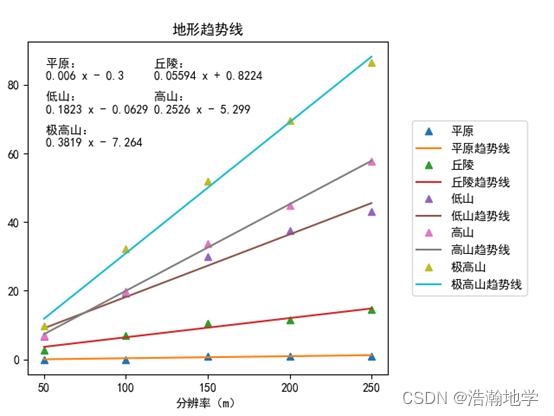
当时的数字地形实验,使用 matplotlib库绘制了一张图表表示不同地形类别在不同分辨率下的rmse值,并分别拟合了一条趋势线。现在来看不足就是地形较多时,需要使用循环更好一点,不然太冗余了。
环境:python 3.9
代码逻辑
导入所需库以及初步设置
# coding=gbk # -*- coding = utf-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.05, right=0.7, top=0.9, bottom=0.1) plt.rcparams['font.sans-serif'] = ['simhei']
准备数据(这里仅展示部分)
resolutions = [50, 100, 150, 200, 250] plain = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1] hill = [2.645751311, 7.071067812, 10.44030651, 11.48912529, 14.4222051]
这里可以改为在excel中读取,尤其是数据多的时候
分别绘制不同数据的趋势线
# 绘制平原趋势线 coefficients_plain = np.polyfit(resolutions, plain, 1) poly_plain = np.poly1d(coefficients_plain) plt.plot(resolutions, plain, '^', label="平原") plt.plot(resolutions, poly_plain(resolutions), label="平原趋势线") # 绘制丘陵趋势线 coefficients_hill = np.polyfit(resolutions, hill, 1) poly_hill = np.poly1d(coefficients_hill) plt.plot(resolutions, hill, '^', label="丘陵") plt.plot(resolutions, poly_hill(resolutions), label="丘陵趋势线")
使用np.polyfit函数拟合一阶多项式(直线),然后使用np.poly1d构造多项式对象。绘制原始数据点(用’^'标记)和对应的拟合趋势线。
计算指标
# 计算平原趋势线的r值和r方 residuals_plain = plain - poly_plain(resolutions) ss_residuals_plain = np.sum(residuals_plain**2) ss_total_plain = np.sum((plain - np.mean(plain))**2) r_squared_plain = 1 - (ss_residuals_plain / ss_total_plain) r_plain = np.sqrt(r_squared_plain) # 计算丘陵趋势线的r值和r方 residuals_hill = hill - poly_hill(resolutions) ss_residuals_hill = np.sum(residuals_hill**2) ss_total_hill = np.sum((hill - np.mean(hill))**2) r_squared_hill = 1 - (ss_residuals_hill / ss_total_hill) r_hill = np.sqrt(r_squared_hill)
计算得到r方和r值
绘图和打印指标
# 设置图例和标题
plt.legend()
plt.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 0.5))
plt.title("地形趋势线")
# 设置坐标轴标题
new_ticks = np.arange(50, 251, 50)
plt.xticks(new_ticks)
plt.xlabel('分辨率(m)')
plt.ylabel('rmse')
formula1 = "平原:{}".format(poly_plain)
plt.text(0.05, 0.95, formula1, transform=plt.gca().transaxes,
fontsize=10, verticalalignment='top')
formula1 = "丘陵:{}".format(poly_hill)
plt.text(0.35, 0.95, formula1, transform=plt.gca().transaxes,
fontsize=10, verticalalignment='top')
# 显示图形
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.show()
# 打印
print("平原趋势线公式:", poly_plain)
print("丘陵趋势线公式:", poly_hill)
print("平原趋势线:")
print("r值:", r_plain)
print("r方:", r_squared_plain)
print()
print("丘陵趋势线:")
print("r值:", r_hill)
print("r方:", r_squared_hill)
print()
完整代码
# coding=gbk
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.05, right=0.7, top=0.9, bottom=0.1)
plt.rcparams['font.sans-serif'] = ['simhei']
resolutions = [50, 100, 150, 200, 250]
plain = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1]
hill = [2.645751311, 7.071067812, 10.44030651, 11.48912529, 14.4222051]
# 绘制平原趋势线
coefficients_plain = np.polyfit(resolutions, plain, 1)
poly_plain = np.poly1d(coefficients_plain)
plt.plot(resolutions, plain, '^', label="平原")
plt.plot(resolutions, poly_plain(resolutions), label="平原趋势线")
# 绘制丘陵趋势线
coefficients_hill = np.polyfit(resolutions, hill, 1)
poly_hill = np.poly1d(coefficients_hill)
plt.plot(resolutions, hill, '^', label="丘陵")
plt.plot(resolutions, poly_hill(resolutions), label="丘陵趋势线")
# 计算平原趋势线的r值和r方
residuals_plain = plain - poly_plain(resolutions)
ss_residuals_plain = np.sum(residuals_plain**2)
ss_total_plain = np.sum((plain - np.mean(plain))**2)
r_squared_plain = 1 - (ss_residuals_plain / ss_total_plain)
r_plain = np.sqrt(r_squared_plain)
# 计算丘陵趋势线的r值和r方
residuals_hill = hill - poly_hill(resolutions)
ss_residuals_hill = np.sum(residuals_hill**2)
ss_total_hill = np.sum((hill - np.mean(hill))**2)
r_squared_hill = 1 - (ss_residuals_hill / ss_total_hill)
r_hill = np.sqrt(r_squared_hill)
# 设置图例和标题
plt.legend()
plt.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 0.5))
plt.title("地形趋势线")
# 设置坐标轴标题
new_ticks = np.arange(50, 251, 50)
plt.xticks(new_ticks)
plt.xlabel('分辨率(m)')
plt.ylabel('rmse')
formula1 = "平原:{}".format(poly_plain)
plt.text(0.05, 0.95, formula1, transform=plt.gca().transaxes,
fontsize=10, verticalalignment='top')
formula1 = "丘陵:{}".format(poly_hill)
plt.text(0.35, 0.95, formula1, transform=plt.gca().transaxes,
fontsize=10, verticalalignment='top')
# 显示图形
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.show()
# 打印
print("平原趋势线公式:", poly_plain)
print("丘陵趋势线公式:", poly_hill)
print("平原趋势线:")
print("r值:", r_plain)
print("r方:", r_squared_plain)
print()
print("丘陵趋势线:")
print("r值:", r_hill)
print("r方:", r_squared_hill)
print()
结果
参考
到此这篇关于python实现线性拟合及绘图的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python 线性拟合及绘图内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论