咱们可以想象一个这样的场景,你这边有大量的文件,现在我需要查找一个 序列号:xxxxxx,我想知道这个 序列号:xxxxxx 在哪个文件中。
在没有使用代码脚本的情况下,你可能需要一个文件一个文件打开,然后按 ctrl+f 来进行搜索查询。
那既然我们会使用 python,何不自己写一个呢?本文将实现这样一个工具,且源码全在文章中,只需要复制粘贴即可使用。
思路
主要思路就是通过打开文件夹,获取文件,一个个遍历查找关键字,流程图如下:
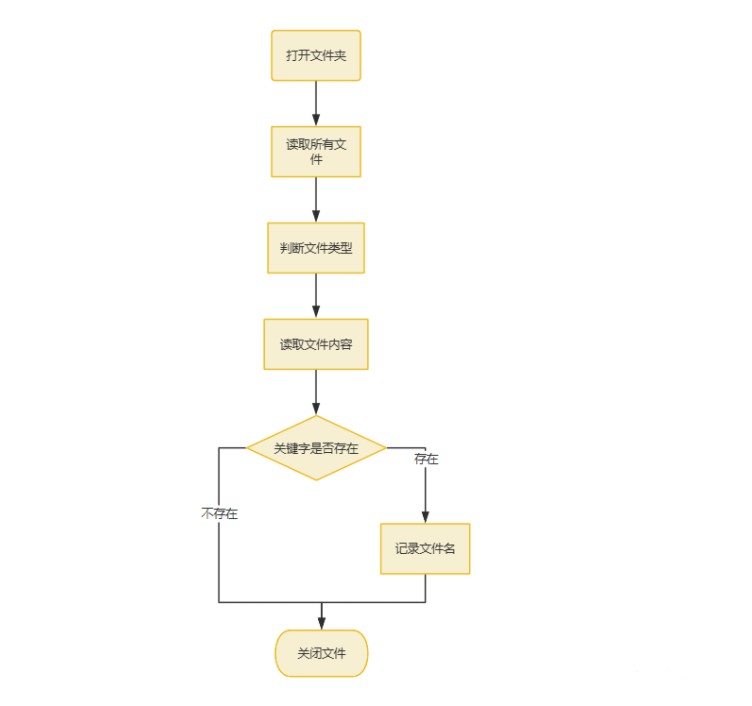
流程图
怎么样,思路非常简单,所以其实实现也不难。
本文将支持少部分文件类型,更多类型需要读者自己实现:
- txt
- docx
- csv
- xlsx
- pptx
读取txt
安装库
pip install chardet
代码
import chardet
def detect_encoding(file_path):
raw_data = none
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
for line in f:
raw_data = line
break
if raw_data is none:
raw_data = f.read()
result = chardet.detect(raw_data)
return result['encoding']
def read_txt(file_path, keywords=''):
is_in = false
encoding = detect_encoding(file_path)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as f:
for line in f:
if line.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in我们使用了 chardet 库来判断 txt 的编码,以应对不同编码的读取方式。
读取docx
安装库
pip install python-docx
代码
from docx import document
def read_docx(file_path, keywords=''):
doc = document(file_path)
is_in = false
for para in doc.paragraphs:
if para.text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in读取csv
代码
import csv
def read_csv(file_path, keywords=''):
is_in = false
encoding = detect_encoding(file_path)
with open(file_path, mode='r', encoding=encoding) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
row_text = ''.join([str(v) for v in row])
if row_text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in读取xlsx
安装库
pip install openpyxl
代码
from openpyxl import load_workbook
def read_xlsx(file_path, keywords=''):
wb = load_workbook(file_path)
sheet_names = wb.sheetnames
is_in = false
for sheet_name in sheet_names:
sheet = wb[sheet_name]
for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=true):
row_text = ''.join([str(v) for v in row])
if row_text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
wb.close()
return is_in读取pptx
安装库
pip install python-pptx
代码
from pptx import presentation
def read_ppt(ppt_file, keywords=''):
prs = presentation(ppt_file)
is_in = false
for slide in prs.slides:
for shape in slide.shapes:
if shape.has_text_frame:
text_frame = shape.text_frame
for paragraph in text_frame.paragraphs:
for run in paragraph.runs:
if run.text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in文件夹递归
为了防止文件夹嵌套导致的问题,我们还有一个文件夹递归的操作。
代码
from pathlib import path
def list_files_recursive(directory):
file_paths = []
for path in path(directory).rglob('*'):
if path.is_file():
file_paths.append(str(path))
return file_paths完整代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pptx import presentation
import chardet
from docx import document
import csv
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from pathlib import path
def detect_encoding(file_path):
raw_data = none
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
for line in f:
raw_data = line
break
if raw_data is none:
raw_data = f.read()
result = chardet.detect(raw_data)
return result['encoding']
def read_txt(file_path, keywords=''):
is_in = false
encoding = detect_encoding(file_path)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as f:
for line in f:
if line.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in
def read_docx(file_path, keywords=''):
doc = document(file_path)
is_in = false
for para in doc.paragraphs:
if para.text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in
def read_csv(file_path, keywords=''):
is_in = false
encoding = detect_encoding(file_path)
with open(file_path, mode='r', encoding=encoding) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
row_text = ''.join([str(v) for v in row])
if row_text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in
def read_xlsx(file_path, keywords=''):
wb = load_workbook(file_path)
sheet_names = wb.sheetnames
is_in = false
for sheet_name in sheet_names:
sheet = wb[sheet_name]
for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=true):
row_text = ''.join([str(v) for v in row])
if row_text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
wb.close()
return is_in
def read_ppt(ppt_file, keywords=''):
prs = presentation(ppt_file)
is_in = false
for slide in prs.slides:
for shape in slide.shapes:
if shape.has_text_frame:
text_frame = shape.text_frame
for paragraph in text_frame.paragraphs:
for run in paragraph.runs:
if run.text.find(keywords) != -1:
is_in = true
break
return is_in
def list_files_recursive(directory):
file_paths = []
for path in path(directory).rglob('*'):
if path.is_file():
file_paths.append(str(path))
return file_paths
if __name__ == '__main__':
keywords = '测试关键字'
file_paths = list_files_recursive(r'测试文件夹')
for file_path in file_paths:
if file_path.endswith('.txt'):
is_in = read_txt(file_path, keywords)
elif file_path.endswith('.docx'):
is_in = read_docx(file_path, keywords)
elif file_path.endswith('.csv'):
is_in = read_csv(file_path, keywords)
elif file_path.endswith('.xlsx'):
is_in = read_xlsx(file_path, keywords)
elif file_path.endswith('.pptx'):
is_in = read_ppt(file_path, keywords)
if is_in:
print(file_path)结尾
现在你可以十分方便地使用代码查找出各种文件中是否存在关键字了
以上就是python实现文件查询关键字功能的示例详解的详细内容,更多关于python查询文件关键字的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!






发表评论