目录
一、消费队列负载均衡概览
rocketmq默认一个主题下有4个消费队列,集群模式下同一消费组内要求每个消费队列在同一时刻只能被一个消费者消费。那么集群模式下多个消费者是如何负载主题的多个消费队列呢?并且如果有新的消费者加入时,消费队列又会如何重新分布呢?
rocketmq消费端每20s周期执行一次消费队列重新负载,每次进行队列重新负载时会从broker实时查询当前消费组内所有消费者,并且对消息队列、消费者列表进行排序,这样新加入的消费者就会在队列重新分布时分配到消费队列从而消费消息。如下所示,是消息拉取与消费队列负载均衡的交互图。
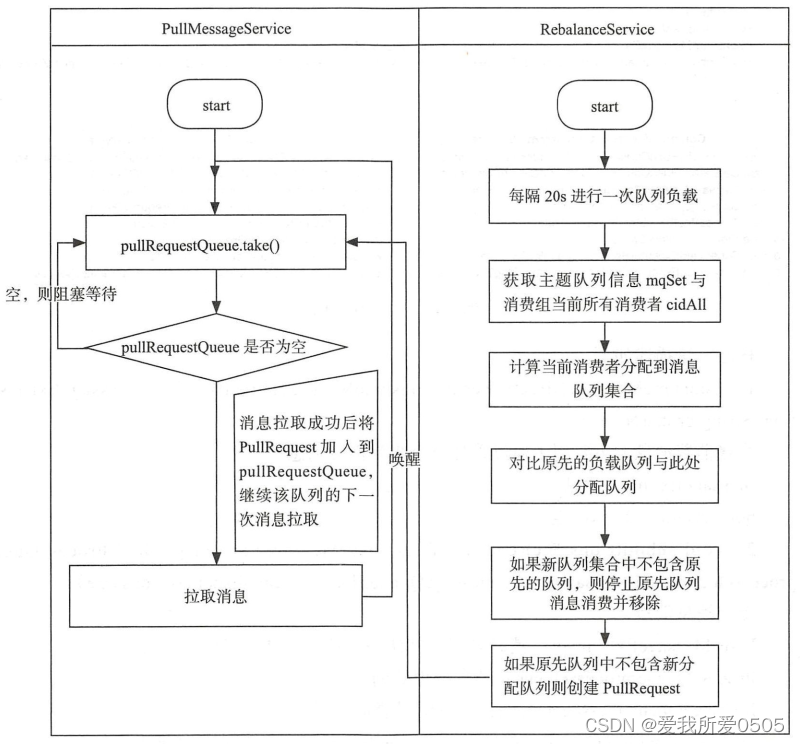
二、消费队列负载均衡实现
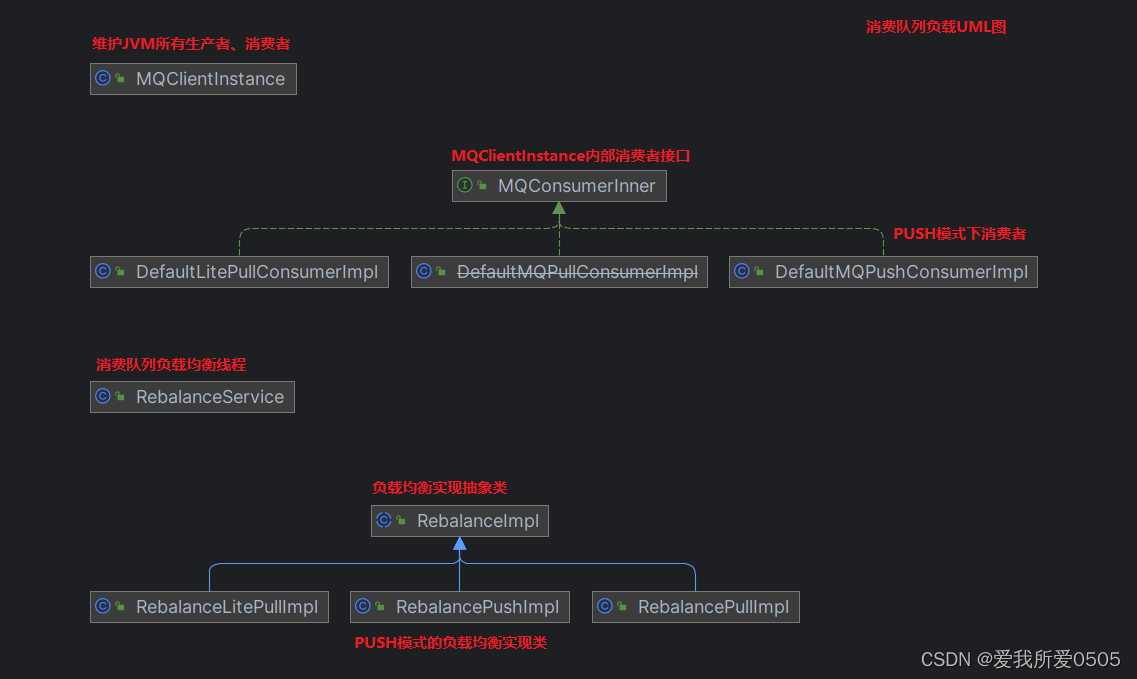
1. 负载均衡uml
2. 启动rebalanceservice线程
参考《rocketmq5.0.0消息消费<一> _ push模式的消息拉取》
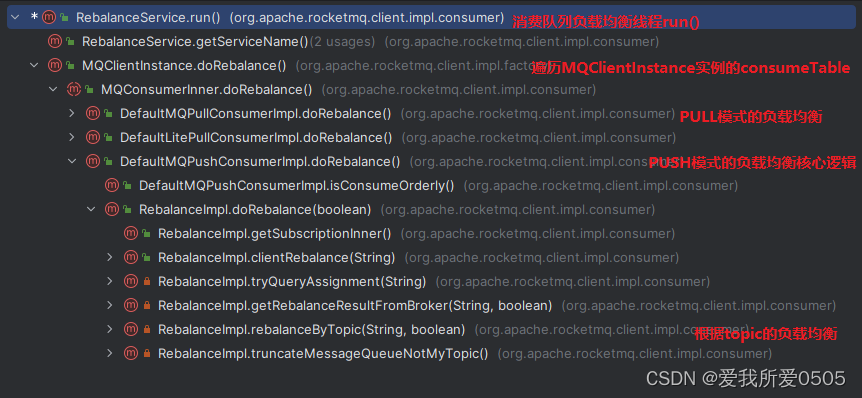
章节,消费者启动时,当前消费者添加到mqclientinstance#consumertable属性中,并启动mqclientinstance实例。启动mqclientinstance实例时,会启动org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceservice消费队列负载均衡服务线程。下图所示是该线程run()调用链。
以下代码是mqclientinstance维护整个jvm的所有生产者和消费者的属性。
// 生产者容器
private final concurrentmap<string/* 生产组 */, mqproducerinner> producertable = new concurrenthashmap<>();
// 消费者容器
private final concurrentmap<string/* 消费组 */, mqconsumerinner> consumertable = new concurrenthashmap<>();org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceservice#run()周期20s执行负载均衡任务。-drocketmq.client.rebalance. waitlnterval参数修改执行周期,默认20s。
@override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getservicename() + " service started");
while (!this.isstopped()) {
// 线程等待20s
this.waitforrunning(waitinterval);
// topic下消费队列的负载均衡
this.mqclientfactory.dorebalance();
}
log.info(this.getservicename() + " service end");
}org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.factory.mqclientinstance#dorebalance方法遍历mqclientinstance实例中所有消费组下消费者。每一个消费者defaultmqpushconsumerimpl拥有一个org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceimpl对象(实现负载均衡),给每个消费者找到一个消费队列(重新负载)。
// 消费队列负载均衡
public void dorebalance() {
for (map.entry<string/* 消费组 */, mqconsumerinner> entry : this.consumertable.entryset()) {
// 获取消费者
mqconsumerinner impl = entry.getvalue();
if (impl != null) {
try {
// 消费者负载均衡
impl.dorebalance();
} catch (throwable e) {
log.error("dorebalance exception", e);
}
}
}
}3. push模式负载均衡
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.defaultmqpushconsumerimpl#dorebalance是push模式的负载均衡的入口方法,其调用链如下。
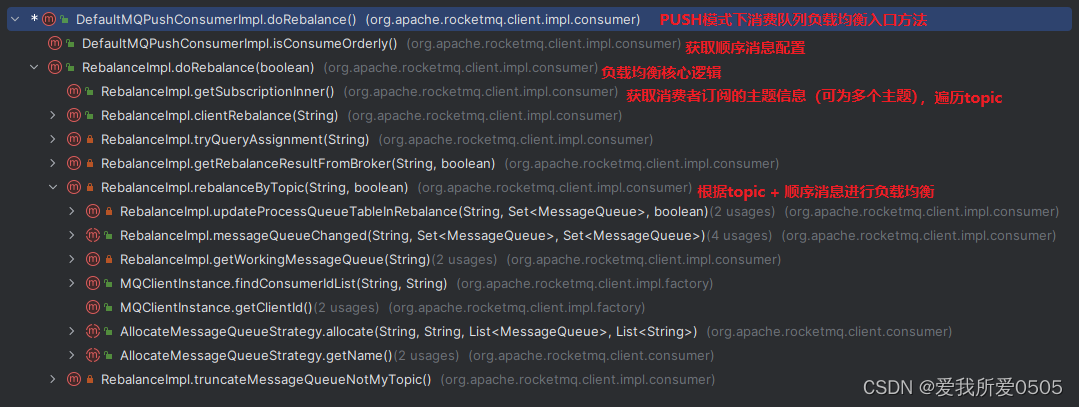
每个消费者defaultmqpushconsumerimpl拥有一个rebalanceimpl对象,其中org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceimpl#dorebalance方法是对消费者的所有订阅主题进行负载均衡,即:消费者的所有订阅主题重新分配一个或多个消费队列来进行消费。其代码如下。注意事项:
- map<string/* topic */, subscriptiondata> subtable:获取当前消费者订阅的主题信息;
- rebalancebytopic():每个主题进行重新负载均衡
/**
* 对消费者订阅的每个topic进行消费队列重新负载
* step1:获取消费者订阅的主题信息,注意:消费者可以订阅多个主题
* step2:遍历消费者的每个topic
* step3:消费者订阅的topic进行消费队列重新负载
* {@link rebalanceimpl#rebalancebytopic(string, boolean)}
* @param isorder 是否顺序消息
* @return true所有topic重新负载成功
*/
public boolean dorebalance(final boolean isorder) {
boolean balanced = true;
// 获取消费者订阅的主题信息,注意:消费者可以订阅多个主题
map<string/* topic */, subscriptiondata> subtable = this.getsubscriptioninner();
if (subtable != null) {
// 遍历消费者的每个topic
for (final map.entry<string, subscriptiondata> entry : subtable.entryset()) {
final string topic = entry.getkey();
try {
if (!clientrebalance(topic) && tryqueryassignment(topic)) {
balanced = this.getrebalanceresultfrombroker(topic, isorder);
} else {
// 消费者订阅的topic进行消费队列重新负载
balanced = this.rebalancebytopic(topic, isorder);
}
} catch (throwable e) {
if (!topic.startswith(mixall.retry_group_topic_prefix)) {
log.warn("rebalance exception", e);
balanced = false;
}
}
}
}
this.truncatemessagequeuenotmytopic();
return balanced;
}org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceimpl#rebalancebytopic方法是对每个主题进行重新负载均衡的核心逻辑,如下代码所示。 这里介绍集群模式下负载均衡,注意事项:
- mqclientinstance#findconsumeridlist():从broker上获取所有订阅该topic且同属一个消费组的所有消费者id。
- 对消费队列、消费者id集合排序:原因是同一个消费组内视图一致,确保同一个消费队列不会被多个消费者分配。
- allocatemessagequeuestrategy#allocate:根据均衡策略,获取当前消费者的消息队列。
- rebalanceimpl#updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance:重新负载后,消费者对应的分配后的消息队列是否变化: 新增、删除(其他消费者占用)。
/**
* 消费者订阅的topic进行消费队列重新负载
* 集群模式下的步骤:
* step1:从主题订阅信息缓存表(topicsubscribeinfotable)中获取当前topic的消费队列
* step2:从broker上获取所有订阅该topic + 同属一个消费组 的所有消费者id
* step3:对消费队列、消费者id排序,很重要,原因是:同一个消费组内视图一致,确保同一个消费队列不会被多个消费者分配
* step4:根据均衡策略,获取当前消费者的消息队列
* {@link allocatemessagequeuestrategy#allocate}
* step5:消费者对应的分配消息队列是否变化: 新增、删除(其他消费者占用)
* {@link rebalanceimpl#updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance}
* @param topic 主题
* @param isorder 是否是顺序消息
* @return true重新分配消息队列成功
*/
private boolean rebalancebytopic(final string topic, final boolean isorder) {
boolean balanced = true;
switch (messagemodel) {
case broadcasting: {
set<messagequeue> mqset = this.topicsubscribeinfotable.get(topic);
if (mqset != null) {
boolean changed = this.updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance(topic, mqset, isorder);
if (changed) {
this.messagequeuechanged(topic, mqset, mqset);
log.info("messagequeuechanged {} {} {} {}", consumergroup, topic, mqset, mqset);
}
balanced = mqset.equals(getworkingmessagequeue(topic));
} else {
this.messagequeuechanged(topic, collections.<messagequeue>emptyset(), collections.<messagequeue>emptyset());
log.warn("dorebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumergroup, topic);
}
break;
}
case clustering: {
// 从主题订阅信息缓存表中获取当前topic的消费队列
set<messagequeue> mqset = this.topicsubscribeinfotable.get(topic);
// 从broker上获取所有订阅该topic + 同属一个消费组 的所有消费者id
list<string> cidall = this.mqclientfactory.findconsumeridlist(topic, consumergroup);
if (null == mqset) {
if (!topic.startswith(mixall.retry_group_topic_prefix)) {
this.messagequeuechanged(topic, collections.<messagequeue>emptyset(), collections.<messagequeue>emptyset());
log.warn("dorebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumergroup, topic);
}
}
if (null == cidall) {
log.warn("dorebalance, {} {}, get consumer id list failed", consumergroup, topic);
}
if (mqset != null && cidall != null) {
list<messagequeue> mqall = new arraylist<messagequeue>();
mqall.addall(mqset);
/*
消费队列、消费者id排序很重要:同一个消费组内视图一致,确保同一个消费队列不会被多个消费者分配
*/
// 消费队列排序
collections.sort(mqall);
// 消费者id排序
collections.sort(cidall);
// 均衡策略
allocatemessagequeuestrategy strategy = this.allocatemessagequeuestrategy;
list<messagequeue> allocateresult = null;
try {
// 根据均衡策略,获取当前消费者的消息队列
allocateresult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumergroup,
this.mqclientfactory.getclientid(), // 当前消费者id
mqall,
cidall);
} catch (throwable e) {
log.error("allocate message queue exception. strategy name: {}, ex: {}", strategy.getname(), e);
return false;
}
set<messagequeue> allocateresultset = new hashset<messagequeue>();
if (allocateresult != null) {
allocateresultset.addall(allocateresult);
}
// 消费者对应的分配消息队列是否变化: 新增、删除(其他消费者占用)
boolean changed = this.updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance(topic, allocateresultset, isorder);
if (changed) {
log.info(
"client rebalanced result changed. allocatemessagequeuestrategyname={}, group={}, topic={}, clientid={}, mqallsize={}, cidallsize={}, rebalanceresultsize={}, rebalanceresultset={}",
strategy.getname(), consumergroup, topic, this.mqclientfactory.getclientid(), mqset.size(), cidall.size(),
allocateresultset.size(), allocateresultset);
this.messagequeuechanged(topic, mqset, allocateresultset);
}
balanced = allocateresultset.equals(getworkingmessagequeue(topic));
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
return balanced;
}org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceimpl#updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance重新分配后消费队列集合与上次负载的分配集合是否改变(新增或删除)来重新拉取消息。如下代码所示。
- 删除(消费队列分配给其他消费者):暂停消费并移除,且持久化待移除消费队列的消费进度。
- 新增(缓存表没有的消费队列):
step1:删除内存中该消费队列的消费进度;
step2:创建broker的消费队列;
step3:从磁盘中获取该消费队列的消费进度(若进度<0时,则根据配置矫正消费进度),创建拉取消息请求。
- 新增消费队列:重新创建拉取请求pullrequest加入到pullmessageservice线程中,唤醒该线程拉取消息rebalanceimpl#dispatchpullrequest。
- 若是顺序消息:是局部顺序消息,尝试向broker请求锁定该消费队列,锁定失败延迟时则重新负载。
/**
* 消费者对应的分配消息队列是否变化
* step1:消费队列缓存表中不在本次均衡分配的消费队列时,则暂停消费并移除,且持久化待移除消费队列的消费进度;
* step2:本次均衡分配的消费队列不在消费队列缓存表中,则新增:
* 1):删除内存中该消费队列的消费进度;
* 2):创建broker的消费队列;
* 3):从磁盘中获取该消费队列的消费进度(若进度<0时,则根据配置矫正消费进度),创建拉取消息请求
* {@link rebalanceimpl#computepullfromwhere}
* step3: 新增消费队列,则创建{@link pullrequest}加入到{@link pullmessageservice},唤醒该线程拉取消息
* {@link rebalanceimpl#dispatchpullrequest}
* step4:顺序消息时,则尝试向broker请求锁定该消费队列,锁定失败延迟重新负载
* @param topic 主题
* @param mqset 本次均衡分配的消费队列
* @param isorder 是否顺序
* @return true变化;false未改变
*/
private boolean updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance(final string topic, final set<messagequeue> mqset,
final boolean isorder) {
boolean changed = false;
// drop process queues no longer belong me 当前消费队列不在分配队列中
hashmap<messagequeue, processqueue> removequeuemap = new hashmap<messagequeue, processqueue>(this.processqueuetable.size());
// 遍历当前消费队列缓存表
iterator<entry<messagequeue, processqueue>> it = this.processqueuetable.entryset().iterator();
while (it.hasnext()) {
entry<messagequeue, processqueue> next = it.next();
messagequeue mq = next.getkey();
processqueue pq = next.getvalue();
// 是该topic的消费队列
if (mq.gettopic().equals(topic)) {
// 当前消费队列不在现有的分配消息队列中,则暂停消费、废弃当前消费队列并移除(分配给其他消费者)
if (!mqset.contains(mq)) {
pq.setdropped(true);
removequeuemap.put(mq, pq);
} else if (pq.ispullexpired() && this.consumetype() == consumetype.consume_passively) {
pq.setdropped(true);
removequeuemap.put(mq, pq);
log.error("[bug]dorebalance, {}, try remove unnecessary mq, {}, because pull is pause, so try to fixed it",
consumergroup, mq);
}
}
}
// remove message queues no longer belong me 移除不在分配的消费队列
for (entry<messagequeue, processqueue> entry : removequeuemap.entryset()) {
messagequeue mq = entry.getkey();
processqueue pq = entry.getvalue();
/*
判断是否将{@link messagequeue}、{@link processqueue}缓存表中移除
a. 持久化待移除的{@link messagequeue}消费进度;
b. 顺序消息时,需先解锁队列
*/
if (this.removeunnecessarymessagequeue(mq, pq)) {
this.processqueuetable.remove(mq);
changed = true;
log.info("dorebalance, {}, remove unnecessary mq, {}", consumergroup, mq);
}
}
// add new message queue 遍历本次负载均衡分配的消费队列,缓存表中没有,则新增的消费队列
boolean allmqlocked = true; // 消费队列是否有锁定(顺序消息使用)
list<pullrequest> pullrequestlist = new arraylist<pullrequest>();
for (messagequeue mq : mqset) {
// 新增的消费队列
if (!this.processqueuetable.containskey(mq)) {
// 若是顺序消息,则尝试向broker请求锁定该消费队列,锁定失败延迟重新负载
if (isorder && !this.lock(mq)) {
log.warn("dorebalance, {}, add a new mq failed, {}, because lock failed", consumergroup, mq);
allmqlocked = false;
continue;
}
// 删除内存中该消费队列的消费进度
this.removedirtyoffset(mq);
// 创建broker的消费队列
processqueue pq = createprocessqueue(topic);
pq.setlocked(true);
// 从磁盘中获取该消费队列的消费进度(若进度<0时,则根据配置矫正消费进度),创建拉取消息请求
long nextoffset = this.computepullfromwhere(mq);
if (nextoffset >= 0) {
processqueue pre = this.processqueuetable.putifabsent(mq, pq);
if (pre != null) {
log.info("dorebalance, {}, mq already exists, {}", consumergroup, mq);
} else {
log.info("dorebalance, {}, add a new mq, {}", consumergroup, mq);
// 创建拉取消息请求
pullrequest pullrequest = new pullrequest();
pullrequest.setconsumergroup(consumergroup);
pullrequest.setnextoffset(nextoffset);
pullrequest.setmessagequeue(mq);
pullrequest.setprocessqueue(pq);
pullrequestlist.add(pullrequest);
changed = true;
}
} else {
log.warn("dorebalance, {}, add new mq failed, {}", consumergroup, mq);
}
}
}
// 锁定消费队列失败,延迟重新负载
if (!allmqlocked) {
mqclientfactory.rebalancelater(500);
}
// 将拉取消息对象{@link pullrequest}加入到{@link pullmessageservice},唤醒该线程拉取消息
this.dispatchpullrequest(pullrequestlist, 500);
return changed;
}根据rebalanceimpl#updateprocessqueuetableinrebalance来判定消费者对应的分配到的消息队列是否变化(新增或删除)时,若是新增,则先删除内存消费进度,再从broker端获取该消费队列的消费进度;若是删除,持久化消费进度同时删除旧的消费队列。
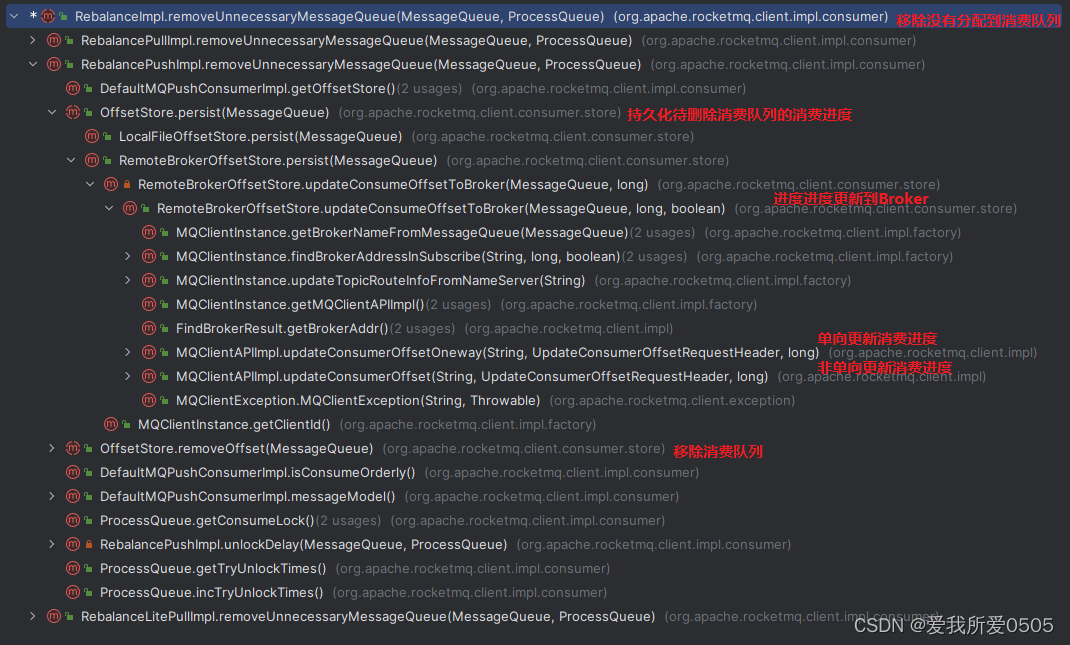
a. 删除操作
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.rebalanceimpl#removeunnecessarymessagequeue负载均衡时删除未分配的消费队列,其调用链如下。
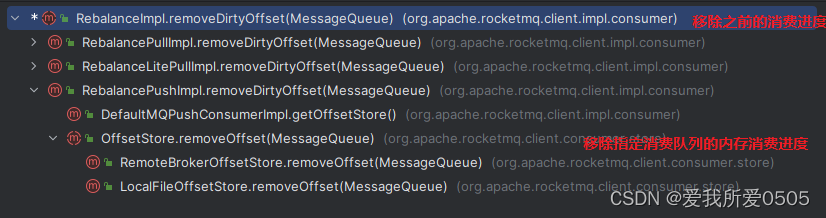
b. 新增操作
先删除该消费队列旧的内存消费进度,执行方法rebalanceimpl#removedirtyoffset,其调用链如下。
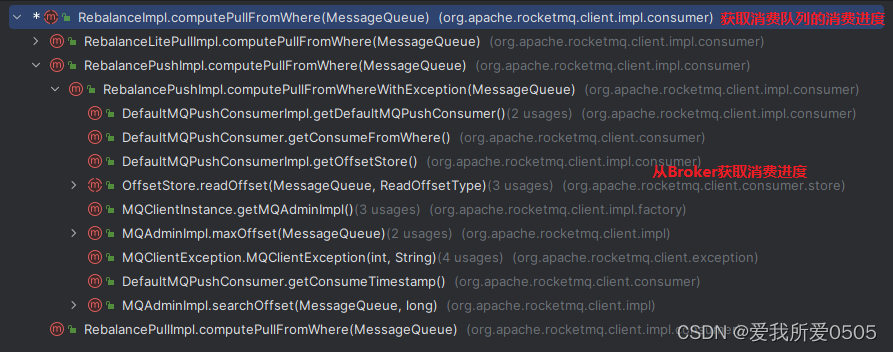
再从broker磁盘获取该消费队列消费进度,执行rebalanceimpl#computepullfromwhere,其调用链如下。
三、负载均衡策略
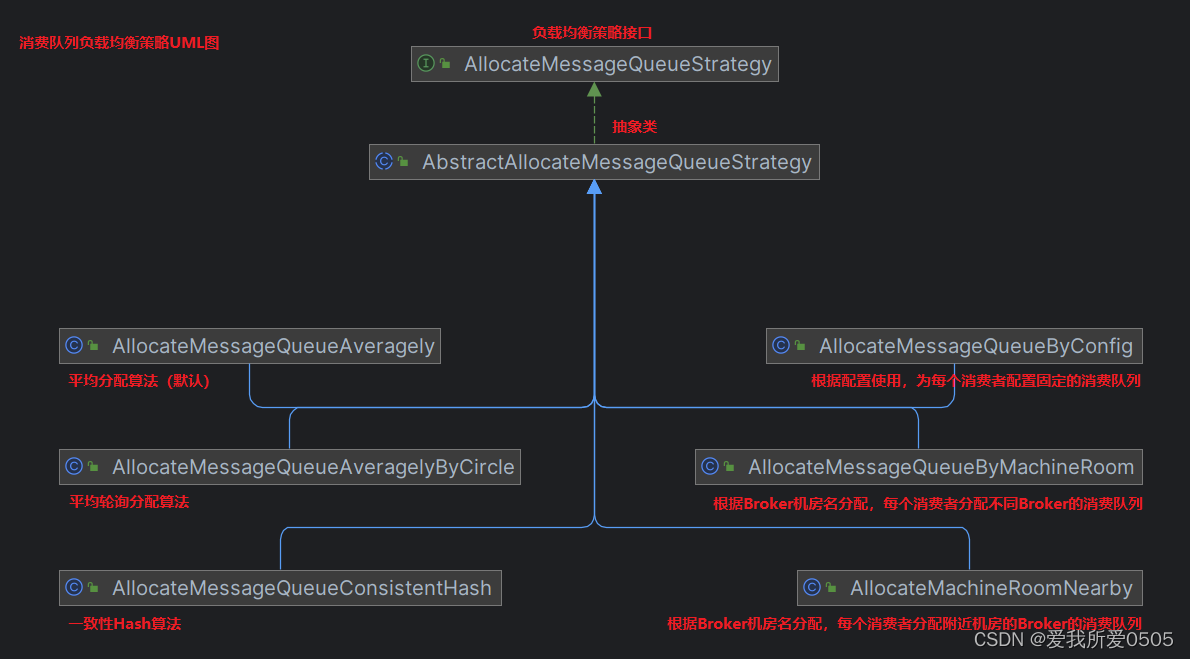
org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.allocatemessagequeuestrategy是消费队列负载均衡策略的接口,其有6个实现类,uml图如下。其中:
- allocatemessagequeueaveragely:平均分配算法(默认),如:8个消息消费队列q1、q2、q3、q4、q5、q6、q7、q8,有3个消费者c1、c2、c3,则分配如下:
c1:q1、q2、q3
c2:q4、q5、q6
c3:q7、q8
- allocatemessagequeueaveragelybycircle:平均轮询算法,如:8个消息消费队列q1、q2、q3、q4、q5、q6、q7、q8,有3个消费者c1、c2、c3,则分配如下:
c1:q1、q4、q7
c2:q2、q5、q8
c3:q3、q6
四、参考资料
rocketmq(十三) rocketmq负载均衡_每天都要进步一点点的博客-csdn博客



发表评论