android binder 详解与实践指南
1. binder 基础概念
1.1 什么是 binder?
binder 是 android 系统中最重要的进程间通信(ipc)机制,它具有以下特点:
- 高性能:相比其他 ipc 机制,binder 只需要一次数据拷贝
- 安全性:基于 c/s 架构,支持身份验证
- 面向对象:可以像调用本地方法一样调用远程方法
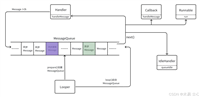
1.2 binder 架构组件
client process → binder driver → server process
↓ ↓
binder proxy binder object2. binder 基础实例
2.1 简单的 binder 服务端
// simplebinderservice.java
package com.example.binderdemo;
import android.app.service;
import android.content.intent;
import android.os.ibinder;
import android.os.remoteexception;
import android.util.log;
public class simplebinderservice extends service {
private static final string tag = "simplebinderservice";
// 定义 aidl 接口的实现
private final isimpleservice.stub binder = new isimpleservice.stub() {
@override
public int add(int a, int b) throws remoteexception {
log.d(tag, "add() called with: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
return a + b;
}
@override
public string greet(string name) throws remoteexception {
log.d(tag, "greet() called with: name = " + name);
return "hello, " + name + "! from binder service";
}
@override
public void senddata(datamodel data) throws remoteexception {
log.d(tag, "senddata() called with: " + data.tostring());
// 处理数据...
}
};
@override
public ibinder onbind(intent intent) {
log.d(tag, "onbind() called");
return binder;
}
@override
public void oncreate() {
super.oncreate();
log.d(tag, "service created");
}
@override
public void ondestroy() {
super.ondestroy();
log.d(tag, "service destroyed");
}
}2.2 定义 aidl 接口
// isimpleservice.aidl
package com.example.binderdemo;
// 定义数据模型
parcelable datamodel;
interface isimpleservice {
int add(int a, int b);
string greet(string name);
void senddata(in datamodel data);
}2.3 数据模型定义
// datamodel.java
package com.example.binderdemo;
import android.os.parcel;
import android.os.parcelable;
public class datamodel implements parcelable {
public int id;
public string message;
public long timestamp;
public datamodel() {}
public datamodel(int id, string message) {
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
this.timestamp = system.currenttimemillis();
}
protected datamodel(parcel in) {
id = in.readint();
message = in.readstring();
timestamp = in.readlong();
}
public static final creator<datamodel> creator = new creator<datamodel>() {
@override
public datamodel createfromparcel(parcel in) {
return new datamodel(in);
}
@override
public datamodel[] newarray(int size) {
return new datamodel[size];
}
};
@override
public int describecontents() {
return 0;
}
@override
public void writetoparcel(parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeint(id);
dest.writestring(message);
dest.writelong(timestamp);
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "datamodel{" +
"id=" + id +
", message='" + message + '\'' +
", timestamp=" + timestamp +
'}';
}
}2.4 客户端实现
// mainactivity.java
package com.example.binderdemo;
import android.content.componentname;
import android.content.context;
import android.content.intent;
import android.content.serviceconnection;
import android.os.bundle;
import android.os.ibinder;
import android.os.remoteexception;
import android.widget.button;
import android.widget.textview;
import androidx.appcompat.app.appcompatactivity;
public class mainactivity extends appcompatactivity {
private static final string tag = "mainactivity";
private isimpleservice simpleservice;
private boolean isbound = false;
private textview resulttext;
private serviceconnection connection = new serviceconnection() {
@override
public void onserviceconnected(componentname name, ibinder service) {
log.d(tag, "service connected");
simpleservice = isimpleservice.stub.asinterface(service);
isbound = true;
updatestatus("service connected");
}
@override
public void onservicedisconnected(componentname name) {
log.d(tag, "service disconnected");
simpleservice = null;
isbound = false;
updatestatus("service disconnected");
}
};
@override
protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main);
resulttext = findviewbyid(r.id.result_text);
button bindbtn = findviewbyid(r.id.bind_btn);
button unbindbtn = findviewbyid(r.id.unbind_btn);
button testbtn = findviewbyid(r.id.test_btn);
bindbtn.setonclicklistener(v -> bindservice());
unbindbtn.setonclicklistener(v -> unbindservice());
testbtn.setonclicklistener(v -> testservice());
}
private void bindservice() {
intent intent = new intent(this, simplebinderservice.class);
bindservice(intent, connection, context.bind_auto_create);
updatestatus("binding service...");
}
private void unbindservice() {
if (isbound) {
unbindservice(connection);
isbound = false;
simpleservice = null;
updatestatus("service unbound");
}
}
private void testservice() {
if (!isbound || simpleservice == null) {
updatestatus("service not bound!");
return;
}
new thread(() -> {
try {
// 测试加法
int result = simpleservice.add(5, 3);
string message = "5 + 3 = " + result;
// 测试问候
string greeting = simpleservice.greet("android developer");
// 测试数据传输
datamodel data = new datamodel(1, "test message");
simpleservice.senddata(data);
runonuithread(() -> updatestatus(
message + "\n" +
greeting + "\n" +
"data sent: " + data.tostring()
));
} catch (remoteexception e) {
runonuithread(() -> updatestatus("error: " + e.getmessage()));
log.e(tag, "remoteexception: ", e);
}
}).start();
}
private void updatestatus(string text) {
resulttext.settext(text);
log.d(tag, text);
}
@override
protected void ondestroy() {
super.ondestroy();
if (isbound) {
unbindservice();
}
}
}2.5 布局文件
<!-- activity_main.xml -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<button
android:id="@+id/bind_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bind service" />
<button
android:id="@+id/unbind_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbind service" />
<button
android:id="@+id/test_btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="test service" />
<textview
android:id="@+id/result_text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margintop="16dp"
android:padding="16dp"
android:background="#f0f0f0"
android:text="status: not connected"
android:textsize="14sp" />
</linearlayout>2.6 androidmanifest 配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.binderdemo">
<application
android:allowbackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/apptheme">
<activity android:name=".mainactivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.main" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.launcher" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name=".simplebinderservice"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false" />
</application>
</manifest>3. 运行结果分析
首次运行应用:
mainactivity: status: not connected
点击 “bind service” 按钮:
simplebinderservice: service created simplebinderservice: onbind() called mainactivity: service connected mainactivity: status: service connected
点击 “test service” 按钮:
simplebinderservice: add() called with: a = 5, b = 3
simplebinderservice: greet() called with: name = android developer
simplebinderservice: senddata() called with: datamodel{id=1, message='test message', timestamp=1641234567890}
mainactivity: 5 + 3 = 8
hello, android developer! from binder service
data sent: datamodel{id=1, message='test message', timestamp=1641234567890}点击 “unbind service” 按钮:
simplebinderservice: service destroyed mainactivity: service unbound
4. 高级 binder 特性
4.1 带回调的 binder 服务
// icallbackservice.aidl
package com.example.binderdemo;
interface icallbackservice {
void registercallback(icallback callback);
void unregistercallback(icallback callback);
void starttask(int taskid);
}
interface icallback {
void ontaskstarted(int taskid);
void ontaskprogress(int taskid, int progress);
void ontaskcompleted(int taskid, string result);
}4.2 回调服务实现
// callbackbinderservice.java
public class callbackbinderservice extends service {
private static final string tag = "callbackbinderservice";
private final list<icallback> callbacks = new copyonwritearraylist<>();
private final icallbackservice.stub binder = new icallbackservice.stub() {
@override
public void registercallback(icallback callback) throws remoteexception {
if (callback != null && !callbacks.contains(callback)) {
callbacks.add(callback);
log.d(tag, "callback registered, total: " + callbacks.size());
}
}
@override
public void unregistercallback(icallback callback) throws remoteexception {
callbacks.remove(callback);
log.d(tag, "callback unregistered, total: " + callbacks.size());
}
@override
public void starttask(int taskid) throws remoteexception {
log.d(tag, "starting task: " + taskid);
new taskexecutor(taskid).start();
}
};
private class taskexecutor extends thread {
private final int taskid;
taskexecutor(int taskid) {
this.taskid = taskid;
}
@override
public void run() {
try {
// 通知任务开始
for (icallback callback : callbacks) {
callback.ontaskstarted(taskid);
}
// 模拟任务执行
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i += 10) {
thread.sleep(200);
// 更新进度
for (icallback callback : callbacks) {
callback.ontaskprogress(taskid, i);
}
}
// 任务完成
for (icallback callback : callbacks) {
callback.ontaskcompleted(taskid, "task " + taskid + " completed successfully");
}
} catch (exception e) {
log.e(tag, "task execution failed", e);
}
}
}
@override
public ibinder onbind(intent intent) {
return binder;
}
}4.3 客户端回调处理
// 在 mainactivity 中添加回调处理
private icallback callback = new icallback.stub() {
@override
public void ontaskstarted(int taskid) throws remoteexception {
runonuithread(() -> updatestatus("task " + taskid + " started"));
}
@override
public void ontaskprogress(int taskid, int progress) throws remoteexception {
runonuithread(() -> updatestatus("task " + taskid + " progress: " + progress + "%"));
}
@override
public void ontaskcompleted(int taskid, string result) throws remoteexception {
runonuithread(() -> updatestatus("task " + taskid + " completed: " + result));
}
};
private void testcallbackservice() {
if (callbackservice != null) {
try {
callbackservice.registercallback(callback);
callbackservice.starttask(1);
} catch (remoteexception e) {
log.e(tag, "callback test failed", e);
}
}
}5. binder 传输数据类型
5.1 支持的数据类型
| 类型 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 基本类型 | int, long, float, double, boolean | int count = 10 |
| string | 字符串 | string name = "android" |
| charsequence | 字符序列 | charsequence text |
| parcelable | 可序列化对象 | datamodel data |
| list | 列表 | list<string> names |
| map | 映射 | map<string, integer> scores |
5.2 复杂数据模型示例
// usermodel.java
public class usermodel implements parcelable {
public int userid;
public string username;
public list<string> permissions;
public map<string, string> attributes;
// parcelable 实现...
@override
public void writetoparcel(parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeint(userid);
dest.writestring(username);
dest.writestringlist(permissions);
dest.writemap(attributes);
}
protected usermodel(parcel in) {
userid = in.readint();
username = in.readstring();
permissions = in.createstringarraylist();
attributes = in.readhashmap(string.class.getclassloader());
}
}6. binder 最佳实践
6.1 性能优化
- 减少跨进程调用:批量处理数据,避免频繁的小数据调用
- 使用合适的参数方向:
in: 客户端到服务端out: 服务端到客户端inout: 双向传输
6.2 错误处理
try {
string result = remoteservice.dosomething(param);
// 处理结果
} catch (remoteexception e) {
// 处理通信错误
log.e(tag, "remote call failed", e);
// 重连或提示用户
} catch (securityexception e) {
// 处理权限错误
log.e(tag, "permission denied", e);
}6.3 内存管理
// 及时注销回调,避免内存泄漏
@override
protected void ondestroy() {
if (isbound && callbackservice != null) {
try {
callbackservice.unregistercallback(callback);
} catch (remoteexception e) {
// 忽略注销时的错误
}
}
unbindservice(connection);
super.ondestroy();
}7. 总结
通过以上实例,你应该掌握了:
- binder 基础架构:理解 c/s 模式和 binder driver 的作用
- aidl 使用:学会定义接口和数据模型
- 服务实现:创建 binder 服务并处理客户端请求
- 客户端编程:绑定服务、调用远程方法、处理回调
- 数据传输:使用 parcelable 传输复杂数据
- 错误处理:妥善处理 remoteexception 等异常
binder 是 android 系统的核心 ipc 机制,熟练掌握 binder 对于开发系统服务、跨进程通信等高级功能至关重要。
到此这篇关于android binder 详解与实践指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关android binder内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论