guzzle中的异步请求
使用guzzle发起异步请求
guzzle是一个php的http客户端,它在发起http请求时不仅可以同步发起,还可以异步发起。
$client = new client();
$request = new request('get', 'http://www.baidu.com');
$promise = $client->sendasync($request)->then(function ($response) {
echo $response->getbody();
});
// todo something
echo 1;
$promise->wait();php发起http请求的几种方式
curl
使用libcurl库,允许你与各种的服务器使用各种类型的协议进行连接和通讯。
stream
通过流的方式获取和发送远程文件,该功能需要ini配置allow_url_fopen=on。关于php的流更多参考php流(stream)的概述与使用详解
在guzzle中可以兼容使用这两种的任意一种或者是用户自定义的http handler
function choose_handler()
{
$handler = null;
if (function_exists('curl_multi_exec') && function_exists('curl_exec')) {
$handler = proxy::wrapsync(new curlmultihandler(), new curlhandler());
} elseif (function_exists('curl_exec')) {
$handler = new curlhandler();
} elseif (function_exists('curl_multi_exec')) {
$handler = new curlmultihandler();
}
if (ini_get('allow_url_fopen')) {
$handler = $handler
? proxy::wrapstreaming($handler, new streamhandler())
: new streamhandler();
} elseif (!$handler) {
throw new \runtimeexception('guzzlehttp requires curl, the '
. 'allow_url_fopen ini setting, or a custom http handler.');
}
return $handler;
}可以看出,guzzle会优先使用curl,然后选择使用stream,proxy::wrapstreaming($handler, new streamhandler()) 是一个流包装器。
public static function wrapstreaming(
callable $default,
callable $streaming
) {
return function (requestinterface $request, array $options) use ($default, $streaming) {
return empty($options['stream'])
? $default($request, $options)
: $streaming($request, $options);
};
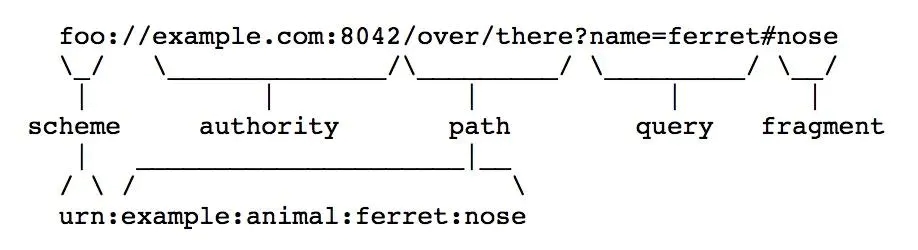
}什么是uri?uri的组成
uri,uniform resource identifier,统一资源标识符。
scheme:[//[user:password@]host[:port]][/]path[?query][#fragment]
请求的组装
guzzle发起请求大致分为两个阶段,第一阶段负责将需要请求的uri组装成各种内部定义的类。
- client类:这是一个发起客户端的调用者,后续所有的调用需要基于这个负责的类实现,它负责提供一个 handler ,这是一个客户端发起http请求的句柄,其中guzzle实现curl和stream调用的无感知就是在这里实现的,同时开发者也可以自定义请求协议。
// 根据系统当前状态,选择一个发起http请求的协议的方法句柄
function choose_handler()
{
$handler = null;
if (function_exists('curl_multi_exec') && function_exists('curl_exec')) {
$handler = proxy::wrapsync(new curlmultihandler(), new curlhandler());
} elseif (function_exists('curl_exec')) {
$handler = new curlhandler();
} elseif (function_exists('curl_multi_exec')) {
$handler = new curlmultihandler();
}
if (ini_get('allow_url_fopen')) {
$handler = $handler
? proxy::wrapstreaming($handler, new streamhandler())
: new streamhandler();
} elseif (!$handler) {
throw new \runtimeexception('guzzlehttp requires curl, the '
. 'allow_url_fopen ini setting, or a custom http handler.');
}
return $handler;
}- request类:负责定义一个uri
- promise类:这个类负责承载类请求发起前的各种准备工作完成后的结果,还包括两个回调(请求成功回调、请求失败回调),同时请求发起中的队列,延迟等处理也是在这个类里。
其中组装阶段最重要的方法是私有方法 private function transfer(requestinterface $request, array $options) ,它负责将用户通过各种方法传入的uri和client类的各种属性组合,然后使用这些属性生成一个新的类 promise 类。
请求的发起
client的各种属性组装完成后就可以使用得到的promise类发起http请求了,这里主要是通过一个 wait() 方法。
同步调用与异步调用
在同步方法内部的调用,同步方法是在内部组装好一个promise之后立刻发起wait()调用。
public function send(requestinterface $request, array $options = [])
{
$options[requestoptions::synchronous] = true;
return $this->sendasync($request, $options)->wait();
}wait的实现
wait() 方法的实现逻辑也很简单,递归调用wait()方法,直到result属性不是promiseinterface实现类或者state不是pending,然后将结果逐层输出。这里说一下这个state的pending状态,这是一个promiseinterface实现类的初始化状态,表示改实现类还没有完成,需要继续wait。
public function wait($unwrap = true)
{
$this->waitifpending();
$inner = $this->result instanceof promiseinterface
? $this->result->wait($unwrap)
: $this->result;
if ($unwrap) {
if ($this->result instanceof promiseinterface
|| $this->state === self::fulfilled
) {
return $inner;
} else {
// it's rejected so "unwrap" and throw an exception.
throw exception_for($inner);
}
}
}waitifpending() : 如果promise类还处于pending状态就执行。主要是执行改实现类的waitfn方法。最外层promise执行完成后执行queue()->run() `` 这个方法内部循环执行队列内方法,直到队列为空。至此,guzzle就能将组装进来的多个request,和各种方法执行完毕。
private function waitifpending()
{
if ($this->state !== self::pending) {
return;
} elseif ($this->waitfn) {
$this->invokewaitfn();
} elseif ($this->waitlist) {
$this->invokewaitlist();
} else {
// if there's not wait function, then reject the promise.
$this->reject('cannot wait on a promise that has '
. 'no internal wait function. you must provide a wait '
. 'function when constructing the promise to be able to '
. 'wait on a promise.');
}
queue()->run();
if ($this->state === self::pending) {
$this->reject('invoking the wait callback did not resolve the promise');
}
}
public function run()
{
/** @var callable $task */
while ($task = array_shift($this->queue)) {
$task();
}
}waitfn是什么
回到前面提到的transfer() 函数。
$handler = $options['handler']; // 返回一个promise类,这个类有一个属性是waitfn return promise\promise_for($handler($request, $options));
这里我们看 $handler 是什么?它是一个handlestack类,就是我们在new client时选择的发起http请求的协议的方法句柄,实例化的类。<br />之后的调用依次是 handlestack->__invoke、redirectmiddleware->__invoke、preparebodymiddleware->__invoke。执行 $fn($request, $options); 方法,经过前面的逐层处理,此时的$fn就是handlestack内部的proxy包装的方法,无论使用哪种协议都会在各自的实现里实例化一个拥有waitfn的promise的实例。
// curl的实现
$promise = new promise(
[$this, 'execute'],
function () use ($id) {
return $this->cancel($id);
}
);由此可以直到waitfn方法就是各自协议的实现类的请求发起方法。then() 方法会将promise本身再封装一层promise,并将原先的waitfn和then()的回调方法打包进waitfnlist属性里。
queue() 是的入队时机
当请求执行完成后依次调用 processmessages()、promise->resolve()、settle()、fulfilledpromise->then(),将请求结果插入队列。
$queue->add(static function () use ($p, $value, $onfulfilled) {
if ($p->getstate() === self::pending) {
try {
$p->resolve($onfulfilled($value));
} catch (\throwable $e) {
$p->reject($e);
} catch (\exception $e) {
$p->reject($e);
}
}
});以上就是php使用guzzle发起的异步请求示例详解的详细内容,更多关于php guzzle异步请求的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!





发表评论