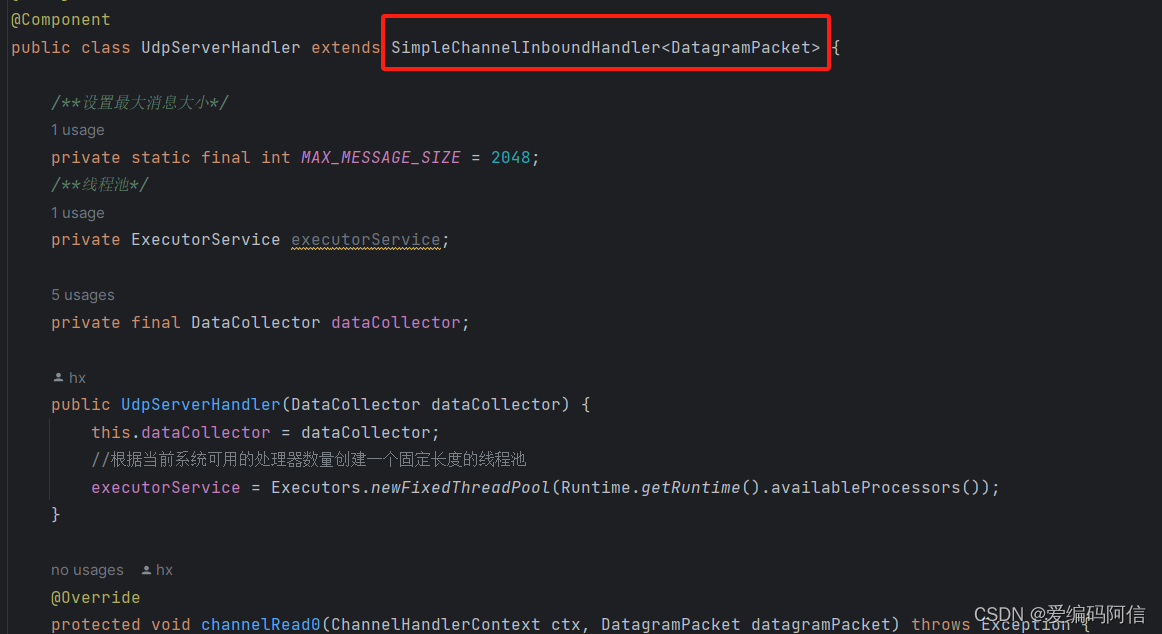
public class udpserverhandler extends simplechannelinboundhandler<datagrampacket> {
/**设置最大消息大小*/
private static final int max_message_size = 2048;
/**线程池*/
private executorservice executorservice;
private final datacollector datacollector;
public udpserverhandler(datacollector datacollector) {
this.datacollector = datacollector;
//根据当前系统可用的处理器数量创建一个固定长度的线程池
executorservice = executors.newfixedthreadpool(runtime.getruntime().availableprocessors());
}
@override
protected void channelread0(channelhandlercontext ctx, datagrampacket datagrampacket) throws exception {
bytebuf buffer = datagrampacket.content();
//确保不会超出最大消息大小
if(buffer.readablebytes() > max_message_size) {
buffer.release();
return;
}
udpdatagram udpdatagram = parseudpdatagram(buffer);
udpdatagram respudpdatagram = datacollector.processudpdatagram(udpdatagram);
if (null != respudpdatagram) {
handlereceiveddata(ctx, respudpdatagram, datagrampacket);
}
}
/**
* 处理接收到的数据
* @param ctx
* @param udpdatagram
*/
public void handlereceiveddata(channelhandlercontext ctx, udpdatagram udpdatagram, datagrampacket datagrampacket) throws executionexception, interruptedexception {
channel channel = ctx.channel();
if (log.isinfoenabled()) {
log.info("received udp message: sessionid: {}, opcode: {}, short messageid: {}",
ctx.channel().id(), udpdatagram.getmessagetypeenum(), udpdatagram.getshortmessageid());
}
byte[] payloadbytes = udpdatagram.getpayloadbytes();
bytebuf copiedbuffer = unpooled.copiedbuffer(payloadbytes);
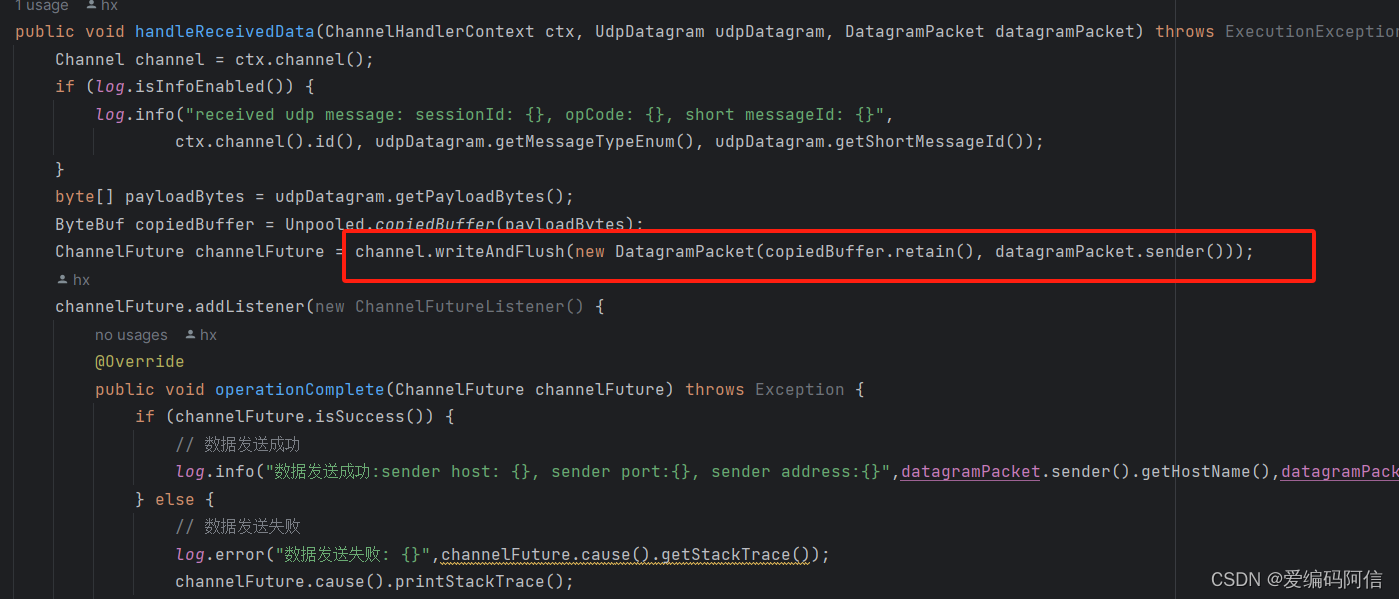
channelfuture channelfuture = channel.writeandflush(new datagrampacket(copiedbuffer.retain(), datagrampacket.sender()));
channelfuture.addlistener(new channelfuturelistener() {
@override
public void operationcomplete(channelfuture channelfuture) throws exception {
if (channelfuture.issuccess()) {
// 数据发送成功
log.info("数据发送成功:sender host: {}, sender port:{}, sender address:{}",datagrampacket.sender().gethostname(),datagrampacket.sender().getport(), datagrampacket.sender().getaddress());
} else {
// 数据发送失败
log.error("数据发送失败: {}",channelfuture.cause().getstacktrace());
channelfuture.cause().printstacktrace();
}
}
});
}
@override
public void handleradded(channelhandlercontext ctx) throws exception {
datacollector.tcpconnect(ctx.channel());
}
@override
public void exceptioncaught(channelhandlercontext ctx, throwable cause) throws exception {
if (log.iswarnenabled()) {
log.warn("udp session throw an exception, sessionid:{} exception message: {}",
ctx.channel().id().aslongtext(), cause.getmessage());
}
}
//当客户端关闭链接时关闭通道
@override
public void handlerremoved(channelhandlercontext ctx) throws exception {
datacollector.tcpchanneldisconnect(ctx.channel());
}
}处理类继承simplechannelinboundhandler类泛型类为datagrampacket
 writeandflush方法中发送的数据类型要是datagrampacket
writeandflush方法中发送的数据类型要是datagrampacket
三、netty中的channeloption常用参数说明
1、channeloption.so_backlog
2、channeloption.so_reuseaddr
3、channeloption.so_keepalive
4、channeloption.so_sndbuf和channeloption.so_rcvbuf
5、channeloption.so_linger
6、channeloption.tcp_nodelay
| so_broadcast | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_broadcast,将消息发送到广播地址。 如果目标中指定的接口支持广播数据包,则启用此选项可让应用程序发送广播消息。 |
| so_keepalive | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_keepalive,保持连接。 在空闲套接字上发送探测,以验证套接字是否仍处于活动状态。 |
| so_sndbuf | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_sndbuf,设置发送缓冲区的大小。 |
| so_rcvbuf | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_rcvbuf,获取接收缓冲区的大小。 |
| so_reuseaddr | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_reuseaddr,本地地址复用。 启用此选项允许绑定已使用的本地地址。 |
| so_linger | 对应套接字层的套接字:so_linger,延迟关闭连接。 启用此选项,在调用close时如果存在未发送的数据时,在close期间将阻止调用应用程序,直到数据被传输或连接超时。 |
| so_backlog | 对应tcp/ip协议中<font color=red>backlog</font>参数,<font color=red>backlog</font>即连接队列,设置tcp中的连接队列大小。如果队列满了,会发送一个econnrefused错误信息给c端,即“ connection refused”。 |
| so_timeout | 等待客户连接的超时时间。 |
| ip_tos | 对应套接字层的套接字:ip_tos,在ip标头中设置服务类型(tos)和优先级。 |
| ip_multicast_addr | 对应ip层的套接字选项:ip_multicast_if,设置应发送多播数据报的传出接口。 |
| ip_multicast_if | 对应ip层的套接字选项:ip_multicast_if2,设置应发送多播数据报的ipv6传出接口。 |
| ip_multicast_ttl | 对应ip层的套接字选项:ip_multicast_ttl,在传出的 多播数据报的ip头中设置生存时间(ttl)。 |
| ip_multicast_loop_disabled | 取消 指定应将 传出的多播数据报的副本 回传到发送主机,只要它是多播组的成员即可。 |
| tcp_nodelay | 对应tcp层的套接字选项:tcp_nodelay,指定tcp是否遵循<font color=#35b998>nagle算法</font> 决定何时发送数据。nagle算法代表通过减少必须发送包的个数来增加网络软件系统的效率。即尽可能发送大块数据避免网络中充斥着大量的小数据块。如果要追求高实时性,需要设置关闭nagle算法;如果需要追求减少网络交互次数,则设置开启nagle算法。
|
channeloption通用配置
| 参数 | 说明 |
| allocator | bytebuf的分配器,默认值为bytebufallocator.default。 |
| rcvbuf_allocator | 用于channel分配接受buffer的分配器,默认值为adaptiverecvbytebufallocator.default,是一个自适应的接受缓冲区分配器,能根据接受到的数据自动调节大小。可选值为fixedrecvbytebufallocator,固定大小的接受缓冲区分配器。 |
| message_size_estimator | 消息大小估算器,默认为defaultmessagesizeestimator.default。估算bytebuf、bytebufholder和fileregion的大小,其中bytebuf和bytebufholder为实际大小,fileregion估算值为0。该值估算的字节数在计算水位时使用,fileregion为0可知fileregion不影响高低水位。 |
| connect_timeout_millis | 连接超时毫秒数,默认值30000毫秒即30秒。 |
| write_spin_count | 一个loop写操作执行的最大次数,默认值为16。也就是说,对于大数据量的写操作至多进行16次,如果16次仍没有全部写完数据,此时会提交一个新的写任务给eventloop,任务将在下次调度继续执行。这样,其他的写请求才能被响应不会因为单个大数据量写请求而耽误。 |
| write_buffer_water_mark | |
| allow_half_closure | 一个连接的远端关闭时本地端是否关闭,默认值为false。值为false时,连接自动关闭;为true时,触发channelinboundhandler的usereventtriggered()方法,事件为channelinputshutdownevent。 |
| auto_read | 自动读取,默认值为true。netty只在必要的时候才设置关心相应的i/o事件。对于读操作,需要调用channel.read()设置关心的i/o事件为op_read,这样若有数据到达才能读取以供用户处理。该值为true时,每次读操作完毕后会自动调用channel.read(),从而有数据到达便能读取;否则,需要用户手动调用channel.read()。需要注意的是:当调用config.setautoread(boolean)方法时,如果状态由false变为true,将会调用channel.read()方法读取数据;由true变为false,将调用config.autoreadcleared()方法终止数据读取。 |




发表评论