一、全局变量是什么
全局变量是指在程序的整个生命周期内都可访问的变量,它的作用范围不限于某个函数、方法或类,而是可以被多个代码模块共享。
学习过java的可能会对此有些陌生,java中并没有全局变量的概念,但是在学习servlet的时候,必然接触过请求域和应用域,所谓的应用域对象servletcontext,也就是servlet上下文对象,在这个对象中绑定的数据可以被所有用户所共享。比如setattribute方法可以向域中绑定数据,getattribute和removeattribute分别可以从域中获取、移除数据。
类比来看,application scope(应用域) 很像 java 的全局变量,因为它在整个应用程序的生命周期内都是可用的,适用于存储全局数据。
另外可以用单例模式来存储“全局变量”:
public class globalmanager {
private static globalmanager instance = new globalmanager();
private string data;
private globalmanager() {} // 私有构造方法,防止外部实例化
public static globalmanager getinstance() {
return instance;
}
public string getdata() {
return data;
}
public void setdata(string data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//设置全局变量
globalmanager.getinstance().setdata("hello");这样读取的时候,就会有固定的输出内容:
system.out.println(globalmanager.getinstance().getdata()); // 输出: hello
在as中application的生命周期覆盖了全过程,不像activity活动页面,一旦页面关闭生命周期就进入destroy,利用全生命特性,可以用来存储全局变量。
二、如何把输入的信息存储到全局变量
先看第一段代码,其作用就是把用户的注册信息保存到全局变量hashmap中。
public class appwriteactivity extends appcompatactivity implements view.onclicklistener, compoundbutton.oncheckedchangelistener {
private edittext et_name; // 声明一个编辑框对象
private edittext et_age; // 声明一个编辑框对象
private edittext et_height; // 声明一个编辑框对象
private edittext et_weight; // 声明一个编辑框对象
private boolean ismarried = false;
private string[] typearray = {"未婚", "已婚"};
@override
protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_app_write);
et_name = findviewbyid(r.id.et_name);
et_age = findviewbyid(r.id.et_age);
et_height = findviewbyid(r.id.et_height);
et_weight = findviewbyid(r.id.et_weight);
checkbox ck_married = findviewbyid(r.id.ck_married);
ck_married.setoncheckedchangelistener(this);
findviewbyid(r.id.btn_save).setonclicklistener(this);
findviewbyid(r.id.btn_intent).setonclicklistener(this);
}
@override
public void oncheckedchanged(compoundbutton buttonview, boolean ischecked) {
ismarried = ischecked;
}
@override
public void onclick(view v) {
if (v.getid() == r.id.btn_save) {
string name = et_name.gettext().tostring();
string age = et_age.gettext().tostring();
string height = et_height.gettext().tostring();
string weight = et_weight.gettext().tostring();
if (textutils.isempty(name)) {
toastutil.show(this, "请先填写姓名");
return;
} else if (textutils.isempty(age)) {
toastutil.show(this, "请先填写年龄");
return;
} else if (textutils.isempty(height)) {
toastutil.show(this, "请先填写身高");
return;
} else if (textutils.isempty(weight)) {
toastutil.show(this, "请先填写体重");
return;
}
// 获取当前应用的application实例
mainapplication app = mainapplication.getinstance();
// 以下直接修改application实例中保存的映射全局变量
app.infomap.put("name", name);
app.infomap.put("age", age);
app.infomap.put("height", height);
app.infomap.put("weight", weight);
app.infomap.put("married", typearray[!ismarried ? 0 : 1]);
app.infomap.put("update_time", dateutil.getnowdatetime("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss"));
toastutil.show(this, "数据已写入全局内存");
}
if (v.getid() == r.id.btn_intent){
// 创建intent对象,启动 appreadactivity
intent intent = new intent(appwriteactivity.this, appreadactivity.class);
// 启动目标activity
startactivity(intent);
}
}
}2.1 mainapplication类
其中,我自定义了一个mainapplication类,具体代码如下:
这个自定义 application 类的作用
存储全局数据
- 定义了
infomap变量,用于存储一些全局信息,比如用户输入的数据。 - 由于
application的生命周期与应用相同(应用启动 -> 关闭),infomap里的数据在应用运行期间都是有效的。
提供 getinstance() 方法,作为单例使用
mainapplication使用mapp作为静态实例,并在oncreate()里初始化它,这样,任何地方都可以通过mainapplication.getinstance()访问application,不用每次都getapplication()。
public class mainapplication extends application {
private static mainapplication mapp;
public hashmap<string,string> infomap =new hashmap<string,string>();
public static mainapplication getinstance(){
return mapp;
}
@override
public void oncreate() {
super.oncreate();
mapp = this;
}
}
2.2 xml文件
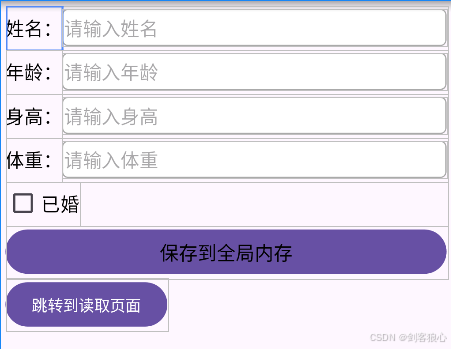
信息收集的页面示意图,其具体代码如下:
<linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="5dp" >
<relativelayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp" >
<textview
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="姓名:"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
<edittext
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginbottom="3dp"
android:layout_margintop="3dp"
android:layout_torightof="@+id/tv_name"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:gravity="left|center"
android:hint="请输入姓名"
android:inputtype="text"
android:maxlength="12"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
</relativelayout>
<relativelayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp" >
<textview
android:id="@+id/tv_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="年龄:"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
<edittext
android:id="@+id/et_age"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginbottom="3dp"
android:layout_margintop="3dp"
android:layout_torightof="@+id/tv_age"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:gravity="left|center"
android:hint="请输入年龄"
android:inputtype="number"
android:maxlength="2"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
</relativelayout>
<relativelayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp" >
<textview
android:id="@+id/tv_height"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="身高:"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
<edittext
android:id="@+id/et_height"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginbottom="3dp"
android:layout_margintop="3dp"
android:layout_torightof="@+id/tv_height"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:gravity="left|center"
android:hint="请输入身高"
android:inputtype="number"
android:maxlength="3"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
</relativelayout>
<relativelayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp" >
<textview
android:id="@+id/tv_weight"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="体重:"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
<edittext
android:id="@+id/et_weight"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginbottom="3dp"
android:layout_margintop="3dp"
android:layout_torightof="@+id/tv_weight"
android:background="@drawable/editext_selector"
android:gravity="left|center"
android:hint="请输入体重"
android:inputtype="numberdecimal"
android:maxlength="5"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
</relativelayout>
<relativelayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp" >
<checkbox
android:id="@+id/ck_married"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:checked="false"
android:text="已婚"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
</relativelayout>
<button
android:id="@+id/btn_save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="保存到全局内存"
android:textcolor="@color/black"
android:textsize="17sp" />
<button
android:id="@+id/btn_intent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="跳转到读取页面"/>
</linearlayout>三、全局变量读取
这里的代码是从全局变量infomap中读取用户的注册信息
public class appreadactivity extends appcompatactivity {
private textview tv_app; // 声明一个文本视图对象
@override
protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_app_read);
tv_app = findviewbyid(r.id.tv_app);
readappmemory(); // 读取全局内存中保存的变量信息
}
// 读取全局内存中保存的变量信息
private void readappmemory() {
string desc = "全局内存中保存的信息如下:";
// 获取当前应用的application实例
mainapplication app = mainapplication.getinstance();
// 获取application实例中保存的映射全局变量
map<string, string> mapparam = app.infomap;
// 遍历映射全局变量内部的键值对信息
for (map.entry<string, string> item_map : mapparam.entryset()) {
desc = string.format("%s\n %s的取值为%s",
desc, item_map.getkey(), item_map.getvalue());
}
if (mapparam.size() <= 0) {
desc = "全局内存中保存的信息为空";
}
tv_app.settext(desc);
}
}
四、修改manifest
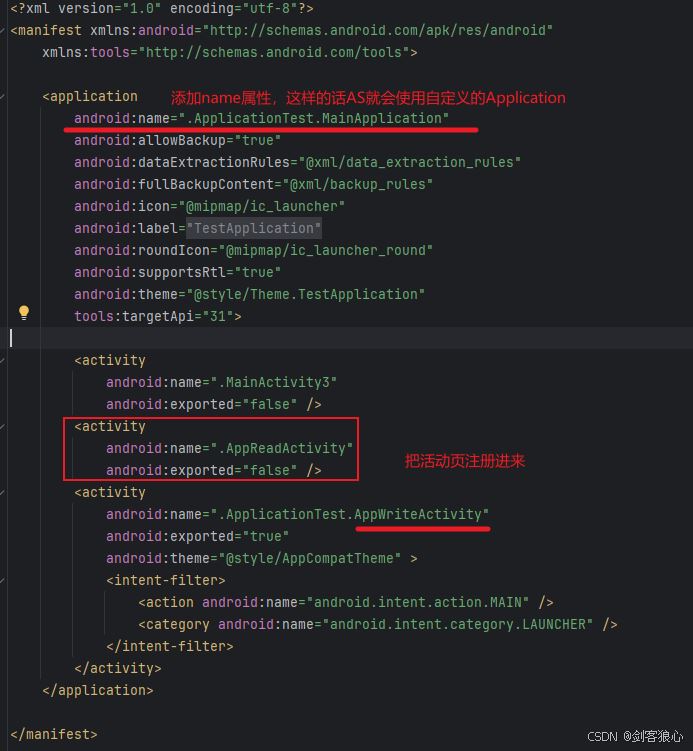
五、效果展示
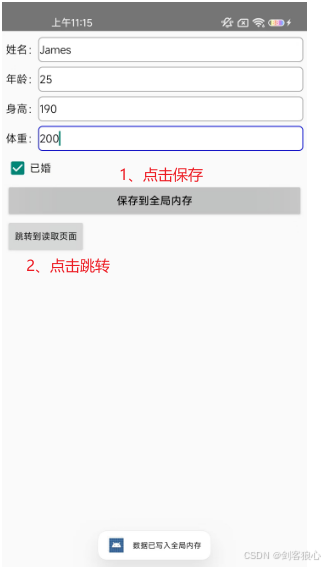
可以看到全局变量的信息已经被页面2所获取。

以上就是android studio如何利用application操作全局变量的代码详解的详细内容,更多关于android studio application全局变量的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!







发表评论