标注工具 labelme 生成的标注文件为json格式,而yolov8中支持的为txt文件格式。以下python代码实现3个功能:
1.将json格式转换成txt格式;
2.将数据集进行随机拆分,生成yolov8支持的目录结构;
3.生成yolov8支持的yaml文件。
代码test_labelme2yolov8.py如下:
import os
import json
import argparse
import colorama
import random
import shutil
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.argumentparser(description="json(labelme) to txt(yolov8)")
parser.add_argument("--dir", required=true, type=str, help="images, json files, and generated txt files, all in the same directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", required=true, type=str, help="txt file that hold indexes and labels, one label per line, for example: face 0")
parser.add_argument("--val_size", default=0.2, type=float, help="the proportion of the validation set to the overall dataset:[0., 0.5]")
parser.add_argument("--name", required=true, type=str, help="the name of the dataset")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def get_labels_index(name):
labels = {} # key,value
with open(name, "r") as file:
for line in file:
# print("line:", line)
key_value = []
for v in line.split(" "):
# print("v:", v)
key_value.append(v.replace("\n", "")) # remove line breaks(\n) at the end of the line
if len(key_value) != 2:
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: each line should have only two values(key value):", len(key_value))
continue
labels[key_value[0]] = key_value[1]
with open(name, "r") as file:
line_num = len(file.readlines())
if line_num != len(labels):
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: there may be duplicate lables:", line_num, len(labels))
return labels
def get_json_files(dir):
jsons = []
for x in os.listdir(dir):
if x.endswith(".json"):
jsons.append(x)
return jsons
def parse_json(name):
with open(name, "r") as file:
data = json.load(file)
width = data["imagewidth"]
height = data["imageheight"]
# print(f"width: {width}; height: {height}")
objects=[]
for shape in data["shapes"]:
if shape["shape_type"] != "rectangle":
print(colorama.fore.yellow + "warning: only the rectangle type is supported:", shape["shape_type"])
continue
object = []
object.append(shape["label"])
object.append(shape["points"])
objects.append(object)
return width, height, objects
def get_box_width_height(box):
dist = lambda val: max(val) - min(val)
x = [pt[0] for pt in box]
y = [pt[1] for pt in box]
return min(x), min(y), dist(x), dist(y)
def bounding_box_normalization(width, height, objects, labels):
boxes = []
for object in objects:
box = [] # class x_center y_center width height
box.append(labels[object[0]])
# print("point:", object[1])
x_min, y_min, box_w, box_h = get_box_width_height(object[1])
box.append(round((float(x_min + box_w / 2.0) / width), 6))
box.append(round((float(y_min + box_h / 2.0) / height), 6))
box.append(round(float(box_w / width), 6))
box.append(round(float(box_h / height), 6))
boxes.append(box)
return boxes
def write_to_txt(dir, json, width, height, objects, labels):
boxes = bounding_box_normalization(width, height, objects, labels)
# print("boxes:", boxes)
name = json[:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
# print("name:", name)
with open(dir + "/" + name, "w") as file:
for item in boxes:
# print("item:", item)
if len(item) != 5:
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: the length must be 5:", len(item))
continue
string = item[0] + " " + str(item[1]) + " " + str(item[2]) + " " + str(item[3]) + " " + str(item[4]) + "\r"
file.write(string)
def json_to_txt(dir, jsons, labels):
for json in jsons:
name = dir + "/" + json
# print("name:", name)
width, height, objects = parse_json(name)
# print(f"width: {width}; height: {height}; objects: {objects}")
write_to_txt(dir, json, width, height, objects, labels)
def is_in_range(value, a, b):
return a <= value <= b
def get_random_sequence(length, val_size):
numbers = list(range(0, length))
val_sequence = random.sample(numbers, int(length*val_size))
# print("val_sequence:", val_sequence)
train_sequence = [x for x in numbers if x not in val_sequence]
# print("train_sequence:", train_sequence)
return train_sequence, val_sequence
def get_files_number(dir):
count = 0
for file in os.listdir(dir):
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dir, file)):
count += 1
return count
def split_train_val(dir, jsons, name, val_size):
if is_in_range(val_size, 0., 0.5) is false:
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: the interval for val_size should be:[0., 0.5]:", val_size)
raise
dst_dir_images_train = "datasets/" + name + "/images/train"
dst_dir_images_val = "datasets/" + name + "/images/val"
dst_dir_labels_train = "datasets/" + name + "/labels/train"
dst_dir_labels_val = "datasets/" + name + "/labels/val"
try:
os.makedirs(dst_dir_images_train) #, exist_ok=true
os.makedirs(dst_dir_images_val)
os.makedirs(dst_dir_labels_train)
os.makedirs(dst_dir_labels_val)
except oserror as e:
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: cannot create directory:", e.strerror)
raise
# supported image formats
img_formats = (".bmp", ".jpeg", ".jpg", ".png", ".webp")
# print("jsons:", jsons)
train_sequence, val_sequence = get_random_sequence(len(jsons), val_size)
for index in train_sequence:
for format in img_formats:
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + format
# print("file:", file)
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_images_train)
break
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_labels_train)
for index in val_sequence:
for format in img_formats:
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + format
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_images_val)
break
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_labels_val)
num_images_train = get_files_number(dst_dir_images_train)
num_images_val = get_files_number(dst_dir_images_val)
num_labels_train = get_files_number(dst_dir_labels_train)
num_labels_val = get_files_number(dst_dir_labels_val)
if num_images_train + num_images_val != len(jsons) or num_labels_train + num_labels_val != len(jsons):
print(colorama.fore.red + "error: the number of files is inconsistent:", num_images_train, num_images_val, num_labels_train, num_labels_val, len(jsons))
raise
def generate_yaml_file(labels, name):
path = os.path.join("datasets", name, name+".yaml")
# print("path:", path)
with open(path, "w") as file:
file.write("path: ../datasets/%s # dataset root dir\n" % name)
file.write("train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path')\n")
file.write("val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path')\n")
file.write("test: # test images (optional)\n\n")
file.write("# classes\n")
file.write("names:\n")
for key, value in labels.items():
# print(f"key: {key}; value: {value}")
file.write(" %d: %s\n" % (int(value), key))
if __name__ == "__main__":
colorama.init()
args = parse_args()
# 1. parse json file and write it to a txt file
labels = get_labels_index(args.labels)
# print("labels:", labels)
jsons = get_json_files(args.dir)
# print("jsons:", jsons)
json_to_txt(args.dir, jsons, labels)
# 2. split the dataset
split_train_val(args.dir, jsons, args.name, args.val_size)
# 3. generate a yaml file
generate_yaml_file(labels, args.name)
print(colorama.fore.green + "====== execution completed ======")代码有些多,主要函数说明如下:
1.函数parse_args:解析输入参数;
2.函数get_labels_index:解析labels文件,数据集中的所有类别及对应的索引,格式labels.txt如下所示:生成yolov8的yaml文件时也需要此文件
face 0
hand 1
eye 2
mouth 3
horse 4
tree 5
bridge 6
house 7
3.函数get_json_files:获取指定目录下的所有json文件;
4.函数parse_json:解析json文件,将txt文件中需要的数据提取出来;
5.函数bounding_box_normalization:将bounding box值归一化到(0,1)区间;
6.函数write_to_txt:将最终结果写入txt文件;
7.函数split_train_val:将数据集随机拆分为训练集和验证集,并按yolov8支持的目录结构存放,根目录为datasets,接着是指定的数据集名,例如为fake,与yolov8中数据集coco8目录结构完全一致
8.函数generate_yaml_file:生成yolov8支持的yaml文件,存放在datasets/数据集名下,例如为fake.yaml
接收4个参数:参数dir为存放数据集的目录;参数labels指定labels文件;参数val_size指定验证集所占的比例;参数name指定新生成的yolov8数据集的名字
这里从网上随机下载了10幅图像,使用labelme进行了标注,执行结果如下图所示:
生成的fake.yaml文件如下图所示:
path: ../datasets/fake # dataset root dir train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') test: # test images (optional) # classes names: 0: face 1: hand 2: eye 3: mouth 4: horse 5: tree 6: bridge 7: house
将生成的fake数据集进行训练,测试代码test_yolov8_detect.py如下:
import argparse
import colorama
from ultralytics import yolo
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.argumentparser(description="yolov8 object detect")
parser.add_argument("--yaml", required=true, type=str, help="yaml file")
parser.add_argument("--epochs", required=true, type=int, help="number of training")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def train(yaml, epochs):
model = yolo("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained model
results = model.train(data=yaml, epochs=epochs, imgsz=640) # train the model
metrics = model.val() # it'll automatically evaluate the data you trained, no arguments needed, dataset and settings remembered
model.export(format="onnx", dynamic=true) # export the model
if __name__ == "__main__":
colorama.init()
args = parse_args()
train(args.yaml, args.epochs)
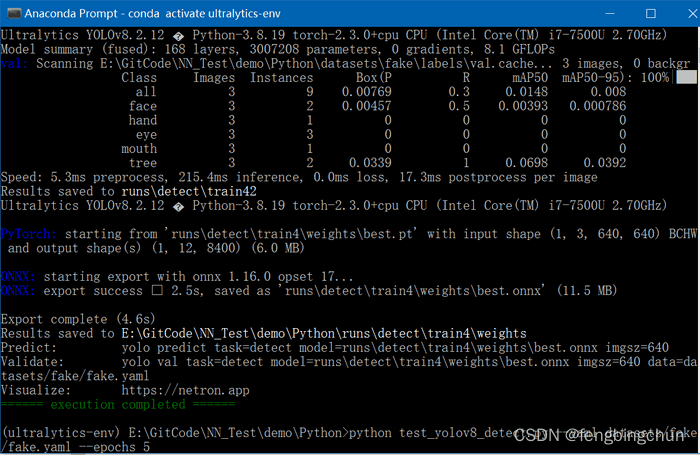
print(colorama.fore.green + "====== execution completed ======")执行结果如下图所示:目前此测试代码接收2个参数:参数yaml指定yaml文件;参数epochs指定训练次数;由以下结果可知,生成的新数据集无需做任何改动即可进行训练
github:https://github.com/fengbingchun/nn_test
到此这篇关于python实现将labelme生成的json格式转换成yolov8支持的txt格式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python json格式转换内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论