lrucache
文章目录
前言
这里分享我的一些博客专栏,都是干货满满的。
项目代码仓库
什么时候会用到缓存(cache)
缓存(cache)通常用于两个速度不同的介质之间,以提高数据访问的速度和效率。这里有几个典型的应用场景:
处理器和内存之间: 处理器(cpu)的运算速度远快于从内存中读取数据的速度。因此,在cpu和内存之间会有多级缓存(l1、l2、甚至l3缓存),用来临时存储即将被cpu使用的数据和指令。这样做可以大幅减少cpu等待数据的时间,提高整体计算效率。
内存和硬盘之间: 内存的访问速度也远快于硬盘(无论是hdd还是ssd)。操作系统会使用一部分内存作为硬盘缓存(有时称为“磁盘缓存”或“缓冲区缓存”),用于临时存储最近访问过的数据和文件。当再次请求这些数据时,可以直接从内存中获得,而不是从较慢的硬盘中读取。
数据库系统中: 数据库管理系统(dbms)也会使用缓存技术来提高查询速度和数据处理效率。缓存可以存储经常访问的查询结果、数据库索引等信息,从而加速后续相同或相似查询的处理速度。
网络请求: 在网络请求中,缓存也是提高数据访问速度的重要技术。例如,web浏览器会缓存访问过的网页资源(如html文件、图片等),当再次访问这些资源时,可以直接从本地缓存读取,而不需要重新从网络下载。
缓存的关键在于它能够存储一份数据副本,在访问速度较慢的介质之前提供快速访问路径。这样,即使背后的存储介质响应较慢,系统性能也不会受到太大影响。然而,缓存管理(如缓存更新、缓存失效策略等)是实现高效缓存系统的一个挑战。正确和高效地使用缓存可以显著提高系统性能,减少数据处理和响应时间。
缓存满了,怎么办?
缓存空间满了之后,更新数据,我要进去,谁出去呢?
什么是lrucache
cache的容量有限,因此当cache的容量用完后,而又有新的内容需要添加进来时, 就需要挑选并舍弃原有的部分内容,从而腾出空间来放新内容。lrucache 的替换原则就是将最近最少使用的内容替换掉。 其实,lru译成最久未使用会更形象, 因为该算法每次替换掉的就是一段时间内最久没有使用过的内容。
lrucache的实现
要设计一个lrucache不难,要设计一个高效的lrucache有难度,即:任意操作都是o(1)。
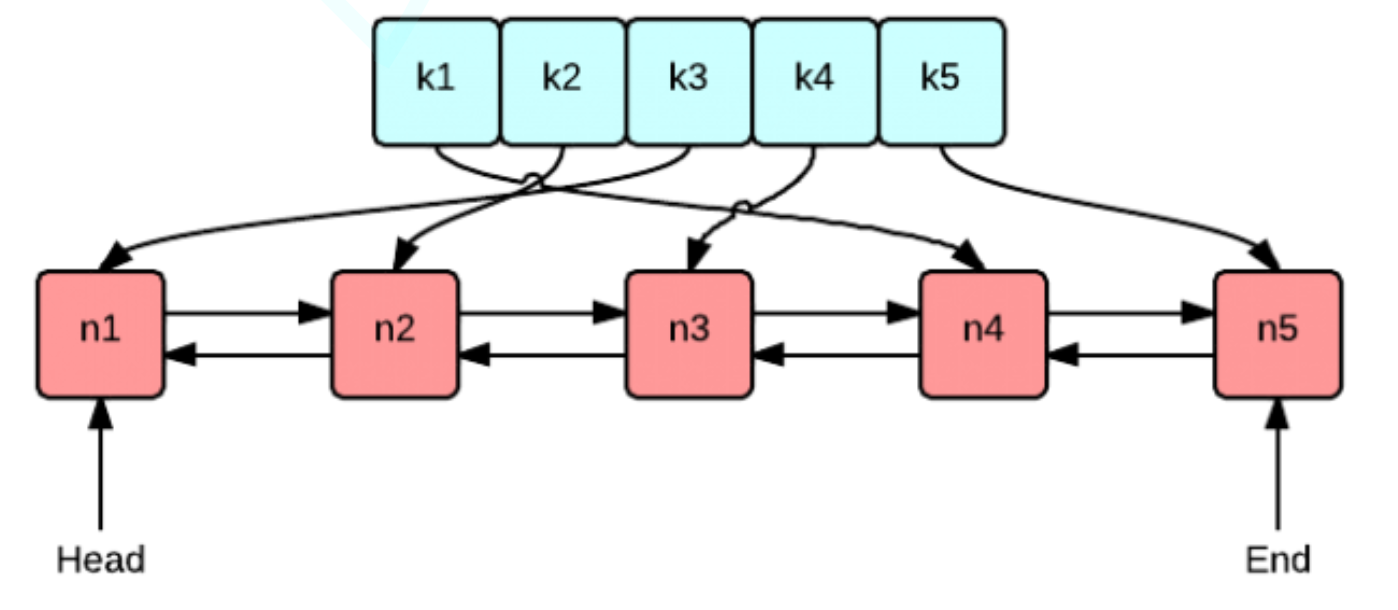
使用双向链表和哈希表的搭配是最高效和经典的。使用双向链表是因为双向链表可以实现任意位置0(1)的插入和删除,使用哈希表是因为哈希表的增删查改也是o(1)。
lrucache对应的oj题实现
我们借助一个oj题来讲解。
class lrucache {
public:
lrucache(int capacity) {
}
int get(int key) {
}
void put(int key, int value) {
}
};
/**
* your lrucache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* lrucache* obj = new lrucache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
首先用一个哈希表,可以保证我们查找是o(1),那么如何保证lru?
我们可以用一个链表,我们认为尾巴是最不常用的,如果数据被用了,就弄到头上去,所以尾巴就一定是要被淘汰的数据。
std::unordered_map<int, int> __hash_map;
std::list<std::pair<int, int>> __lru_list;
此时这种设计:
- get是o(1)
- 新增是o(1)
- 但是更新是o(n)
为什么?因为我们要更新数据,就要找到这个数据,就要遍历链表。
那怎么办?
哈希表里面存链表节点的指针就行了。
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<std::pair<int, int>>::iterator> __hash_map;
std::list<std::pair<int, int>> __lru_list;
题目的实现如下:
#include <unordered_map>
#include <list>
#include <utility>
class lrucache
{
private:
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<std::pair<int, int>>::iterator> __hash_map;
std::list<std::pair<int, int>> __lru_list;
size_t __capacity;
public:
lrucache(int capacity)
: __capacity(capacity) {}
int get(int key)
{
auto res = __hash_map.find(key);
if (res == __hash_map.end())
return -1;
// 更新链表节点位置
auto it = res->second;
/*
方法一: erase + push_front
注意记得erase之后更新迭代器,防止迭代器失效
方法二:转移节点的接口,stl::list提供了
*/
__lru_list.splice(__lru_list.begin(), __lru_list, it);
return it->second;
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
// 1. 新增 2. 更新
auto res = __hash_map.find(key);
if (res == __hash_map.end())
{
// 新增,如果满了,先删除数据
/*
这里用哈希表求size比较细节,这里一定是o(1)
但是list有些版本下入过没有维护size这个字段,求一次size()就是o(n)了
*/
if (__capacity == __hash_map.size())
{
std::pair<int, int> back = __lru_list.back();
__hash_map.erase(back.first);
__lru_list.pop_back();
}
// 加入数据
__lru_list.push_front(std::make_pair(key, value));
__hash_map[key] = __lru_list.begin();
}
else
{
// 更新
auto it = res->second;
it->second = value; // 更新
__lru_list.splice(__lru_list.begin(), __lru_list, it);
}
}
};
lrucache对应的stl风格实现
同时我也实现了一个stl模式的类模版,实现也非常简单,也欢迎大家补充。
#include <unordered_map>
#include <list>
#include <utility>
template <class key_type, class value_type, size_t capacity = 10>
class lrucache
{
private:
std::unordered_map<key_type, typename std::list<std::pair<key_type, value_type>>::iterator> __hash_map;
std::list<std::pair<key_type, value_type>> __lru_list;
size_t __capacity = capacity;
public:
lrucache() {}
value_type get(key_type key)
{
auto res = __hash_map.find(key);
if (res == __hash_map.end())
return -1;
// 更新链表节点位置
auto it = res->second;
__lru_list.splice(__lru_list.begin(), __lru_list, it);
return it->second;
}
void put(key_type key, value_type value)
{
// 1. 新增 2. 更新
auto res = __hash_map.find(key);
if (res == __hash_map.end())
{
if (__capacity == __hash_map.size())
{
auto back = __lru_list.back();
__hash_map.erase(back.first);
__lru_list.pop_back();
}
// 加入数据
__lru_list.push_front(std::make_pair(key, value));
__hash_map[key] = __lru_list.begin();
}
else
{
// 更新
auto it = res->second;
it->second = value; // 更新
__lru_list.splice(__lru_list.begin(), __lru_list, it);
}
}
public:
void clear()
{
__hash_map.clear();
__lru_list.clear();
}
size_t size() { return __hash_map.size(); }
bool empty() { return this->size() == 0; }
};




发表评论